Samhita Marri
Precision Harvesting in Cluttered Environments: Integrating End Effector Design with Dual Camera Perception
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Due to labor shortages in specialty crop industries, a need for robotic automation to increase agricultural efficiency and productivity has arisen. Previous manipulation systems perform well in harvesting in uncluttered and structured environments. High tunnel environments are more compact and cluttered in nature, requiring a rethinking of the large form factor systems and grippers. We propose a novel codesigned framework incorporating a global detection camera and a local eye-in-hand camera that demonstrates precise localization of small fruits via closed-loop visual feedback and reliable error handling. Field experiments in high tunnels show our system can reach an average of 85.0\% of cherry tomato fruit in 10.98s on average.
PlantTrack: Task-Driven Plant Keypoint Tracking with Zero-Shot Sim2Real Transfer
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:Tracking plant features is crucial for various agricultural tasks like phenotyping, pruning, or harvesting, but the unstructured, cluttered, and deformable nature of plant environments makes it a challenging task. In this context, the recent advancements in foundational models show promise in addressing this challenge. In our work, we propose PlantTrack where we utilize DINOv2 which provides high-dimensional features, and train a keypoint heatmap predictor network to identify the locations of semantic features such as fruits and leaves which are then used as prompts for point tracking across video frames using TAPIR. We show that with as few as 20 synthetic images for training the keypoint predictor, we achieve zero-shot Sim2Real transfer, enabling effective tracking of plant features in real environments.
Gazebo Plants: Simulating Plant-Robot Interaction with Cosserat Rods
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:Robotic harvesting has the potential to positively impact agricultural productivity, reduce costs, improve food quality, enhance sustainability, and to address labor shortage. In the rapidly advancing field of agricultural robotics, the necessity of training robots in a virtual environment has become essential. Generating training data to automatize the underlying computer vision tasks such as image segmentation, object detection and classification, also heavily relies on such virtual environments as synthetic data is often required to overcome the shortage and lack of variety of real data sets. However, physics engines commonly employed within the robotics community, such as ODE, Simbody, Bullet, and DART, primarily support motion and collision interaction of rigid bodies. This inherent limitation hinders experimentation and progress in handling non-rigid objects such as plants and crops. In this contribution, we present a plugin for the Gazebo simulation platform based on Cosserat rods to model plant motion. It enables the simulation of plants and their interaction with the environment. We demonstrate that, using our plugin, users can conduct harvesting simulations in Gazebo by simulating a robotic arm picking fruits and achieve results comparable to real-world experiments.
Visual Servoing for Pose Control of Soft Continuum Arm in a Structured Environment
Feb 11, 2022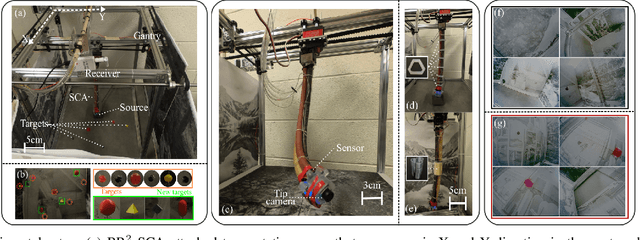
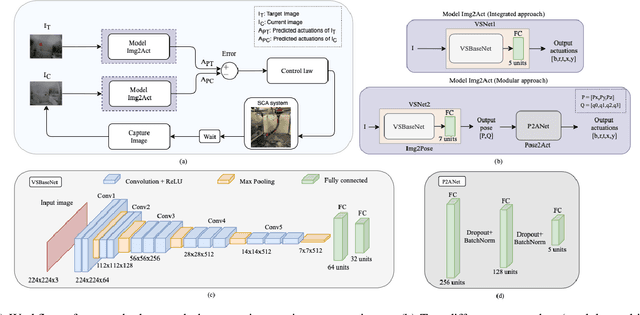
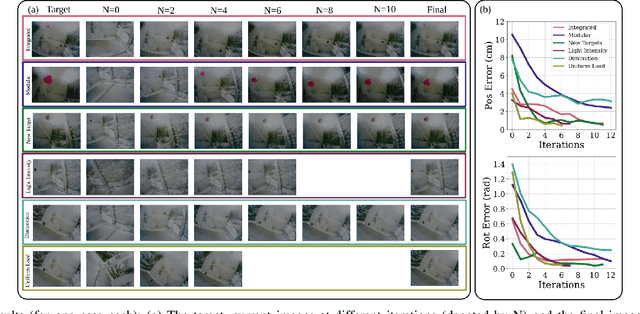
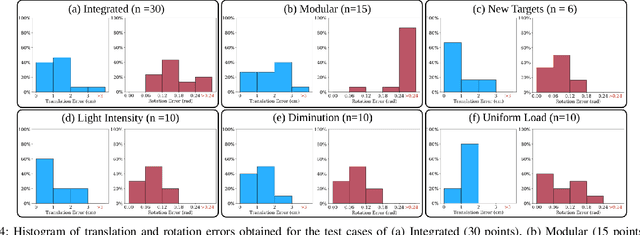
Abstract:For soft continuum arms, visual servoing is a popular control strategy that relies on visual feedback to close the control loop. However, robust visual servoing is challenging as it requires reliable feature extraction from the image, accurate control models and sensors to perceive the shape of the arm, both of which can be hard to implement in a soft robot. This letter circumvents these challenges by presenting a deep neural network-based method to perform smooth and robust 3D positioning tasks on a soft arm by visual servoing using a camera mounted at the distal end of the arm. A convolutional neural network is trained to predict the actuations required to achieve the desired pose in a structured environment. Integrated and modular approaches for estimating the actuations from the image are proposed and are experimentally compared. A proportional control law is implemented to reduce the error between the desired and current image as seen by the camera. The model together with the proportional feedback control makes the described approach robust to several variations such as new targets, lighting, loads, and diminution of the soft arm. Furthermore, the model lends itself to be transferred to a new environment with minimal effort.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge