Ruiqi Shu
Advancing Ocean State Estimation with efficient and scalable AI
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Accurate and efficient global ocean state estimation remains a grand challenge for Earth system science, hindered by the dual bottlenecks of computational scalability and degraded data fidelity in traditional data assimilation (DA) and deep learning (DL) approaches. Here we present an AI-driven Data Assimilation Framework for Ocean (ADAF-Ocean) that directly assimilates multi-source and multi-scale observations, ranging from sparse in-situ measurements to 4 km satellite swaths, without any interpolation or data thinning. Inspired by Neural Processes, ADAF-Ocean learns a continuous mapping from heterogeneous inputs to ocean states, preserving native data fidelity. Through AI-driven super-resolution, it reconstructs 0.25$^\circ$ mesoscale dynamics from coarse 1$^\circ$ fields, which ensures both efficiency and scalability, with just 3.7\% more parameters than the 1$^\circ$ configuration. When coupled with a DL forecasting system, ADAF-Ocean extends global forecast skill by up to 20 days compared to baselines without assimilation. This framework establishes a computationally viable and scientifically rigorous pathway toward real-time, high-resolution Earth system monitoring.
NeuralOM: Neural Ocean Model for Subseasonal-to-Seasonal Simulation
May 27, 2025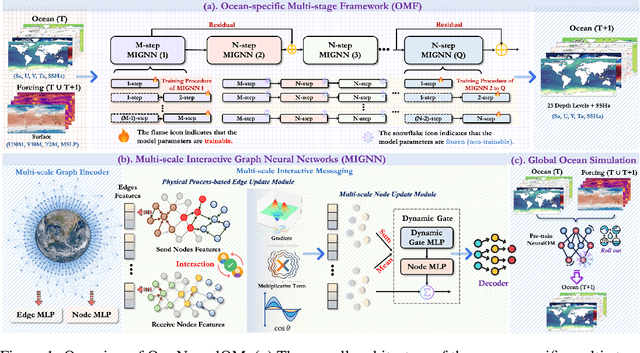
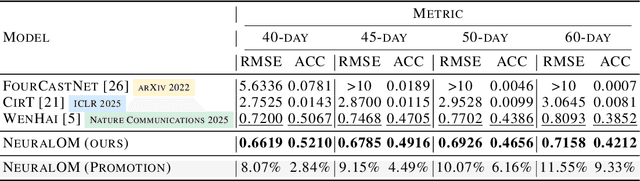
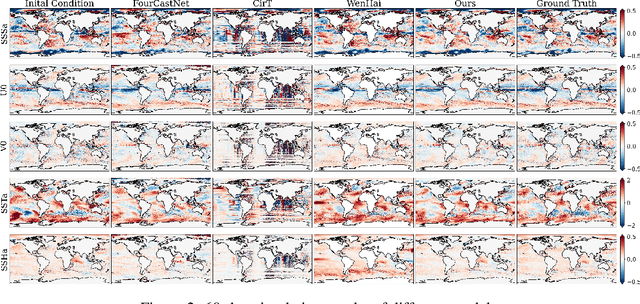
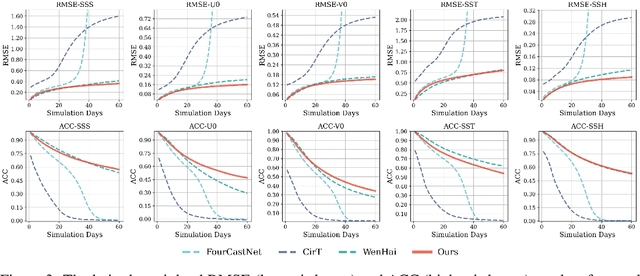
Abstract:Accurate Subseasonal-to-Seasonal (S2S) ocean simulation is critically important for marine research, yet remains challenging due to its substantial thermal inertia and extended time delay. Machine learning (ML)-based models have demonstrated significant advancements in simulation accuracy and computational efficiency compared to traditional numerical methods. Nevertheless, a significant limitation of current ML models for S2S ocean simulation is their inadequate incorporation of physical consistency and the slow-changing properties of the ocean system. In this work, we propose a neural ocean model (NeuralOM) for S2S ocean simulation with a multi-scale interactive graph neural network to emulate diverse physical phenomena associated with ocean systems effectively. Specifically, we propose a multi-stage framework tailored to model the ocean's slowly changing nature. Additionally, we introduce a multi-scale interactive messaging module to capture complex dynamical behaviors, such as gradient changes and multiplicative coupling relationships inherent in ocean dynamics. Extensive experimental evaluations confirm that our proposed NeuralOM outperforms state-of-the-art models in S2S and extreme event simulation. The codes are available at https://github.com/YuanGao-YG/NeuralOM.
Advanced long-term earth system forecasting by learning the small-scale nature
May 26, 2025Abstract:Reliable long-term forecast of Earth system dynamics is heavily hampered by instabilities in current AI models during extended autoregressive simulations. These failures often originate from inherent spectral bias, leading to inadequate representation of critical high-frequency, small-scale processes and subsequent uncontrolled error amplification. We present Triton, an AI framework designed to address this fundamental challenge. Inspired by increasing grids to explicitly resolve small scales in numerical models, Triton employs a hierarchical architecture processing information across multiple resolutions to mitigate spectral bias and explicitly model cross-scale dynamics. We demonstrate Triton's superior performance on challenging forecast tasks, achieving stable year-long global temperature forecasts, skillful Kuroshio eddy predictions till 120 days, and high-fidelity turbulence simulations preserving fine-scale structures all without external forcing, with significantly surpassing baseline AI models in long-term stability and accuracy. By effectively suppressing high-frequency error accumulation, Triton offers a promising pathway towards trustworthy AI-driven simulation for climate and earth system science.
Turb-L1: Achieving Long-term Turbulence Tracing By Tackling Spectral Bias
May 25, 2025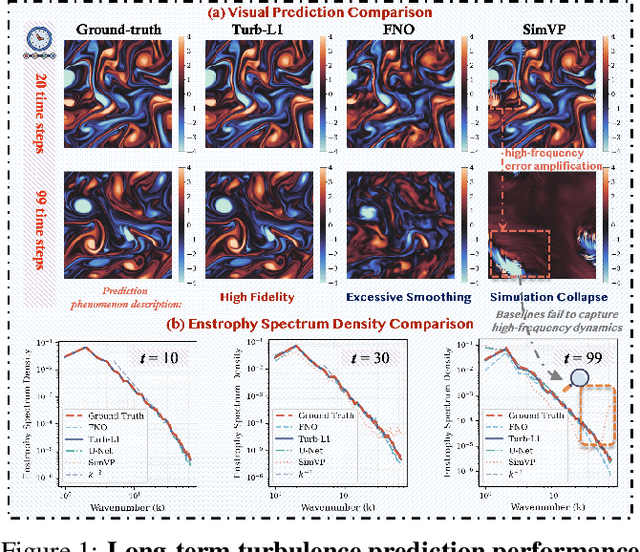
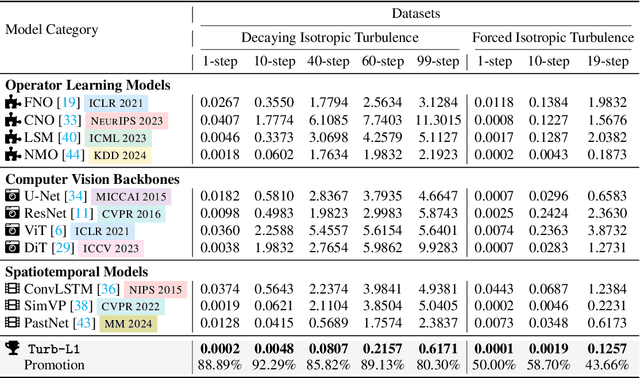
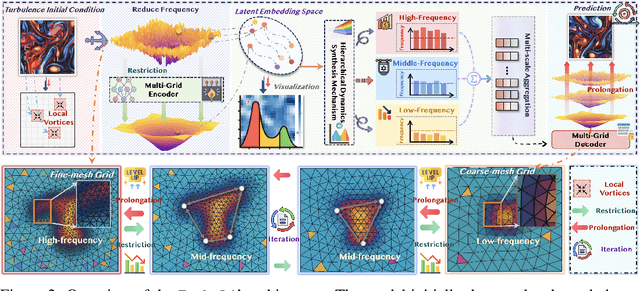
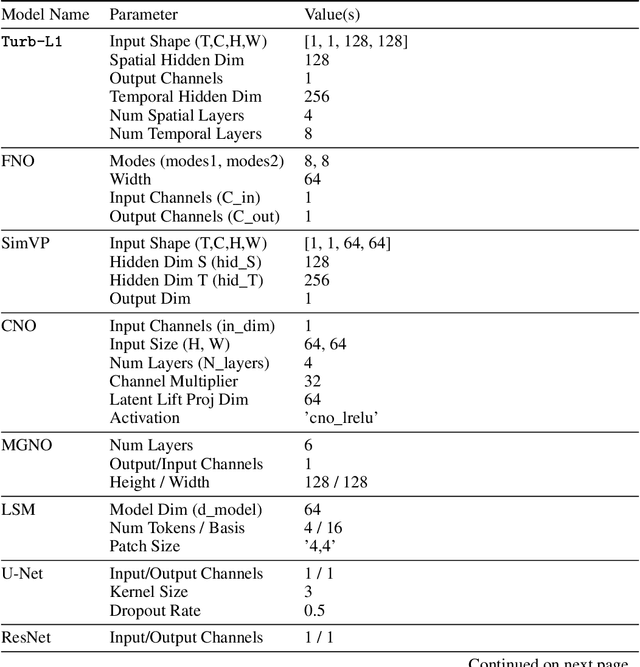
Abstract:Accurately predicting the long-term evolution of turbulence is crucial for advancing scientific understanding and optimizing engineering applications. However, existing deep learning methods face significant bottlenecks in long-term autoregressive prediction, which exhibit excessive smoothing and fail to accurately track complex fluid dynamics. Our extensive experimental and spectral analysis of prevailing methods provides an interpretable explanation for this shortcoming, identifying Spectral Bias as the core obstacle. Concretely, spectral bias is the inherent tendency of models to favor low-frequency, smooth features while overlooking critical high-frequency details during training, thus reducing fidelity and causing physical distortions in long-term predictions. Building on this insight, we propose Turb-L1, an innovative turbulence prediction method, which utilizes a Hierarchical Dynamics Synthesis mechanism within a multi-grid architecture to explicitly overcome spectral bias. It accurately captures cross-scale interactions and preserves the fidelity of high-frequency dynamics, enabling reliable long-term tracking of turbulence evolution. Extensive experiments on the 2D turbulence benchmark show that Turb-L1 demonstrates excellent performance: (I) In long-term predictions, it reduces Mean Squared Error (MSE) by $80.3\%$ and increases Structural Similarity (SSIM) by over $9\times$ compared to the SOTA baseline, significantly improving prediction fidelity. (II) It effectively overcomes spectral bias, accurately reproducing the full enstrophy spectrum and maintaining physical realism in high-wavenumber regions, thus avoiding the spectral distortions or spurious energy accumulation seen in other methods.
BeamVQ: Beam Search with Vector Quantization to Mitigate Data Scarcity in Physical Spatiotemporal Forecasting
Feb 26, 2025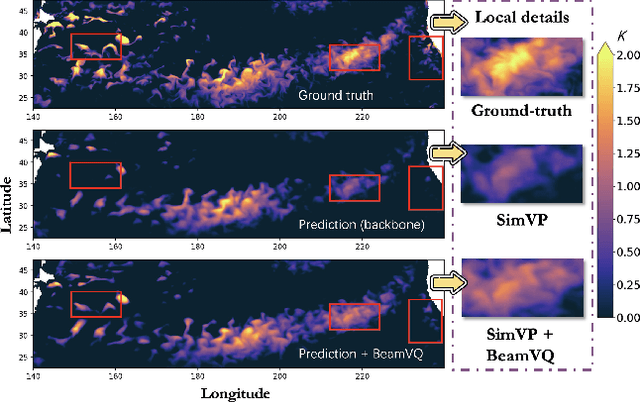
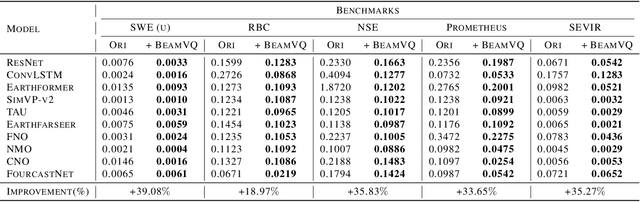
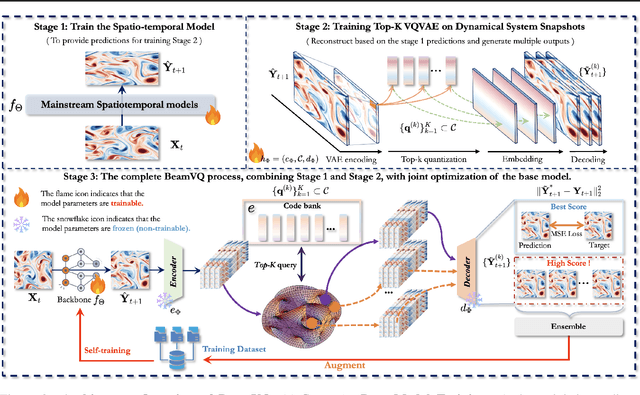
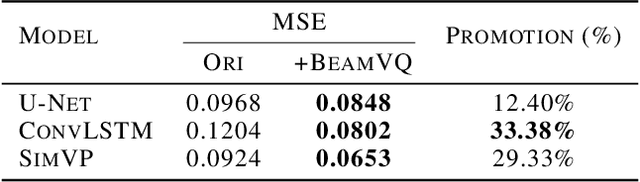
Abstract:In practice, physical spatiotemporal forecasting can suffer from data scarcity, because collecting large-scale data is non-trivial, especially for extreme events. Hence, we propose \method{}, a novel probabilistic framework to realize iterative self-training with new self-ensemble strategies, achieving better physical consistency and generalization on extreme events. Following any base forecasting model, we can encode its deterministic outputs into a latent space and retrieve multiple codebook entries to generate probabilistic outputs. Then BeamVQ extends the beam search from discrete spaces to the continuous state spaces in this field. We can further employ domain-specific metrics (e.g., Critical Success Index for extreme events) to filter out the top-k candidates and develop the new self-ensemble strategy by combining the high-quality candidates. The self-ensemble can not only improve the inference quality and robustness but also iteratively augment the training datasets during continuous self-training. Consequently, BeamVQ realizes the exploration of rare but critical phenomena beyond the original dataset. Comprehensive experiments on different benchmarks and backbones show that BeamVQ consistently reduces forecasting MSE (up to 39%), enhancing extreme events detection and proving its effectiveness in handling data scarcity.
Improved Forecasts of Global Extreme Marine Heatwaves Through a Physics-guided Data-driven Approach
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:The unusually warm sea surface temperature events known as marine heatwaves (MHWs) have a profound impact on marine ecosystems. Accurate prediction of extreme MHWs has significant scientific and financial worth. However, existing methods still have certain limitations, especially in the most extreme MHWs. In this study, to address these issues, based on the physical nature of MHWs, we created a novel deep learning neural network that is capable of accurate 10-day MHW forecasting. Our framework significantly improves the forecast ability of extreme MHWs through two specially designed modules inspired by numerical models: a coupler and a probabilistic data argumentation. The coupler simulates the driving effect of atmosphere on MHWs while the probabilistic data argumentation approaches significantly boost the forecast ability of extreme MHWs based on the idea of ensemble forecast. Compared with traditional numerical prediction, our framework has significantly higher accuracy and requires fewer computational resources. What's more, explainable AI methods show that wind forcing is the primary driver of MHW evolution and reveal its relation with air-sea heat exchange. Overall, our model provides a framework for understanding MHWs' driving processes and operational forecasts in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge