Ronan Riochet
Occlusion resistant learning of intuitive physics from videos
Apr 30, 2020



Abstract:To reach human performance on complex tasks, a key ability for artificial systems is to understand physical interactions between objects, and predict future outcomes of a situation. This ability, often referred to as intuitive physics, has recently received attention and several methods were proposed to learn these physical rules from video sequences. Yet, most of these methods are restricted to the case where no, or only limited, occlusions occur. In this work we propose a probabilistic formulation of learning intuitive physics in 3D scenes with significant inter-object occlusions. In our formulation, object positions are modeled as latent variables enabling the reconstruction of the scene. We then propose a series of approximations that make this problem tractable. Object proposals are linked across frames using a combination of a recurrent interaction network, modeling the physics in object space, and a compositional renderer, modeling the way in which objects project onto pixel space. We demonstrate significant improvements over state-of-the-art in the intuitive physics benchmark of IntPhys. We apply our method to a second dataset with increasing levels of occlusions, showing it realistically predicts segmentation masks up to 30 frames in the future. Finally, we also show results on predicting motion of objects in real videos.
IntPhys: A Framework and Benchmark for Visual Intuitive Physics Reasoning
Jun 26, 2018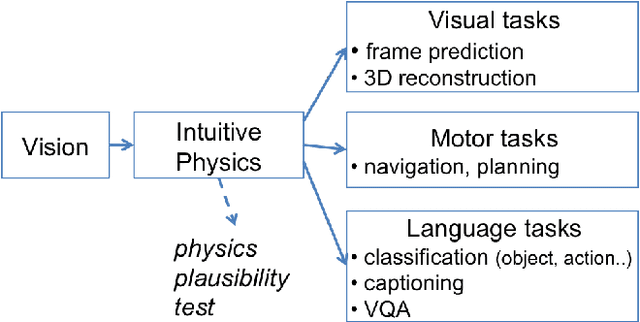

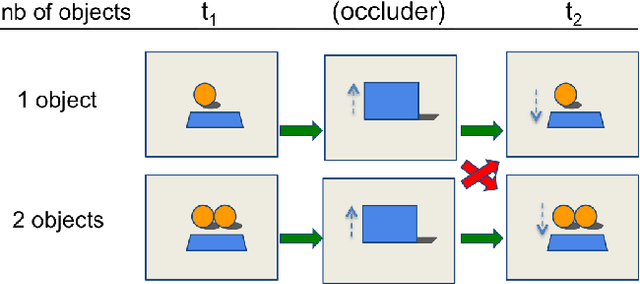
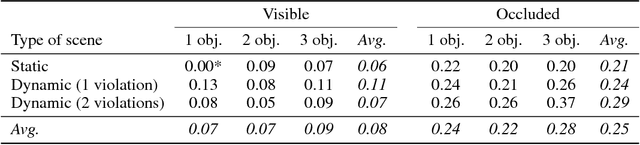
Abstract:In order to reach human performance on complex visual tasks, artificial systems need to incorporate a significant amount of understanding of the world in terms of macroscopic objects, movements, forces, etc. Inspired by work on intuitive physics in infants, we propose an evaluation framework which diagnoses how much a given system understands about physics by testing whether it can tell apart well matched videos of possible versus impossible events. The test requires systems to compute a physical plausibility score over an entire video. It is free of bias and can test a range of specific physical reasoning skills. We then describe the first release of a benchmark dataset aimed at learning intuitive physics in an unsupervised way, using videos constructed with a game engine. We describe two Deep Neural Network baseline systems trained with a future frame prediction objective and tested on the possible versus impossible discrimination task. The analysis of their results compared to human data gives novel insights in the potentials and limitations of next frame prediction architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge