Ryosuke Takanami
A Comprehensive Survey on Physical Risk Control in the Era of Foundation Model-enabled Robotics
May 19, 2025Abstract:Recent Foundation Model-enabled robotics (FMRs) display greatly improved general-purpose skills, enabling more adaptable automation than conventional robotics. Their ability to handle diverse tasks thus creates new opportunities to replace human labor. However, unlike general foundation models, FMRs interact with the physical world, where their actions directly affect the safety of humans and surrounding objects, requiring careful deployment and control. Based on this proposition, our survey comprehensively summarizes robot control approaches to mitigate physical risks by covering all the lifespan of FMRs ranging from pre-deployment to post-accident stage. Specifically, we broadly divide the timeline into the following three phases: (1) pre-deployment phase, (2) pre-incident phase, and (3) post-incident phase. Throughout this survey, we find that there is much room to study (i) pre-incident risk mitigation strategies, (ii) research that assumes physical interaction with humans, and (iii) essential issues of foundation models themselves. We hope that this survey will be a milestone in providing a high-resolution analysis of the physical risks of FMRs and their control, contributing to the realization of a good human-robot relationship.
GenDOM: Generalizable One-shot Deformable Object Manipulation with Parameter-Aware Policy
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:Due to the inherent uncertainty in their deformability during motion, previous methods in deformable object manipulation, such as rope and cloth, often required hundreds of real-world demonstrations to train a manipulation policy for each object, which hinders their applications in our ever-changing world. To address this issue, we introduce GenDOM, a framework that allows the manipulation policy to handle different deformable objects with only a single real-world demonstration. To achieve this, we augment the policy by conditioning it on deformable object parameters and training it with a diverse range of simulated deformable objects so that the policy can adjust actions based on different object parameters. At the time of inference, given a new object, GenDOM can estimate the deformable object parameters with only a single real-world demonstration by minimizing the disparity between the grid density of point clouds of real-world demonstrations and simulations in a differentiable physics simulator. Empirical validations on both simulated and real-world object manipulation setups clearly show that our method can manipulate different objects with a single demonstration and significantly outperforms the baseline in both environments (a 62% improvement for in-domain ropes and a 15% improvement for out-of-distribution ropes in simulation, as well as a 26% improvement for ropes and a 50% improvement for cloths in the real world), demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach in one-shot deformable object manipulation.
GenORM: Generalizable One-shot Rope Manipulation with Parameter-Aware Policy
Jun 20, 2023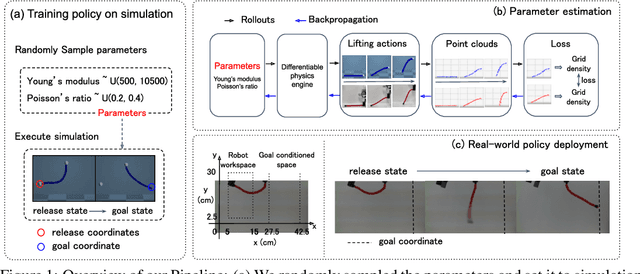
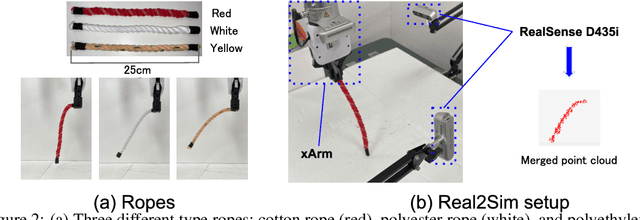
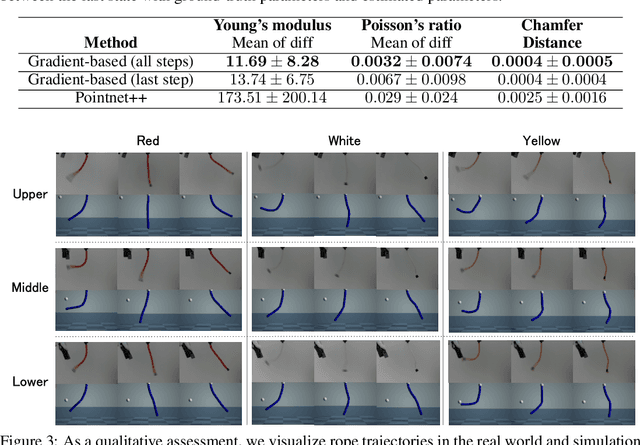
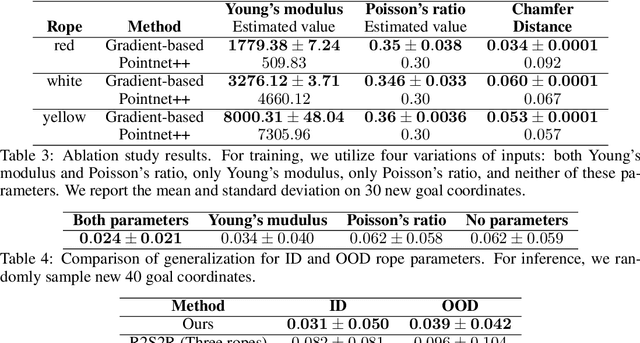
Abstract:Due to the inherent uncertainty in their deformability during motion, previous methods in rope manipulation often require hundreds of real-world demonstrations to train a manipulation policy for each rope, even for simple tasks such as rope goal reaching, which hinder their applications in our ever-changing world. To address this issue, we introduce GenORM, a framework that allows the manipulation policy to handle different deformable ropes with a single real-world demonstration. To achieve this, we augment the policy by conditioning it on deformable rope parameters and training it with a diverse range of simulated deformable ropes so that the policy can adjust actions based on different rope parameters. At the time of inference, given a new rope, GenORM estimates the deformable rope parameters by minimizing the disparity between the grid density of point clouds of real-world demonstrations and simulations. With the help of a differentiable physics simulator, we require only a single real-world demonstration. Empirical validations on both simulated and real-world rope manipulation setups clearly show that our method can manipulate different ropes with a single demonstration and significantly outperforms the baseline in both environments (62% improvement in in-domain ropes, and 15% improvement in out-of-distribution ropes in simulation, 26% improvement in real-world), demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach in one-shot rope manipulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge