Sébastien Henwood
MemSE: Fast MSE Prediction for Noisy Memristor-Based DNN Accelerators
May 03, 2022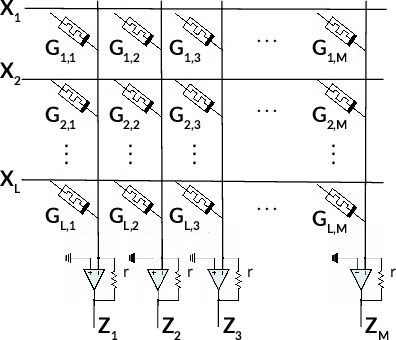
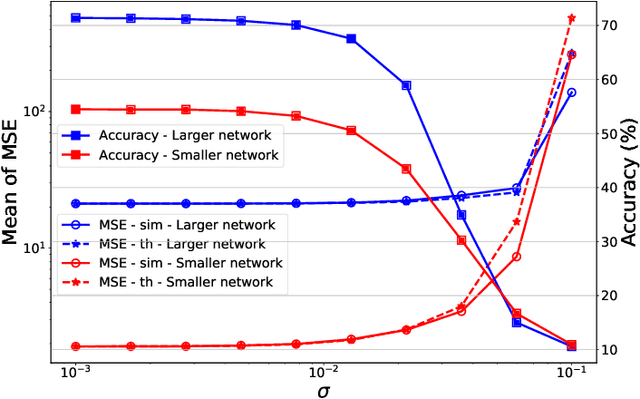
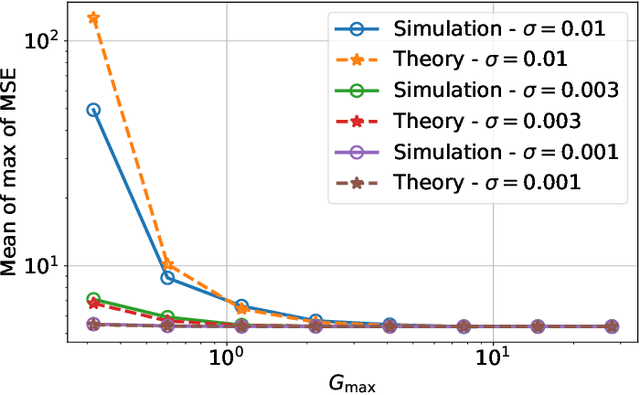
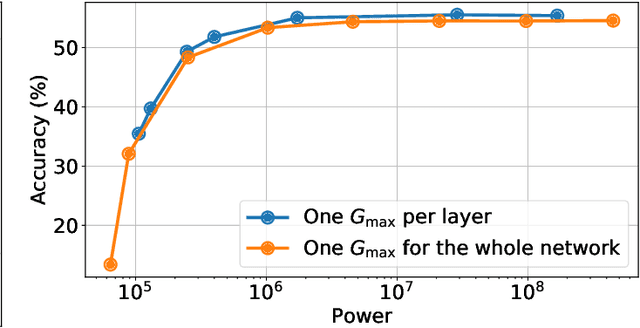
Abstract:Memristors enable the computation of matrix-vector multiplications (MVM) in memory and, therefore, show great potential in highly increasing the energy efficiency of deep neural network (DNN) inference accelerators. However, computations in memristors suffer from hardware non-idealities and are subject to different sources of noise that may negatively impact system performance. In this work, we theoretically analyze the mean squared error of DNNs that use memristor crossbars to compute MVM. We take into account both the quantization noise, due to the necessity of reducing the DNN model size, and the programming noise, stemming from the variability during the programming of the memristance value. Simulations on pre-trained DNN models showcase the accuracy of the analytical prediction. Furthermore the proposed method is almost two order of magnitude faster than Monte-Carlo simulation, thus making it possible to optimize the implementation parameters to achieve minimal error for a given power constraint.
Layerwise Noise Maximisation to Train Low-Energy Deep Neural Networks
Dec 23, 2019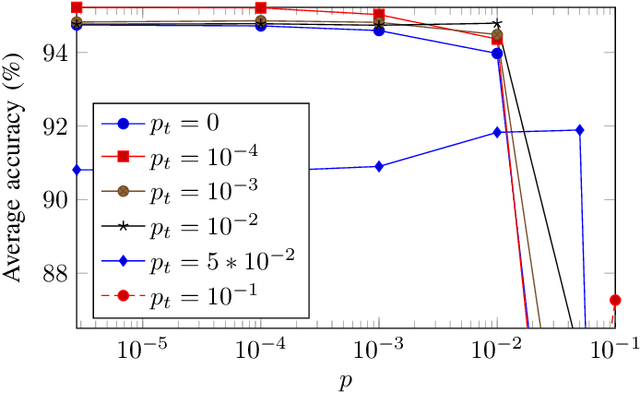
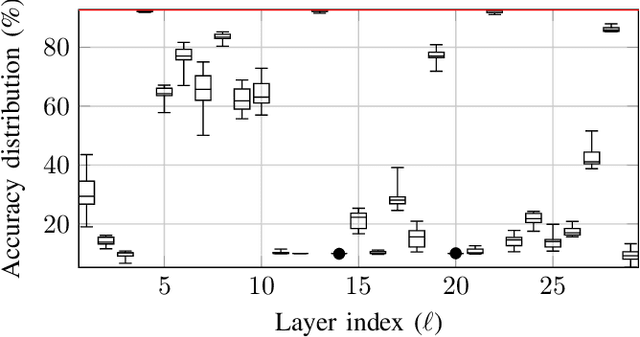
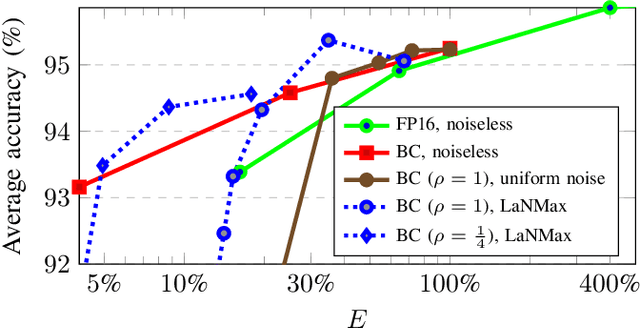
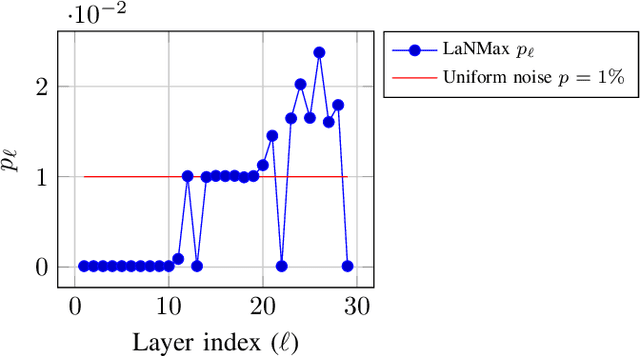
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) depend on the storage of a large number of parameters, which consumes an important portion of the energy used during inference. This paper considers the case where the energy usage of memory elements can be reduced at the cost of reduced reliability. A training algorithm is proposed to optimize the reliability of the storage separately for each layer of the network, while incurring a negligible complexity overhead compared to a conventional stochastic gradient descent training. For an exponential energy-reliability model, the proposed training approach can decrease the memory energy consumption of a DNN with binary parameters by 3.3$\times$ at isoaccuracy, compared to a reliable implementation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge