Robert W. Sumner
VQ-Style: Disentangling Style and Content in Motion with Residual Quantized Representations
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Human motion data is inherently rich and complex, containing both semantic content and subtle stylistic features that are challenging to model. We propose a novel method for effective disentanglement of the style and content in human motion data to facilitate style transfer. Our approach is guided by the insight that content corresponds to coarse motion attributes while style captures the finer, expressive details. To model this hierarchy, we employ Residual Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoders (RVQ-VAEs) to learn a coarse-to-fine representation of motion. We further enhance the disentanglement by integrating contrastive learning and a novel information leakage loss with codebook learning to organize the content and the style across different codebooks. We harness this disentangled representation using our simple and effective inference-time technique Quantized Code Swapping, which enables motion style transfer without requiring any fine-tuning for unseen styles. Our framework demonstrates strong versatility across multiple inference applications, including style transfer, style removal, and motion blending.
Search3D: Hierarchical Open-Vocabulary 3D Segmentation
Sep 27, 2024
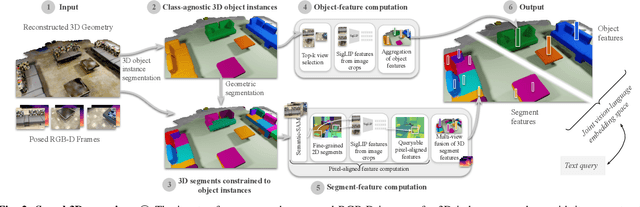
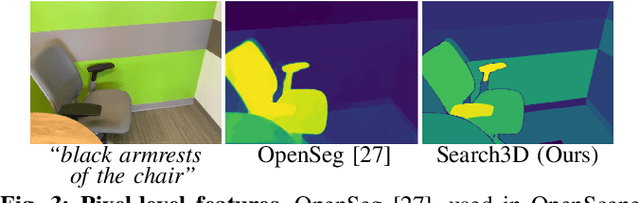

Abstract:Open-vocabulary 3D segmentation enables the exploration of 3D spaces using free-form text descriptions. Existing methods for open-vocabulary 3D instance segmentation primarily focus on identifying object-level instances in a scene. However, they face challenges when it comes to understanding more fine-grained scene entities such as object parts, or regions described by generic attributes. In this work, we introduce Search3D, an approach that builds a hierarchical open-vocabulary 3D scene representation, enabling the search for entities at varying levels of granularity: fine-grained object parts, entire objects, or regions described by attributes like materials. Our method aims to expand the capabilities of open vocabulary instance-level 3D segmentation by shifting towards a more flexible open-vocabulary 3D search setting less anchored to explicit object-centric queries, compared to prior work. To ensure a systematic evaluation, we also contribute a scene-scale open-vocabulary 3D part segmentation benchmark based on MultiScan, along with a set of open-vocabulary fine-grained part annotations on ScanNet++. We verify the effectiveness of Search3D across several tasks, demonstrating that our approach outperforms baselines in scene-scale open-vocabulary 3D part segmentation, while maintaining strong performance in segmenting 3D objects and materials.
OpenMask3D: Open-Vocabulary 3D Instance Segmentation
Jun 23, 2023Abstract:We introduce the task of open-vocabulary 3D instance segmentation. Traditional approaches for 3D instance segmentation largely rely on existing 3D annotated datasets, which are restricted to a closed-set of object categories. This is an important limitation for real-life applications where one might need to perform tasks guided by novel, open-vocabulary queries related to objects from a wide variety. Recently, open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding methods have emerged to address this problem by learning queryable features per each point in the scene. While such a representation can be directly employed to perform semantic segmentation, existing methods have limitations in their ability to identify object instances. In this work, we address this limitation, and propose OpenMask3D, which is a zero-shot approach for open-vocabulary 3D instance segmentation. Guided by predicted class-agnostic 3D instance masks, our model aggregates per-mask features via multi-view fusion of CLIP-based image embeddings. We conduct experiments and ablation studies on the ScanNet200 dataset to evaluate the performance of OpenMask3D, and provide insights about the open-vocabulary 3D instance segmentation task. We show that our approach outperforms other open-vocabulary counterparts, particularly on the long-tail distribution. Furthermore, OpenMask3D goes beyond the limitations of close-vocabulary approaches, and enables the segmentation of object instances based on free-form queries describing object properties such as semantics, geometry, affordances, and material properties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge