Salik Ram Khanal
Center for Precision and Automated Agricultural Systems, Washington State University
Integrating Feature Selection and Machine Learning for Nitrogen Assessment in Grapevine Leaves using In-Field Hyperspectral Imaging
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Nitrogen (N) is one of the most crucial nutrients in vineyards, affecting plant growth and subsequent products such as wine and juice. Because soil N has high spatial and temporal variability, it is desirable to accurately estimate the N concentration of grapevine leaves and manage fertilization at the individual plant level to optimally meet plant needs. In this study, we used in-field hyperspectral images with wavelengths ranging from $400 to 1000nm of four different grapevine cultivars collected from distinct vineyards and over two growth stages during two growing seasons to develop models for predicting N concentration at the leaf-level and canopy-level. After image processing, two feature selection methods were employed to identify the optimal set of spectral bands that were responsive to leaf N concentrations. The selected spectral bands were used to train and test two different Machine Learning (ML) models, Gradient Boosting and XGBoost, for predicting nitrogen concentrations. The comparison of selected bands for both leaf-level and canopy-level datasets showed that most of the spectral regions identified by the feature selection methods were across both methods and the dataset types (leaf- and canopy-level datasets), particularly in the key regions, 500-525nm, 650-690nm, 750-800nm, and 900-950nm. These findings indicated the robustness of these spectral regions for predicting nitrogen content. The results for N prediction demonstrated that the ML model achieved an R square of 0.49 for canopy-level data and an R square of 0.57 for leaf-level data, despite using different sets of selected spectral bands for each analysis level. The study demonstrated the potential of using in-field hyperspectral imaging and the use of spectral data in integrated feature selection and ML techniques to monitor N status in vineyards.
Paddy Disease Detection and Classification Using Computer Vision Techniques: A Mobile Application to Detect Paddy Disease
Dec 08, 2024Abstract:Plant diseases significantly impact our food supply, causing problems for farmers, economies reliant on agriculture, and global food security. Accurate and timely plant disease diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and minimizing yield losses. Despite advancements in agricultural technology, a precise and early diagnosis remains a challenge, especially in underdeveloped regions where agriculture is crucial and agricultural experts are scarce. However, adopting Deep Learning applications can assist in accurately identifying diseases without needing plant pathologists. In this study, the effectiveness of various computer vision models for detecting paddy diseases is evaluated and proposed the best deep learning-based disease detection system. Both classification and detection using the Paddy Doctor dataset, which contains over 20,000 annotated images of paddy leaves for disease diagnosis are tested and evaluated. For detection, we utilized the YOLOv8 model-based model were used for paddy disease detection and CNN models and the Vision Transformer were used for disease classification. The average mAP50 of 69% for detection tasks was achieved and the Vision Transformer classification accuracy was 99.38%. It was found that detection models are effective at identifying multiple diseases simultaneously with less computing power, whereas classification models, though computationally expensive, exhibit better performance for classifying single diseases. Additionally, a mobile application was developed to enable farmers to identify paddy diseases instantly. Experiments with the app showed encouraging results in utilizing the trained models for both disease classification and treatment guidance.
Real-time Strawberry Detection Based on Improved YOLOv5s Architecture for Robotic Harvesting in open-field environment
Sep 01, 2023Abstract:This study proposed a YOLOv5-based custom object detection model to detect strawberries in an outdoor environment. The original architecture of the YOLOv5s was modified by replacing the C3 module with the C2f module in the backbone network, which provided a better feature gradient flow. Secondly, the Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast in the final layer of the backbone network of YOLOv5s was combined with Cross Stage Partial Net to improve the generalization ability over the strawberry dataset in this study. The proposed architecture was named YOLOv5s-Straw. The RGB images dataset of the strawberry canopy with three maturity classes (immature, nearly mature, and mature) was collected in open-field environment and augmented through a series of operations including brightness reduction, brightness increase, and noise adding. To verify the superiority of the proposed method for strawberry detection in open-field environment, four competitive detection models (YOLOv3-tiny, YOLOv5s, YOLOv5s-C2f, and YOLOv8s) were trained, and tested under the same computational environment and compared with YOLOv5s-Straw. The results showed that the highest mean average precision of 80.3% was achieved using the proposed architecture whereas the same was achieved with YOLOv3-tiny, YOLOv5s, YOLOv5s-C2f, and YOLOv8s were 73.4%, 77.8%, 79.8%, 79.3%, respectively. Specifically, the average precision of YOLOv5s-Straw was 82.1% in the immature class, 73.5% in the nearly mature class, and 86.6% in the mature class, which were 2.3% and 3.7%, respectively, higher than that of the latest YOLOv8s. The model included 8.6*10^6 network parameters with an inference speed of 18ms per image while the inference speed of YOLOv8s had a slower inference speed of 21.0ms and heavy parameters of 11.1*10^6, which indicates that the proposed model is fast enough for real time strawberry detection and localization for the robotic picking.
Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Unlocking the Potential of Large Language Models for AI-Assisted Medical Education
Jun 30, 2023



Abstract:Artificial intelligence is gaining traction in more ways than ever before. The popularity of language models and AI-based businesses has soared since ChatGPT was made available to the general public via OpenAI. It is becoming increasingly common for people to use ChatGPT both professionally and personally. Considering the widespread use of ChatGPT and the reliance people place on it, this study determined how reliable ChatGPT can be for answering complex medical and clinical questions. Harvard University gross anatomy along with the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) questionnaire were used to accomplish the objective. The paper evaluated the obtained results using a 2-way ANOVA and posthoc analysis. Both showed systematic covariation between format and prompt. Furthermore, the physician adjudicators independently rated the outcome's accuracy, concordance, and insight. As a result of the analysis, ChatGPT-generated answers were found to be more context-oriented and represented a better model for deductive reasoning than regular Google search results. Furthermore, ChatGPT obtained 58.8% on logical questions and 60% on ethical questions. This means that the ChatGPT is approaching the passing range for logical questions and has crossed the threshold for ethical questions. The paper believes ChatGPT and other language learning models can be invaluable tools for e-learners; however, the study suggests that there is still room to improve their accuracy. In order to improve ChatGPT's performance in the future, further research is needed to better understand how it can answer different types of questions.
Screening Autism Spectrum Disorder in childrens using Deep Learning Approach : Evaluating the classification model of YOLOv8 by comparing with other models
Jun 25, 2023


Abstract:Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition that presents significant challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. Early intervention plays a pivotal role in enhancing cognitive abilities and reducing autistic symptoms in children with ASD. Numerous clinical studies have highlighted distinctive facial characteristics that distinguish ASD children from typically developing (TD) children. In this study, we propose a practical solution for ASD screening using facial images using YoloV8 model. By employing YoloV8, a deep learning technique, on a dataset of Kaggle, we achieved exceptional results. Our model achieved a remarkable 89.64% accuracy in classification and an F1-score of 0.89. Our findings provide support for the clinical observations regarding facial feature discrepancies between children with ASD. The high F1-score obtained demonstrates the potential of deep learning models in screening children with ASD. We conclude that the newest version of YoloV8 which is usually used for object detection can be used for classification problem of Austistic and Non-autistic images.
Machine Vision System for Early-stage Apple Flowers and Flower Clusters Detection for Precision Thinning and Pollination
Apr 19, 2023Abstract:Early-stage identification of fruit flowers that are in both opened and unopened condition in an orchard environment is significant information to perform crop load management operations such as flower thinning and pollination using automated and robotic platforms. These operations are important in tree-fruit agriculture to enhance fruit quality, manage crop load, and enhance the overall profit. The recent development in agricultural automation suggests that this can be done using robotics which includes machine vision technology. In this article, we proposed a vision system that detects early-stage flowers in an unstructured orchard environment using YOLOv5 object detection algorithm. For the robotics implementation, the position of a cluster of the flower blossom is important to navigate the robot and the end effector. The centroid of individual flowers (both open and unopen) was identified and associated with flower clusters via K-means clustering. The accuracy of the opened and unopened flower detection is achieved up to mAP of 81.9% in commercial orchard images.
Performance Analysis and Evaluation of Cloud Vision Emotion APIs
Mar 23, 2023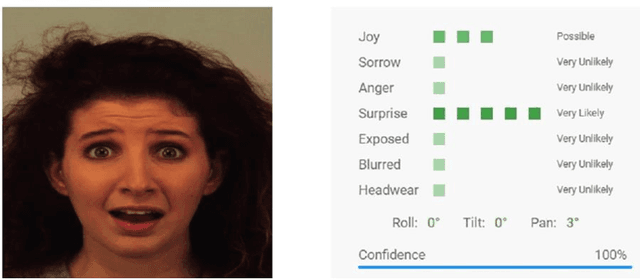
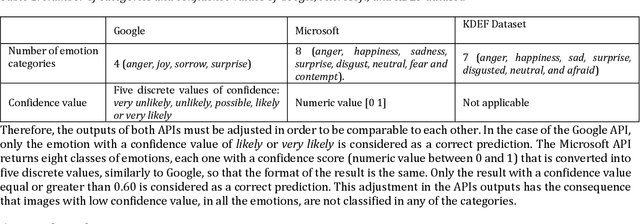

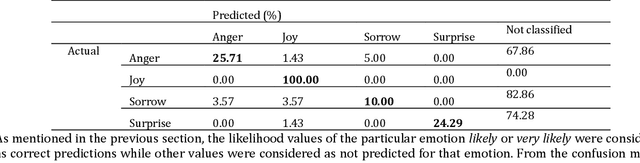
Abstract:Facial expression is a way of communication that can be used to interact with computers or other electronic devices and the recognition of emotion from faces is an emerging practice with application in many fields. There are many cloud-based vision application programming interfaces available that recognize emotion from facial images and video. In this article, the performances of two well-known APIs were compared using a public dataset of 980 images of facial emotions. For these experiments, a client program was developed which iterates over the image set, calls the cloud services, and caches the results of the emotion detection for each image. The performance was evaluated in each class of emotions using prediction accuracy. It has been found that the prediction accuracy for each emotion varies according to the cloud service being used. Similarly, each service provider presents a strong variation of performance according to the class being analyzed, as can be seen with more detail in this artilects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge