Sanghyun Yi
Hardware-Friendly Static Quantization Method for Video Diffusion Transformers
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:Diffusion Transformers for video generation have gained significant research interest since the impressive performance of SORA. Efficient deployment of such generative-AI models on GPUs has been demonstrated with dynamic quantization. However, resource-constrained devices cannot support dynamic quantization, and need static quantization of the models for their efficient deployment on AI processors. In this paper, we propose a novel method for the post-training quantization of OpenSora\cite{opensora}, a Video Diffusion Transformer, without relying on dynamic quantization techniques. Our approach employs static quantization, achieving video quality comparable to FP16 and dynamically quantized ViDiT-Q methods, as measured by CLIP, and VQA metrics. In particular, we utilize per-step calibration data to adequately provide a post-training statically quantized model for each time step, incorporating channel-wise quantization for weights and tensor-wise quantization for activations. By further applying the smooth-quantization technique, we can obtain high-quality video outputs with the statically quantized models. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that static quantization can be a viable alternative to dynamic quantization for video diffusion transformers, offering a more efficient approach without sacrificing performance.
Towards Coherent and Engaging Spoken Dialog Response Generation Using Automatic Conversation Evaluators
May 02, 2019
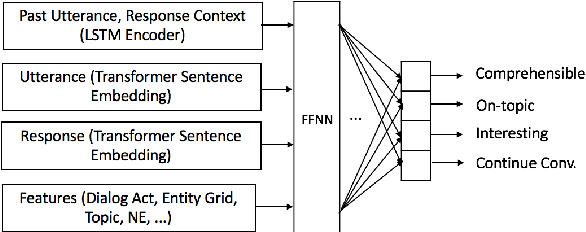


Abstract:Encoder-decoder based neural architectures serve as the basis of state-of-the-art approaches in end-to-end open domain dialog systems. Since most of such systems are trained with a maximum likelihood(MLE) objective they suffer from issues such as lack of generalizability and the generic response problem, i.e., a system response that can be an answer to a large number of user utterances, e.g., "Maybe, I don't know." Having explicit feedback on the relevance and interestingness of a system response at each turn can be a useful signal for mitigating such issues and improving system quality by selecting responses from different approaches. Towards this goal, we present a system that evaluates chatbot responses at each dialog turn for coherence and engagement. Our system provides explicit turn-level dialog quality feedback, which we show to be highly correlated with human evaluation. To show that incorporating this feedback in the neural response generation models improves dialog quality, we present two different and complementary mechanisms to incorporate explicit feedback into a neural response generation model: reranking and direct modification of the loss function during training. Our studies show that a response generation model that incorporates these combined feedback mechanisms produce more engaging and coherent responses in an open-domain spoken dialog setting, significantly improving the response quality using both automatic and human evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge