Rodrigo Alves
Czech Technical University in Prague
Reflecting in the Reflection: Integrating a Socratic Questioning Framework into Automated AI-Based Question Generation
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Designing good reflection questions is pedagogically important but time-consuming and unevenly supported across teachers. This paper introduces a reflection-in-reflection framework for automated generation of reflection questions with large language models (LLMs). Our approach coordinates two role-specialized agents, a Student-Teacher and a Teacher-Educator, that engage in a Socratic multi-turn dialogue to iteratively refine a single question given a teacher-specified topic, key concepts, student level, and optional instructional materials. The Student-Teacher proposes candidate questions with brief rationales, while the Teacher-Educator evaluates them along clarity, depth, relevance, engagement, and conceptual interconnections, responding only with targeted coaching questions or a fixed signal to stop the dialogue. We evaluate the framework in an authentic lower-secondary ICT setting on the topic, using GPT-4o-mini as the backbone model and a stronger GPT- 4-class LLM as an external evaluator in pairwise comparisons of clarity, relevance, depth, and overall quality. First, we study how interaction design and context (dynamic vs.fixed iteration counts; presence or absence of student level and materials) affect question quality. Dynamic stopping combined with contextual information consistently outperforms fixed 5- or 10-step refinement, with very long dialogues prone to drift or over-complication. Second, we show that our two-agent protocol produces questions that are judged substantially more relevant and deeper, and better overall, than a one-shot baseline using the same backbone model.
From Knots to Knobs: Towards Steerable Collaborative Filtering Using Sparse Autoencoders
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Sparse autoencoders (SAEs) have recently emerged as pivotal tools for introspection into large language models. SAEs can uncover high-quality, interpretable features at different levels of granularity and enable targeted steering of the generation process by selectively activating specific neurons in their latent activations. Our paper is the first to apply this approach to collaborative filtering, aiming to extract similarly interpretable features from representations learned purely from interaction signals. In particular, we focus on a widely adopted class of collaborative autoencoders (CFAEs) and augment them by inserting an SAE between their encoder and decoder networks. We demonstrate that such representation is largely monosemantic and propose suitable mapping functions between semantic concepts and individual neurons. We also evaluate a simple yet effective method that utilizes this representation to steer the recommendations in a desired direction.
Conv4Rec: A 1-by-1 Convolutional AutoEncoder for User Profiling through Joint Analysis of Implicit and Explicit Feedbacks
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:We introduce a new convolutional AutoEncoder architecture for user modelling and recommendation tasks with several improvements over the state of the art. Firstly, our model has the flexibility to learn a set of associations and combinations between different interaction types in a way that carries over to each user and item. Secondly, our model is able to learn jointly from both the explicit ratings and the implicit information in the sampling pattern (which we refer to as `implicit feedback'). It can also make separate predictions for the probability of consuming content and the likelihood of granting it a high rating if observed. This not only allows the model to make predictions for both the implicit and explicit feedback, but also increases the informativeness of the predictions: in particular, our model can identify items which users would not have been likely to consume naturally, but would be likely to enjoy if exposed to them. Finally, we provide several generalization bounds for our model, which to the best of our knowledge, are among the first generalization bounds for auto-encoders in a Recommender Systems setting; we also show that optimizing our loss function guarantees the recovery of the exact sampling distribution over interactions up to a small error in total variation. In experiments on several real-life datasets, we achieve state-of-the-art performance on both the implicit and explicit feedback prediction tasks despite relying on a single model for both, and benefiting from additional interpretability in the form of individual predictions for the probabilities of each possible rating.
The Future is Sparse: Embedding Compression for Scalable Retrieval in Recommender Systems
May 16, 2025Abstract:Industry-scale recommender systems face a core challenge: representing entities with high cardinality, such as users or items, using dense embeddings that must be accessible during both training and inference. However, as embedding sizes grow, memory constraints make storage and access increasingly difficult. We describe a lightweight, learnable embedding compression technique that projects dense embeddings into a high-dimensional, sparsely activated space. Designed for retrieval tasks, our method reduces memory requirements while preserving retrieval performance, enabling scalable deployment under strict resource constraints. Our results demonstrate that leveraging sparsity is a promising approach for improving the efficiency of large-scale recommenders. We release our code at https://github.com/recombee/CompresSAE.
Reasoning-Grounded Natural Language Explanations for Language Models
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:We propose a large language model explainability technique for obtaining faithful natural language explanations by grounding the explanations in a reasoning process. When converted to a sequence of tokens, the outputs of the reasoning process can become part of the model context and later be decoded to natural language as the model produces either the final answer or the explanation. To improve the faithfulness of the explanations, we propose to use a joint predict-explain approach, in which the answers and explanations are inferred directly from the reasoning sequence, without the explanations being dependent on the answers and vice versa. We demonstrate the plausibility of the proposed technique by achieving a high alignment between answers and explanations in several problem domains, observing that language models often simply copy the partial decisions from the reasoning sequence into the final answers or explanations. Furthermore, we show that the proposed use of reasoning can also improve the quality of the answers.
Bridging Offline-Online Evaluation with a Time-dependent and Popularity Bias-free Offline Metric for Recommenders
Aug 14, 2023Abstract:The evaluation of recommendation systems is a complex task. The offline and online evaluation metrics for recommender systems are ambiguous in their true objectives. The majority of recently published papers benchmark their methods using ill-posed offline evaluation methodology that often fails to predict true online performance. Because of this, the impact that academic research has on the industry is reduced. The aim of our research is to investigate and compare the online performance of offline evaluation metrics. We show that penalizing popular items and considering the time of transactions during the evaluation significantly improves our ability to choose the best recommendation model for a live recommender system. Our results, averaged over five large-size real-world live data procured from recommenders, aim to help the academic community to understand better offline evaluation and optimization criteria that are more relevant for real applications of recommender systems.
Generalization Bounds for Inductive Matrix Completion in Low-noise Settings
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:We study inductive matrix completion (matrix completion with side information) under an i.i.d. subgaussian noise assumption at a low noise regime, with uniform sampling of the entries. We obtain for the first time generalization bounds with the following three properties: (1) they scale like the standard deviation of the noise and in particular approach zero in the exact recovery case; (2) even in the presence of noise, they converge to zero when the sample size approaches infinity; and (3) for a fixed dimension of the side information, they only have a logarithmic dependence on the size of the matrix. Differently from many works in approximate recovery, we present results both for bounded Lipschitz losses and for the absolute loss, with the latter relying on Talagrand-type inequalities. The proofs create a bridge between two approaches to the theoretical analysis of matrix completion, since they consist in a combination of techniques from both the exact recovery literature and the approximate recovery literature.
* 30 Pages, 1 figure; Accepted for publication at AAAI 2023
Orthogonal Inductive Matrix Completion
Apr 23, 2020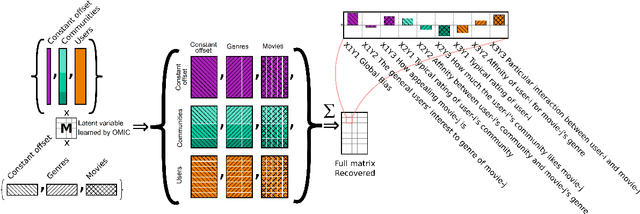
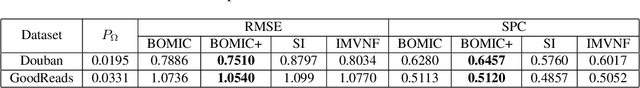
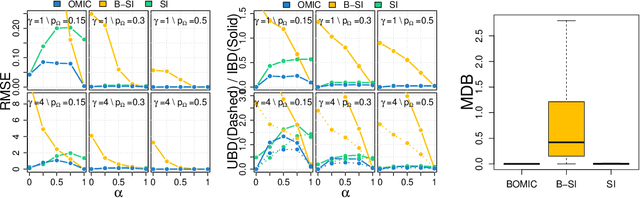
Abstract:We propose orthogonal inductive matrix completion (OMIC), an interpretable model composed of a sum of matrix completion terms, each with orthonormal side information. We can inject prior knowledge about the eigenvectors of the ground truth matrix, whilst maintaining the representation capability of the model. We present a provably converging algorithm that optimizes all components of the model simultaneously, using nuclear-norm regularisation. Our method is backed up by \textit{distribution-free} learning guarantees that improve with the quality of the injected knowledge. As a special case of our general framework, we study a model consisting of a sum of user and item biases (generic behaviour), a non-inductive term (specific behaviour), and an inductive term using side information. Our theoretical analysis shows that $\epsilon$-recovering the ground truth matrix requires at most $O\left( \frac{n+m+(\sqrt{n}+\sqrt{m})\sqrt{rmn}C}{\epsilon^2}\right)$ entries, where $r$ (resp. $C$) is the rank (resp. maximum entry) of the bias-free part of the ground truth matrix. We analyse the performance of OMIC on several synthetic and real datasets. On synthetic datasets with a sliding scale of user bias relevance, we show that OMIC better adapts to different regimes than other methods and can recover the ground truth. On real life datasets containing user/items recommendations and relevant side information, we find that OMIC surpasses the state of the art, with the added benefit of greater interpretability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge