Sabeen Ahmed
Reliable Radiologic Skeletal Muscle Area Assessment -- A Biomarker for Cancer Cachexia Diagnosis
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Cancer cachexia is a common metabolic disorder characterized by severe muscle atrophy which is associated with poor prognosis and quality of life. Monitoring skeletal muscle area (SMA) longitudinally through computed tomography (CT) scans, an imaging modality routinely acquired in cancer care, is an effective way to identify and track this condition. However, existing tools often lack full automation and exhibit inconsistent accuracy, limiting their potential for integration into clinical workflows. To address these challenges, we developed SMAART-AI (Skeletal Muscle Assessment-Automated and Reliable Tool-based on AI), an end-to-end automated pipeline powered by deep learning models (nnU-Net 2D) trained on mid-third lumbar level CT images with 5-fold cross-validation, ensuring generalizability and robustness. SMAART-AI incorporates an uncertainty-based mechanism to flag high-error SMA predictions for expert review, enhancing reliability. We combined the SMA, skeletal muscle index, BMI, and clinical data to train a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) model designed to predict cachexia at the time of cancer diagnosis. Tested on the gastroesophageal cancer dataset, SMAART-AI achieved a Dice score of 97.80% +/- 0.93%, with SMA estimated across all four datasets in this study at a median absolute error of 2.48% compared to manual annotations with SliceOmatic. Uncertainty metrics-variance, entropy, and coefficient of variation-strongly correlated with SMA prediction errors (0.83, 0.76, and 0.73 respectively). The MLP model predicts cachexia with 79% precision, providing clinicians with a reliable tool for early diagnosis and intervention. By combining automation, accuracy, and uncertainty awareness, SMAART-AI bridges the gap between research and clinical application, offering a transformative approach to managing cancer cachexia.
Multimodal AI-driven Biomarker for Early Detection of Cancer Cachexia
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Cancer cachexia is a multifactorial syndrome characterized by progressive muscle wasting, metabolic dysfunction, and systemic inflammation, leading to reduced quality of life and increased mortality. Despite extensive research, no single definitive biomarker exists, as cachexia-related indicators such as serum biomarkers, skeletal muscle measurements, and metabolic abnormalities often overlap with other conditions. Existing composite indices, including the Cancer Cachexia Index (CXI), Modified CXI (mCXI), and Cachexia Score (CASCO), integrate multiple biomarkers but lack standardized thresholds, limiting their clinical utility. This study proposes a multimodal AI-based biomarker for early cancer cachexia detection, leveraging open-source large language models (LLMs) and foundation models trained on medical data. The approach integrates heterogeneous patient data, including demographics, disease status, lab reports, radiological imaging (CT scans), and clinical notes, using a machine learning framework that can handle missing data. Unlike previous AI-based models trained on curated datasets, this method utilizes routinely collected clinical data, enhancing real-world applicability. Additionally, the model incorporates confidence estimation, allowing the identification of cases requiring expert review for precise clinical interpretation. Preliminary findings demonstrate that integrating multiple data modalities improves cachexia prediction accuracy at the time of cancer diagnosis. The AI-based biomarker dynamically adapts to patient-specific factors such as age, race, ethnicity, weight, cancer type, and stage, avoiding the limitations of fixed-threshold biomarkers. This multimodal AI biomarker provides a scalable and clinically viable solution for early cancer cachexia detection, facilitating personalized interventions and potentially improving treatment outcomes and patient survival.
SeNMo: A Self-Normalizing Deep Learning Model for Enhanced Multi-Omics Data Analysis in Oncology
May 13, 2024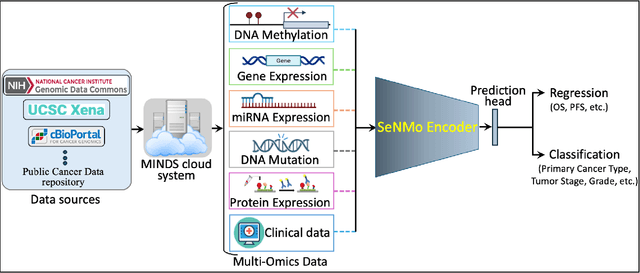
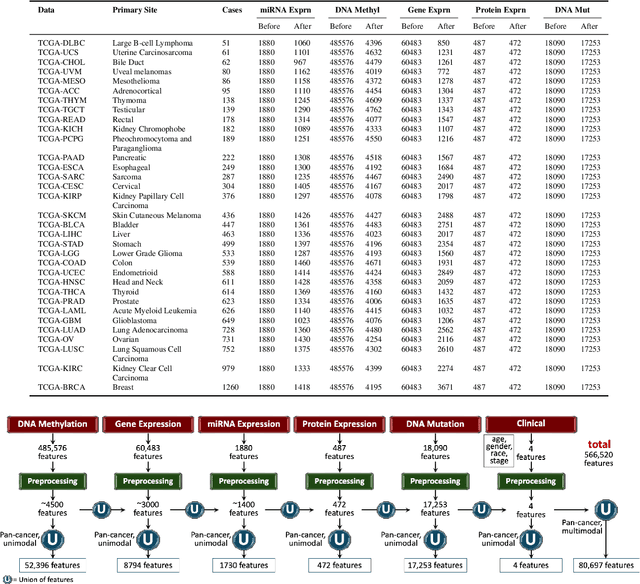


Abstract:Multi-omics research has enhanced our understanding of cancer heterogeneity and progression. Investigating molecular data through multi-omics approaches is crucial for unraveling the complex biological mechanisms underlying cancer, thereby enabling effective diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies. However, predicting patient outcomes through integration of all available multi-omics data is an under-study research direction. Here, we present SeNMo (Self-normalizing Network for Multi-omics), a deep neural network trained on multi-omics data across 33 cancer types. SeNMo is efficient in handling multi-omics data characterized by high-width (many features) and low-length (fewer samples) attributes. We trained SeNMo for the task of overall survival using pan-cancer data involving 33 cancer sites from Genomics Data Commons (GDC). The training data includes gene expression, DNA methylation, miRNA expression, DNA mutations, protein expression modalities, and clinical data. We evaluated the model's performance in predicting overall survival using concordance index (C-Index). SeNMo performed consistently well in training regime, with the validation C-Index of 0.76 on GDC's public data. In the testing regime, SeNMo performed with a C-Index of 0.758 on a held-out test set. The model showed an average accuracy of 99.8% on the task of classifying the primary cancer type on the pan-cancer test cohort. SeNMo proved to be a mini-foundation model for multi-omics oncology data because it demonstrated robust performance, and adaptability not only across molecular data types but also on the classification task of predicting the primary cancer type of patients. SeNMo can be further scaled to any cancer site and molecular data type. We believe SeNMo and similar models are poised to transform the oncology landscape, offering hope for more effective, efficient, and patient-centric cancer care.
Transformers in Time-series Analysis: A Tutorial
Apr 28, 2022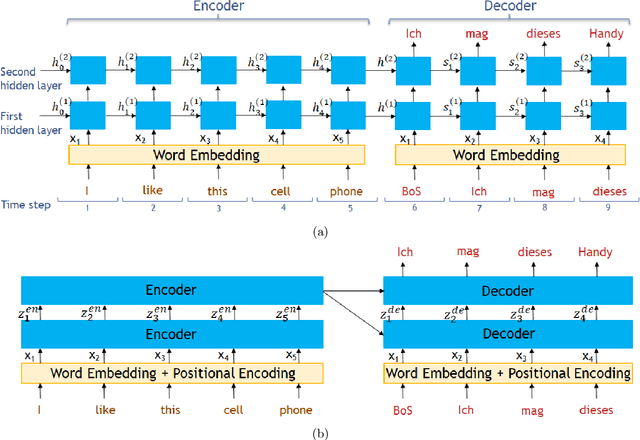
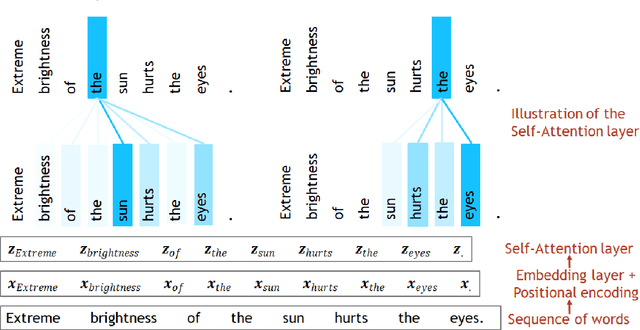
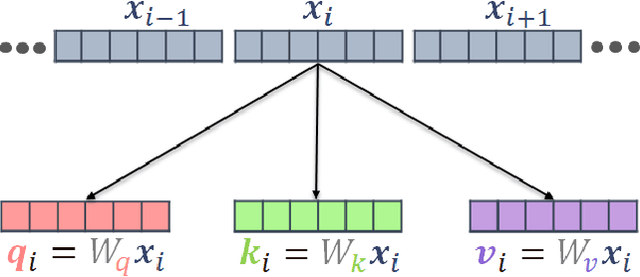
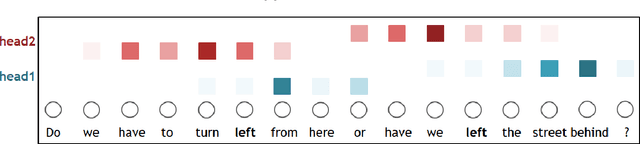
Abstract:Transformer architecture has widespread applications, particularly in Natural Language Processing and computer vision. Recently Transformers have been employed in various aspects of time-series analysis. This tutorial provides an overview of the Transformer architecture, its applications, and a collection of examples from recent research papers in time-series analysis. We delve into an explanation of the core components of the Transformer, including the self-attention mechanism, positional encoding, multi-head, and encoder/decoder. Several enhancements to the initial, Transformer architecture are highlighted to tackle time-series tasks. The tutorial also provides best practices and techniques to overcome the challenge of effectively training Transformers for time-series analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge