Ruoqi Sun
Tensor Low-Rank Reconstruction for Semantic Segmentation
Aug 02, 2020



Abstract:Context information plays an indispensable role in the success of semantic segmentation. Recently, non-local self-attention based methods are proved to be effective for context information collection. Since the desired context consists of spatial-wise and channel-wise attentions, 3D representation is an appropriate formulation. However, these non-local methods describe 3D context information based on a 2D similarity matrix, where space compression may lead to channel-wise attention missing. An alternative is to model the contextual information directly without compression. However, this effort confronts a fundamental difficulty, namely the high-rank property of context information. In this paper, we propose a new approach to model the 3D context representations, which not only avoids the space compression but also tackles the high-rank difficulty. Here, inspired by tensor canonical-polyadic decomposition theory (i.e, a high-rank tensor can be expressed as a combination of rank-1 tensors.), we design a low-rank-to-high-rank context reconstruction framework (i.e, RecoNet). Specifically, we first introduce the tensor generation module (TGM), which generates a number of rank-1 tensors to capture fragments of context feature. Then we use these rank-1 tensors to recover the high-rank context features through our proposed tensor reconstruction module (TRM). Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art on various public datasets. Additionally, our proposed method has more than 100 times less computational cost compared with conventional non-local-based methods.
Mask-aware Photorealistic Face Attribute Manipulation
Apr 24, 2018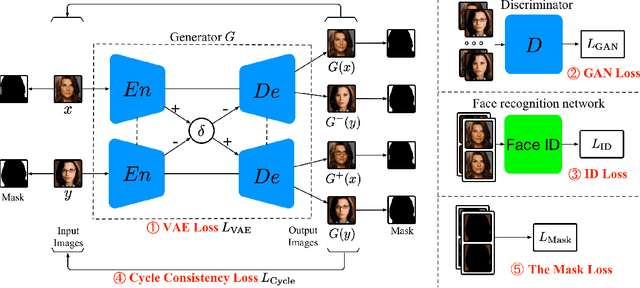
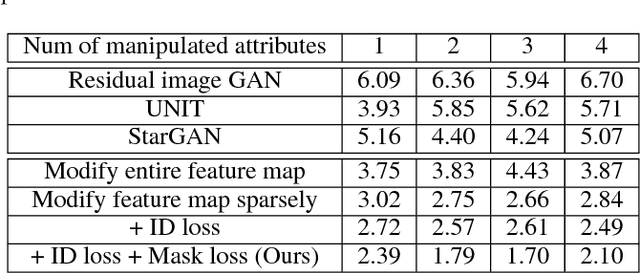


Abstract:The task of face attribute manipulation has found increasing applications, but still remains challeng- ing with the requirement of editing the attributes of a face image while preserving its unique details. In this paper, we choose to combine the Variational AutoEncoder (VAE) and Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) for photorealistic image genera- tion. We propose an effective method to modify a modest amount of pixels in the feature maps of an encoder, changing the attribute strength contin- uously without hindering global information. Our training objectives of VAE and GAN are reinforced by the supervision of face recognition loss and cy- cle consistency loss for faithful preservation of face details. Moreover, we generate facial masks to en- force background consistency, which allows our training to focus on manipulating the foreground face rather than background. Experimental results demonstrate our method, called Mask-Adversarial AutoEncoder (M-AAE), can generate high-quality images with changing attributes and outperforms prior methods in detail preservation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge