Rongkang Dong
Multi-level distortion-aware deformable network for omnidirectional image super-resolution
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:As augmented reality and virtual reality applications gain popularity, image processing for OmniDirectional Images (ODIs) has attracted increasing attention. OmniDirectional Image Super-Resolution (ODISR) is a promising technique for enhancing the visual quality of ODIs. Before performing super-resolution, ODIs are typically projected from a spherical surface onto a plane using EquiRectangular Projection (ERP). This projection introduces latitude-dependent geometric distortion in ERP images: distortion is minimal near the equator but becomes severe toward the poles, where image content is stretched across a wider area. However, existing ODISR methods have limited sampling ranges and feature extraction capabilities, which hinder their ability to capture distorted patterns over large areas. To address this issue, we propose a novel Multi-level Distortion-aware Deformable Network (MDDN) for ODISR, designed to expand the sampling range and receptive field. Specifically, the feature extractor in MDDN comprises three parallel branches: a deformable attention mechanism (serving as the dilation=1 path) and two dilated deformable convolutions with dilation rates of 2 and 3. This architecture expands the sampling range to include more distorted patterns across wider areas, generating dense and comprehensive features that effectively capture geometric distortions in ERP images. The representations extracted from these deformable feature extractors are adaptively fused in a multi-level feature fusion module. Furthermore, to reduce computational cost, a low-rank decomposition strategy is applied to dilated deformable convolutions. Extensive experiments on publicly available datasets demonstrate that MDDN outperforms state-of-the-art methods, underscoring its effectiveness and superiority in ODISR.
Vision-Language Model Guided Image Restoration
Dec 19, 2025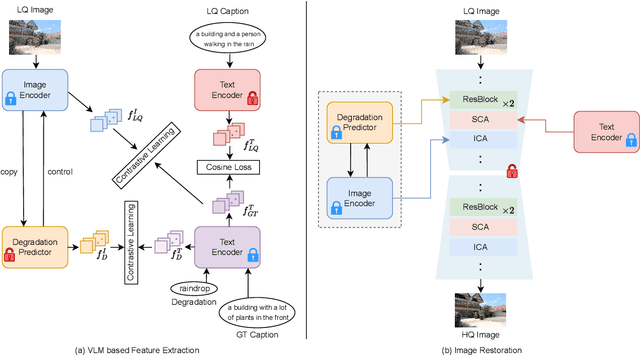
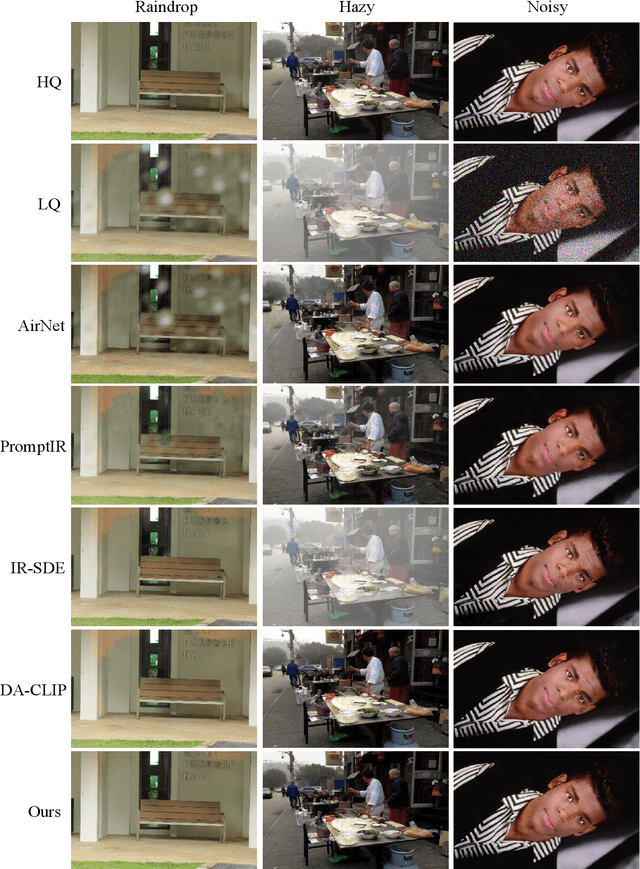
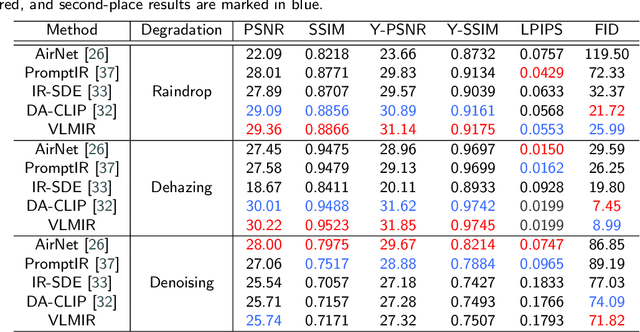

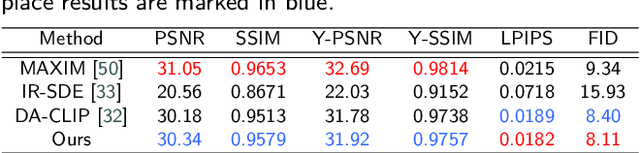
Abstract:Many image restoration (IR) tasks require both pixel-level fidelity and high-level semantic understanding to recover realistic photos with fine-grained details. However, previous approaches often struggle to effectively leverage both the visual and linguistic knowledge. Recent efforts have attempted to incorporate Vision-language models (VLMs), which excel at aligning visual and textual features, into universal IR. Nevertheless, these methods fail to utilize the linguistic priors to ensure semantic coherence during the restoration process. To address this issue, in this paper, we propose the Vision-Language Model Guided Image Restoration (VLMIR) framework, which leverages the rich vision-language priors of VLMs, such as CLIP, to enhance IR performance through improved visual perception and semantic understanding. Our approach consists of two stages: VLM-based feature extraction and diffusion-based image restoration. In the first stage, we extract complementary visual and linguistic representations of input images by condensing the visual perception and high-level semantic priors through VLMs. Specifically, we align the embeddings of captions from low-quality and high-quality images using a cosine similarity loss with LoRA fine-tuning, and employ a degradation predictor to decompose degradation and clean image content embeddings. These complementary visual and textual embeddings are then integrated into a diffusion-based model via cross-attention mechanisms for enhanced restoration. Extensive experiments and ablation studies demonstrate that VLMIR achieves superior performance across both universal and degradation-specific IR tasks, underscoring the critical role of integrated visual and linguistic knowledge from VLMs in advancing image restoration capabilities.
Towards Multi-View Consistent Style Transfer with One-Step Diffusion via Vision Conditioning
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:The stylization of 3D scenes is an increasingly attractive topic in 3D vision. Although image style transfer has been extensively researched with promising results, directly applying 2D style transfer methods to 3D scenes often fails to preserve the structural and multi-view properties of 3D environments, resulting in unpleasant distortions in images from different viewpoints. To address these issues, we leverage the remarkable generative prior of diffusion-based models and propose a novel style transfer method, OSDiffST, based on a pre-trained one-step diffusion model (i.e., SD-Turbo) for rendering diverse styles in multi-view images of 3D scenes. To efficiently adapt the pre-trained model for multi-view style transfer on small datasets, we introduce a vision condition module to extract style information from the reference style image to serve as conditional input for the diffusion model and employ LoRA in diffusion model for adaptation. Additionally, we consider color distribution alignment and structural similarity between the stylized and content images using two specific loss functions. As a result, our method effectively preserves the structural information and multi-view consistency in stylized images without any 3D information. Experiments show that our method surpasses other promising style transfer methods in synthesizing various styles for multi-view images of 3D scenes. Stylized images from different viewpoints generated by our method achieve superior visual quality, with better structural integrity and less distortion. The source code is available at https://github.com/YushenZuo/OSDiffST.
Geometric Distortion Guided Transformer for Omnidirectional Image Super-Resolution
Jun 16, 2024



Abstract:As virtual and augmented reality applications gain popularity, omnidirectional image (ODI) super-resolution has become increasingly important. Unlike 2D plain images that are formed on a plane, ODIs are projected onto spherical surfaces. Applying established image super-resolution methods to ODIs, therefore, requires performing equirectangular projection (ERP) to map the ODIs onto a plane. ODI super-resolution needs to take into account geometric distortion resulting from ERP. However, without considering such geometric distortion of ERP images, previous deep-learning-based methods only utilize a limited range of pixels and may easily miss self-similar textures for reconstruction. In this paper, we introduce a novel Geometric Distortion Guided Transformer for Omnidirectional image Super-Resolution (GDGT-OSR). Specifically, a distortion modulated rectangle-window self-attention mechanism, integrated with deformable self-attention, is proposed to better perceive the distortion and thus involve more self-similar textures. Distortion modulation is achieved through a newly devised distortion guidance generator that produces guidance by exploiting the variability of distortion across latitudes. Furthermore, we propose a dynamic feature aggregation scheme to adaptively fuse the features from different self-attention modules. We present extensive experimental results on public datasets and show that the new GDGT-OSR outperforms methods in existing literature.
Resource-Constrained Edge AI with Early Exit Prediction
Jun 19, 2022



Abstract:By leveraging the data sample diversity, the early-exit network recently emerges as a prominent neural network architecture to accelerate the deep learning inference process. However, intermediate classifiers of the early exits introduce additional computation overhead, which is unfavorable for resource-constrained edge artificial intelligence (AI). In this paper, we propose an early exit prediction mechanism to reduce the on-device computation overhead in a device-edge co-inference system supported by early-exit networks. Specifically, we design a low-complexity module, namely the Exit Predictor, to guide some distinctly "hard" samples to bypass the computation of the early exits. Besides, considering the varying communication bandwidth, we extend the early exit prediction mechanism for latency-aware edge inference, which adapts the prediction thresholds of the Exit Predictor and the confidence thresholds of the early-exit network via a few simple regression models. Extensive experiment results demonstrate the effectiveness of the Exit Predictor in achieving a better tradeoff between accuracy and on-device computation overhead for early-exit networks. Besides, compared with the baseline methods, the proposed method for latency-aware edge inference attains higher inference accuracy under different bandwidth conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge