Søren Kaae Sønderby
Sequential Neural Models with Stochastic Layers
Nov 13, 2016



Abstract:How can we efficiently propagate uncertainty in a latent state representation with recurrent neural networks? This paper introduces stochastic recurrent neural networks which glue a deterministic recurrent neural network and a state space model together to form a stochastic and sequential neural generative model. The clear separation of deterministic and stochastic layers allows a structured variational inference network to track the factorization of the model's posterior distribution. By retaining both the nonlinear recursive structure of a recurrent neural network and averaging over the uncertainty in a latent path, like a state space model, we improve the state of the art results on the Blizzard and TIMIT speech modeling data sets by a large margin, while achieving comparable performances to competing methods on polyphonic music modeling.
Auxiliary Deep Generative Models
Jun 16, 2016



Abstract:Deep generative models parameterized by neural networks have recently achieved state-of-the-art performance in unsupervised and semi-supervised learning. We extend deep generative models with auxiliary variables which improves the variational approximation. The auxiliary variables leave the generative model unchanged but make the variational distribution more expressive. Inspired by the structure of the auxiliary variable we also propose a model with two stochastic layers and skip connections. Our findings suggest that more expressive and properly specified deep generative models converge faster with better results. We show state-of-the-art performance within semi-supervised learning on MNIST, SVHN and NORB datasets.
Ladder Variational Autoencoders
May 27, 2016



Abstract:Variational Autoencoders are powerful models for unsupervised learning. However deep models with several layers of dependent stochastic variables are difficult to train which limits the improvements obtained using these highly expressive models. We propose a new inference model, the Ladder Variational Autoencoder, that recursively corrects the generative distribution by a data dependent approximate likelihood in a process resembling the recently proposed Ladder Network. We show that this model provides state of the art predictive log-likelihood and tighter log-likelihood lower bound compared to the purely bottom-up inference in layered Variational Autoencoders and other generative models. We provide a detailed analysis of the learned hierarchical latent representation and show that our new inference model is qualitatively different and utilizes a deeper more distributed hierarchy of latent variables. Finally, we observe that batch normalization and deterministic warm-up (gradually turning on the KL-term) are crucial for training variational models with many stochastic layers.
Autoencoding beyond pixels using a learned similarity metric
Feb 10, 2016



Abstract:We present an autoencoder that leverages learned representations to better measure similarities in data space. By combining a variational autoencoder with a generative adversarial network we can use learned feature representations in the GAN discriminator as basis for the VAE reconstruction objective. Thereby, we replace element-wise errors with feature-wise errors to better capture the data distribution while offering invariance towards e.g. translation. We apply our method to images of faces and show that it outperforms VAEs with element-wise similarity measures in terms of visual fidelity. Moreover, we show that the method learns an embedding in which high-level abstract visual features (e.g. wearing glasses) can be modified using simple arithmetic.
Recurrent Spatial Transformer Networks
Sep 17, 2015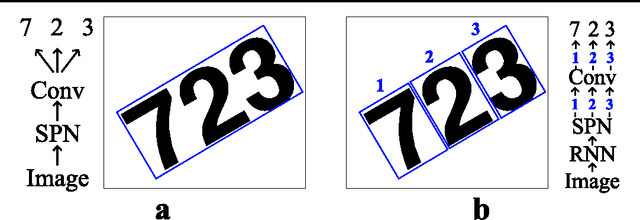
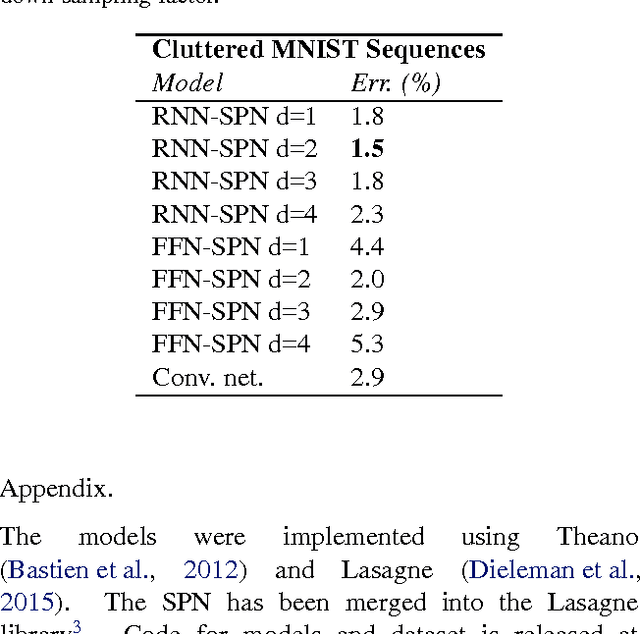
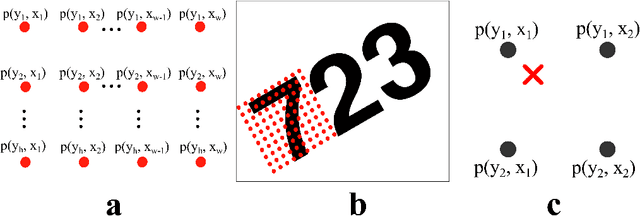

Abstract:We integrate the recently proposed spatial transformer network (SPN) [Jaderberg et. al 2015] into a recurrent neural network (RNN) to form an RNN-SPN model. We use the RNN-SPN to classify digits in cluttered MNIST sequences. The proposed model achieves a single digit error of 1.5% compared to 2.9% for a convolutional networks and 2.0% for convolutional networks with SPN layers. The SPN outputs a zoomed, rotated and skewed version of the input image. We investigate different down-sampling factors (ratio of pixel in input and output) for the SPN and show that the RNN-SPN model is able to down-sample the input images without deteriorating performance. The down-sampling in RNN-SPN can be thought of as adaptive down-sampling that minimizes the information loss in the regions of interest. We attribute the superior performance of the RNN-SPN to the fact that it can attend to a sequence of regions of interest.
Convolutional LSTM Networks for Subcellular Localization of Proteins
Mar 06, 2015



Abstract:Machine learning is widely used to analyze biological sequence data. Non-sequential models such as SVMs or feed-forward neural networks are often used although they have no natural way of handling sequences of varying length. Recurrent neural networks such as the long short term memory (LSTM) model on the other hand are designed to handle sequences. In this study we demonstrate that LSTM networks predict the subcellular location of proteins given only the protein sequence with high accuracy (0.902) outperforming current state of the art algorithms. We further improve the performance by introducing convolutional filters and experiment with an attention mechanism which lets the LSTM focus on specific parts of the protein. Lastly we introduce new visualizations of both the convolutional filters and the attention mechanisms and show how they can be used to extract biological relevant knowledge from the LSTM networks.
Protein Secondary Structure Prediction with Long Short Term Memory Networks
Jan 04, 2015



Abstract:Prediction of protein secondary structure from the amino acid sequence is a classical bioinformatics problem. Common methods use feed forward neural networks or SVMs combined with a sliding window, as these models does not naturally handle sequential data. Recurrent neural networks are an generalization of the feed forward neural network that naturally handle sequential data. We use a bidirectional recurrent neural network with long short term memory cells for prediction of secondary structure and evaluate using the CB513 dataset. On the secondary structure 8-class problem we report better performance (0.674) than state of the art (0.664). Our model includes feed forward networks between the long short term memory cells, a path that can be further explored.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge