Prabin Sharma
Sensors and Systems for Monitoring Mental Fatigue: A systematic review
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:Mental fatigue is a leading cause of motor vehicle accidents, medical errors, loss of workplace productivity, and student disengagements in e-learning environment. Development of sensors and systems that can reliably track mental fatigue can prevent accidents, reduce errors, and help increase workplace productivity. This review provides a critical summary of theoretical models of mental fatigue, a description of key enabling sensor technologies, and a systematic review of recent studies using biosensor-based systems for tracking mental fatigue in humans. We conducted a systematic search and review of recent literature which focused on detection and tracking of mental fatigue in humans. The search yielded 57 studies (N=1082), majority of which used electroencephalography (EEG) based sensors for tracking mental fatigue. We found that EEG-based sensors can provide a moderate to good sensitivity for fatigue detection. Notably, we found no incremental benefit of using high-density EEG sensors for application in mental fatigue detection. Given the findings, we provide a critical discussion on the integration of wearable EEG and ambient sensors in the context of achieving real-world monitoring. Future work required to advance and adapt the technologies toward widespread deployment of wearable sensors and systems for fatigue monitoring in semi-autonomous and autonomous industries is examined.
Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Unlocking the Potential of Large Language Models for AI-Assisted Medical Education
Jun 30, 2023



Abstract:Artificial intelligence is gaining traction in more ways than ever before. The popularity of language models and AI-based businesses has soared since ChatGPT was made available to the general public via OpenAI. It is becoming increasingly common for people to use ChatGPT both professionally and personally. Considering the widespread use of ChatGPT and the reliance people place on it, this study determined how reliable ChatGPT can be for answering complex medical and clinical questions. Harvard University gross anatomy along with the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) questionnaire were used to accomplish the objective. The paper evaluated the obtained results using a 2-way ANOVA and posthoc analysis. Both showed systematic covariation between format and prompt. Furthermore, the physician adjudicators independently rated the outcome's accuracy, concordance, and insight. As a result of the analysis, ChatGPT-generated answers were found to be more context-oriented and represented a better model for deductive reasoning than regular Google search results. Furthermore, ChatGPT obtained 58.8% on logical questions and 60% on ethical questions. This means that the ChatGPT is approaching the passing range for logical questions and has crossed the threshold for ethical questions. The paper believes ChatGPT and other language learning models can be invaluable tools for e-learners; however, the study suggests that there is still room to improve their accuracy. In order to improve ChatGPT's performance in the future, further research is needed to better understand how it can answer different types of questions.
Screening Autism Spectrum Disorder in childrens using Deep Learning Approach : Evaluating the classification model of YOLOv8 by comparing with other models
Jun 25, 2023


Abstract:Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition that presents significant challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. Early intervention plays a pivotal role in enhancing cognitive abilities and reducing autistic symptoms in children with ASD. Numerous clinical studies have highlighted distinctive facial characteristics that distinguish ASD children from typically developing (TD) children. In this study, we propose a practical solution for ASD screening using facial images using YoloV8 model. By employing YoloV8, a deep learning technique, on a dataset of Kaggle, we achieved exceptional results. Our model achieved a remarkable 89.64% accuracy in classification and an F1-score of 0.89. Our findings provide support for the clinical observations regarding facial feature discrepancies between children with ASD. The high F1-score obtained demonstrates the potential of deep learning models in screening children with ASD. We conclude that the newest version of YoloV8 which is usually used for object detection can be used for classification problem of Austistic and Non-autistic images.
Performance Analysis and Evaluation of Cloud Vision Emotion APIs
Mar 23, 2023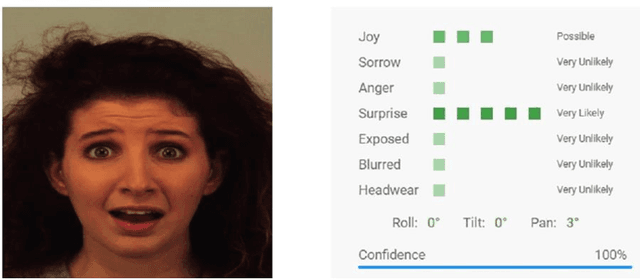
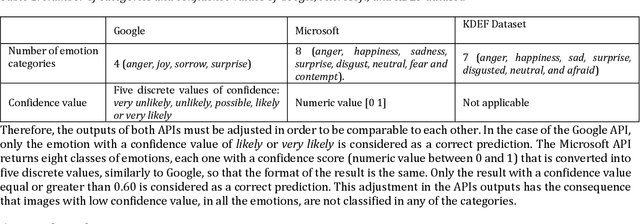

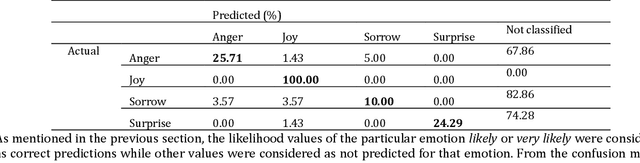
Abstract:Facial expression is a way of communication that can be used to interact with computers or other electronic devices and the recognition of emotion from faces is an emerging practice with application in many fields. There are many cloud-based vision application programming interfaces available that recognize emotion from facial images and video. In this article, the performances of two well-known APIs were compared using a public dataset of 980 images of facial emotions. For these experiments, a client program was developed which iterates over the image set, calls the cloud services, and caches the results of the emotion detection for each image. The performance was evaluated in each class of emotions using prediction accuracy. It has been found that the prediction accuracy for each emotion varies according to the cloud service being used. Similarly, each service provider presents a strong variation of performance according to the class being analyzed, as can be seen with more detail in this artilects.
Towards blind user's indoor navigation: a comparative study of beacons and decawave for indoor accurate location
Dec 02, 2019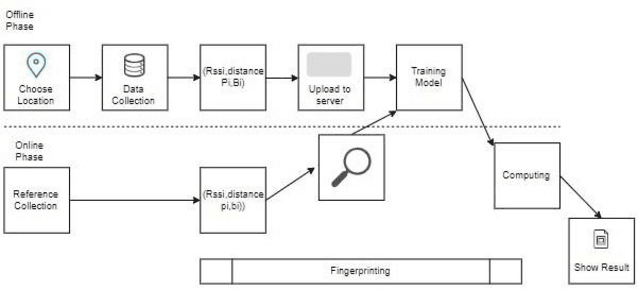
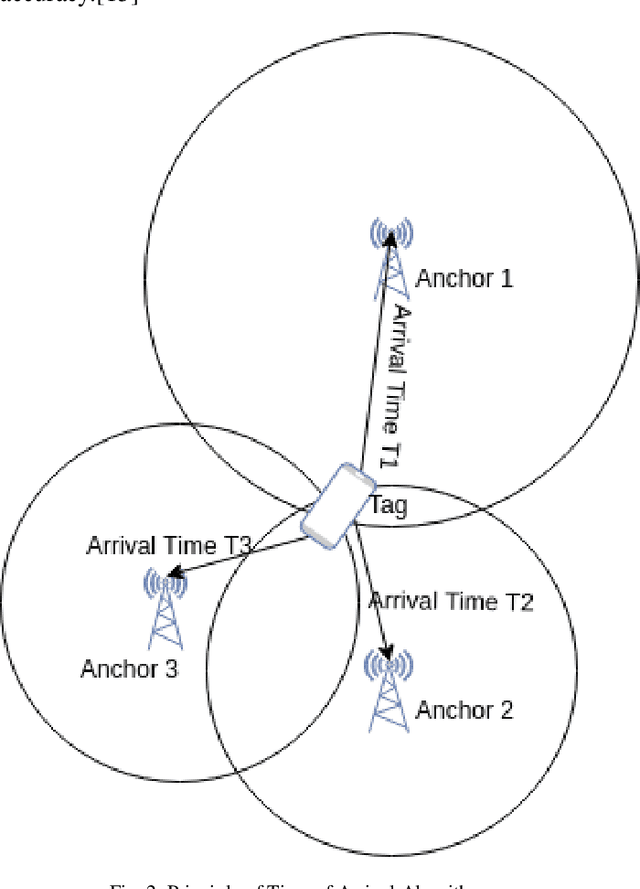
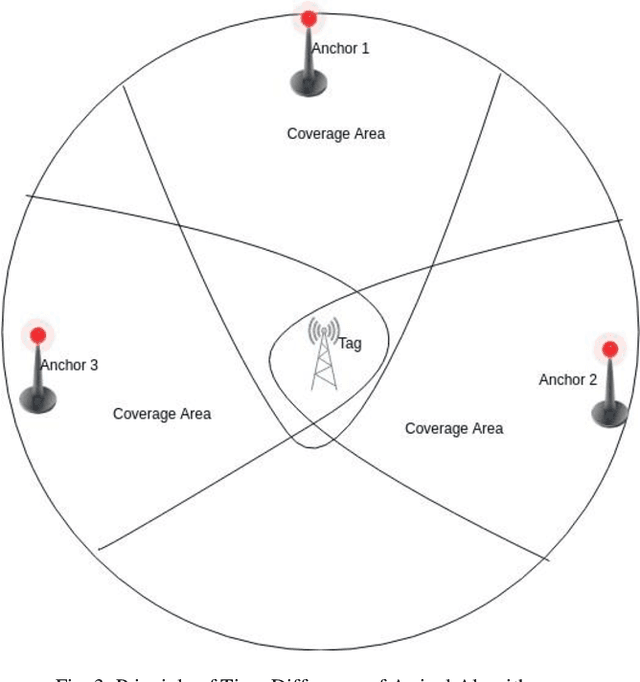
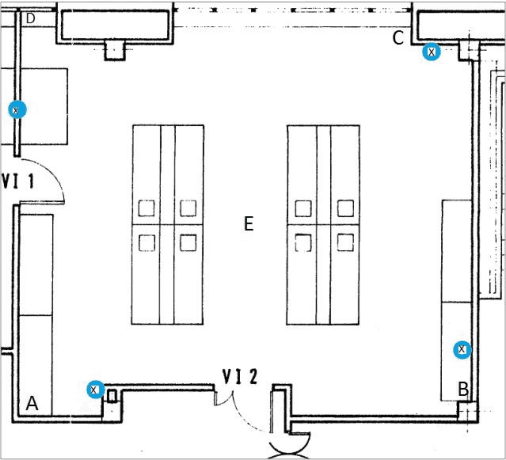
Abstract:There are many systems for indoor navigation specially built for visually impaired people but only some has good accuracy for navigation. While there are solutions like global navigation satellite systems for the localization outdoors, problems arise in urban scenarios and indoors due to insufficient or failed signal reception. To build a support system for navigation for visually impaired people, in this paper we present a comparison of indoor localization and navigation system, which performs continuous and real-time processing using commercially available systems (Beacons and Decawave) under the same experimental condition for the performance analysis. Error is calculated and analyzed using Euclidean distance and standard deviation for both the cases. We used Navigine Platform for this navigation system which allows both Tri-lateration as well as Fingerprinting algorithms. For calculating location we have used the concept of Time of Arrival and time of difference of arrivals. Taking into concern about the blind people, location is important as well as accuracy is necessity because small measurement in the walk is important to them. With this concern, in this paper, we are showing the comparative study of beacons and Decawave. The study and the accuracy tests of those systems for the blind people/user's in navigating indoor are presented in this paper.
Student Engagement Detection Using Emotion Analysis, Eye Tracking and Head Movement with Machine Learning
Sep 18, 2019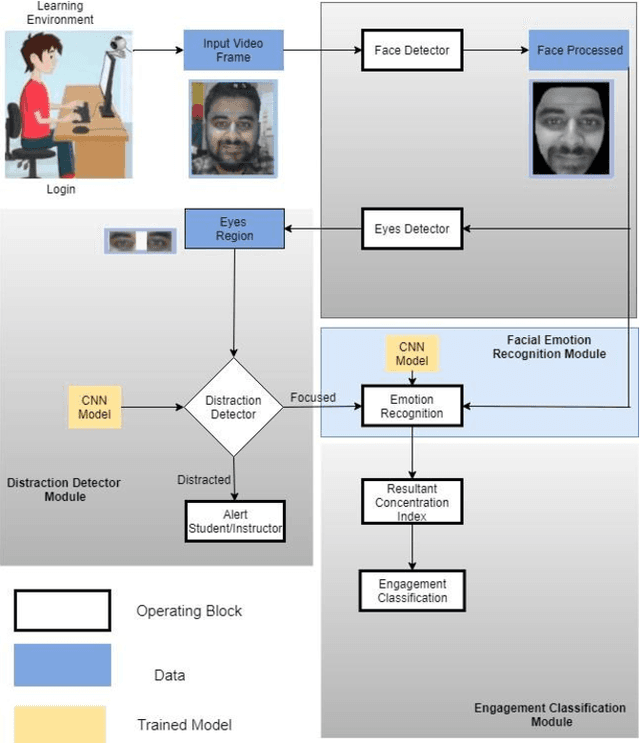
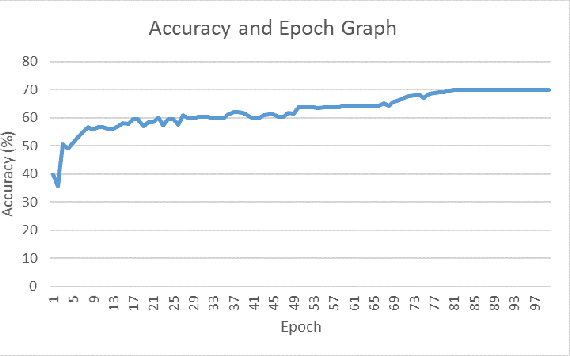
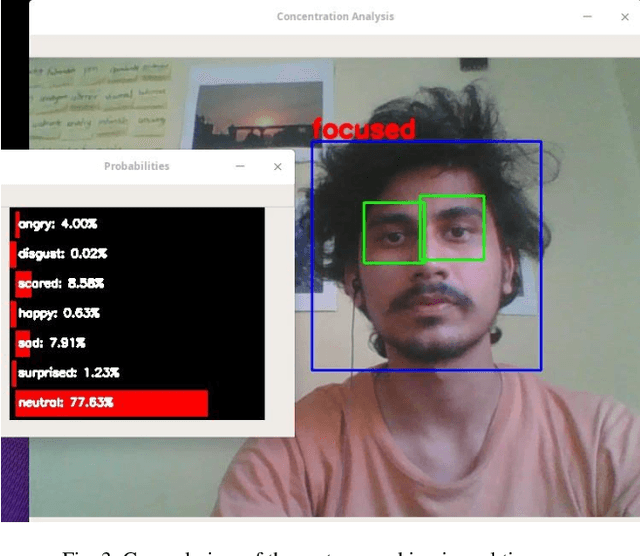
Abstract:With the increase of distance learning, in general, and e-learning, in particular, having a system capable of determining the engagement of students is of primordial importance, and one of the biggest challenges, both for teachers, researchers and policy makers. Here, we present a system to detect the engagement level of the students. It uses only information provided by the typical built-in web-camera present in a laptop computer, and was designed to work in real time. We combine information about the movements of the eyes and head, and facial emotions to produce a concentration index with three classes of engagement: "very engaged", "nominally engaged" and "not engaged at all". The system was tested in a typical e-learning scenario, and the results show that it correctly identifies each period of time where students were "very engaged", "nominally engaged" and "not engaged at all". Additionally, the results also show that the students with best scores also have higher concentration indexes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge