Ryan Shea
Columbia University
Generalizable Reinforcement Learning with Biologically Inspired Hyperdimensional Occupancy Grid Maps for Exploration and Goal-Directed Path Planning
Feb 13, 2025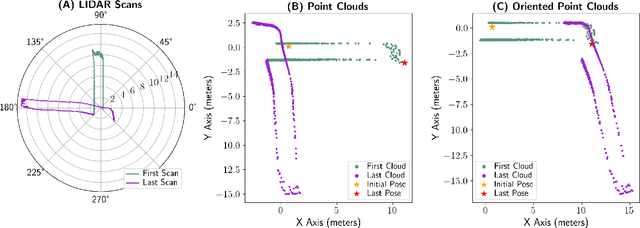
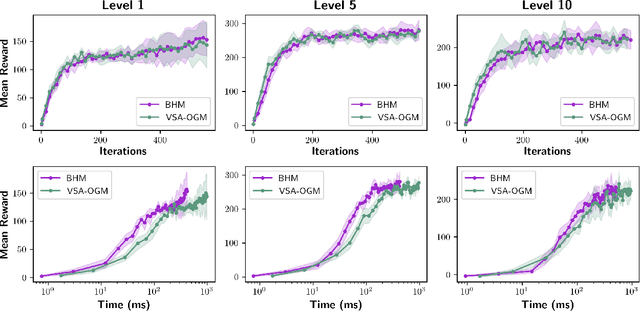
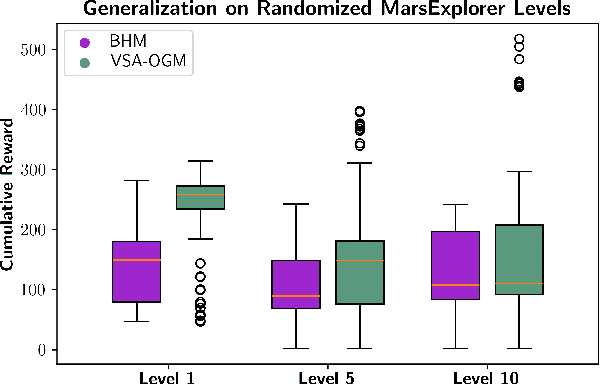
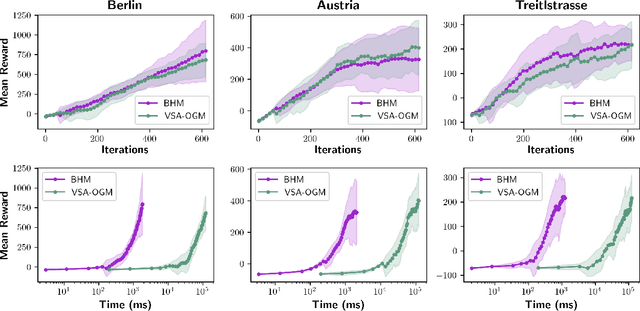
Abstract:Real-time autonomous systems utilize multi-layer computational frameworks to perform critical tasks such as perception, goal finding, and path planning. Traditional methods implement perception using occupancy grid mapping (OGM), segmenting the environment into discretized cells with probabilistic information. This classical approach is well-established and provides a structured input for downstream processes like goal finding and path planning algorithms. Recent approaches leverage a biologically inspired mathematical framework known as vector symbolic architectures (VSA), commonly known as hyperdimensional computing, to perform probabilistic OGM in hyperdimensional space. This approach, VSA-OGM, provides native compatibility with spiking neural networks, positioning VSA-OGM as a potential neuromorphic alternative to conventional OGM. However, for large-scale integration, it is essential to assess the performance implications of VSA-OGM on downstream tasks compared to established OGM methods. This study examines the efficacy of VSA-OGM against a traditional OGM approach, Bayesian Hilbert Maps (BHM), within reinforcement learning based goal finding and path planning frameworks, across a controlled exploration environment and an autonomous driving scenario inspired by the F1-Tenth challenge. Our results demonstrate that VSA-OGM maintains comparable learning performance across single and multi-scenario training configurations while improving performance on unseen environments by approximately 47%. These findings highlight the increased generalizability of policy networks trained with VSA-OGM over BHM, reinforcing its potential for real-world deployment in diverse environments.
ACE: A LLM-based Negotiation Coaching System
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:The growing prominence of LLMs has led to an increase in the development of AI tutoring systems. These systems are crucial in providing underrepresented populations with improved access to valuable education. One important area of education that is unavailable to many learners is strategic bargaining related to negotiation. To address this, we develop a LLM-based Assistant for Coaching nEgotiation (ACE). ACE not only serves as a negotiation partner for users but also provides them with targeted feedback for improvement. To build our system, we collect a dataset of negotiation transcripts between MBA students. These transcripts come from trained negotiators and emulate realistic bargaining scenarios. We use the dataset, along with expert consultations, to design an annotation scheme for detecting negotiation mistakes. ACE employs this scheme to identify mistakes and provide targeted feedback to users. To test the effectiveness of ACE-generated feedback, we conducted a user experiment with two consecutive trials of negotiation and found that it improves negotiation performances significantly compared to a system that doesn't provide feedback and one which uses an alternative method of providing feedback.
A Fairness-Driven Method for Learning Human-Compatible Negotiation Strategies
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Despite recent advancements in AI and NLP, negotiation remains a difficult domain for AI agents. Traditional game theoretic approaches that have worked well for two-player zero-sum games struggle in the context of negotiation due to their inability to learn human-compatible strategies. On the other hand, approaches that only use human data tend to be domain-specific and lack the theoretical guarantees provided by strategies grounded in game theory. Motivated by the notion of fairness as a criterion for optimality in general sum games, we propose a negotiation framework called FDHC which incorporates fairness into both the reward design and search to learn human-compatible negotiation strategies. Our method includes a novel, RL+search technique called LGM-Zero which leverages a pre-trained language model to retrieve human-compatible offers from large action spaces. Our results show that our method is able to achieve more egalitarian negotiation outcomes and improve negotiation quality.
Building Persona Consistent Dialogue Agents with Offline Reinforcement Learning
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:Maintaining a consistent persona is a key quality for any open domain dialogue system. Current state-of-the-art systems do this by training agents with supervised learning or online reinforcement learning (RL). However, systems trained with supervised learning often lack consistency as they are never punished for uttering contradictions. Additional training with RL can alleviate some of these issues, however the training process is expensive. Instead, we propose an offline RL framework to improve the persona consistency of dialogue systems. Our framework allows us to combine the advantages of previous methods as we can inexpensively train our model on existing data as in supervised learning, while punishing and rewarding specific utterances as in RL. We also introduce a simple importance sampling method to reduce the variance of importance weights in offline RL training which we call Variance-Reducing MLE-Initialized (VaRMI) importance sampling. Our automatic and human evaluations show that our framework improves both the persona consistency and dialogue quality of a state-of-the-art social chatbot.
User Adaptive Language Learning Chatbots with a Curriculum
Apr 11, 2023Abstract:Along with the development of systems for natural language understanding and generation, dialog systems have been widely adopted for language learning and practicing. Many current educational dialog systems perform chitchat, where the generated content and vocabulary are not constrained. However, for learners in a school setting, practice through dialog is more effective if it aligns with students' curriculum and focuses on textbook vocabulary. Therefore, we adapt lexically constrained decoding to a dialog system, which urges the dialog system to include curriculum-aligned words and phrases in its generated utterances. We adopt a generative dialog system, BlenderBot3, as our backbone model and evaluate our curriculum-based dialog system with middle school students learning English as their second language. The constrained words and phrases are derived from their textbooks, suggested by their English teachers. The evaluation result demonstrates that the dialog system with curriculum infusion improves students' understanding of target words and increases their interest in practicing English.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge