Robert Grupp
The Impact of Machine Learning on 2D/3D Registration for Image-guided Interventions: A Systematic Review and Perspective
Aug 04, 2021



Abstract:Image-based navigation is widely considered the next frontier of minimally invasive surgery. It is believed that image-based navigation will increase the access to reproducible, safe, and high-precision surgery as it may then be performed at acceptable costs and effort. This is because image-based techniques avoid the need of specialized equipment and seamlessly integrate with contemporary workflows. Further, it is expected that image-based navigation will play a major role in enabling mixed reality environments and autonomous, robotic workflows. A critical component of image guidance is 2D/3D registration, a technique to estimate the spatial relationships between 3D structures, e.g., volumetric imagery or tool models, and 2D images thereof, such as fluoroscopy or endoscopy. While image-based 2D/3D registration is a mature technique, its transition from the bench to the bedside has been restrained by well-known challenges, including brittleness of the optimization objective, hyperparameter selection, and initialization, difficulties around inconsistencies or multiple objects, and limited single-view performance. One reason these challenges persist today is that analytical solutions are likely inadequate considering the complexity, variability, and high-dimensionality of generic 2D/3D registration problems. The recent advent of machine learning-based approaches to imaging problems that, rather than specifying the desired functional mapping, approximate it using highly expressive parametric models holds promise for solving some of the notorious challenges in 2D/3D registration. In this manuscript, we review the impact of machine learning on 2D/3D registration to systematically summarize the recent advances made by introduction of this novel technology. Grounded in these insights, we then offer our perspective on the most pressing needs, significant open problems, and possible next steps.
Automatic Annotation of Hip Anatomy in Fluoroscopy for Robust and Efficient 2D/3D Registration
Nov 16, 2019



Abstract:Fluoroscopy is the standard imaging modality used to guide hip surgery and is therefore a natural sensor for computer-assisted navigation. In order to efficiently solve the complex registration problems presented during navigation, human-assisted annotations of the intraoperative image are typically required. This manual initialization interferes with the surgical workflow and diminishes any advantages gained from navigation. We propose a method for fully automatic registration using annotations produced by a neural network. Neural networks are trained to simultaneously segment anatomy and identify landmarks in fluoroscopy. Training data is obtained using an intraoperatively incompatible 2D/3D registration of hip anatomy. Ground truth 2D labels are established using projected 3D annotations. Intraoperative registration couples an intensity-based strategy with annotations inferred by the network and requires no human assistance. Ground truth labels were obtained in 366 fluoroscopic images across 6 cadaveric specimens. In a leave-one-subject-out experiment, networks obtained mean dice coefficients for left and right hemipelves, left and right femurs of 0.86, 0.87, 0.90, and 0.84. The mean 2D landmark error was 5.0 mm. The pelvis was registered within 1 degree for 86% of the images when using the proposed intraoperative approach with an average runtime of 7 seconds. In comparison, an intensity-only approach without manual initialization, registered the pelvis to 1 degree in 18% of images. We have created the first accurately annotated, non-synthetic, dataset of hip fluoroscopy. By using these annotations as training data for neural networks, state of the art performance in fluoroscopic segmentation and landmark localization was achieved. Integrating these annotations allows for a robust, fully automatic, and efficient intraoperative registration during fluoroscopic navigation of the hip.
Fast and Automatic Periacetabular Osteotomy Fragment Pose Estimation Using Intraoperatively Implanted Fiducials and Single-View Fluoroscopy
Oct 22, 2019



Abstract:Accurate and consistent mental interpretation of fluoroscopy to determine the position and orientation of acetabular bone fragments in 3D space is difficult. We propose a computer assisted approach that uses a single fluoroscopic view and quickly reports the pose of an acetabular fragment without any user input or initialization. Intraoperatively, but prior to any osteotomies, two constellations of metallic ball-bearings (BBs) are injected into the wing of a patient's ilium and lateral superior pubic ramus. One constellation is located on the expected acetabular fragment, and the other is located on the remaining, larger, pelvis fragment. The 3D locations of each BB are reconstructed using three fluoroscopic views and 2D/3D registrations to a preoperative CT scan of the pelvis. The relative pose of the fragment is established by estimating the movement of the two BB constellations using a single fluoroscopic view taken after osteotomy and fragment relocation. BB detection and inter-view correspondences are automatically computed throughout the processing pipeline. The proposed method was evaluated on a multitude of fluoroscopic images collected from six cadaveric surgeries performed bilaterally on three specimens. Mean fragment rotation error was 2.4 +/- 1.0 degrees, mean translation error was 2.1 +/- 0.6 mm, and mean 3D lateral center edge angle error was 1.0 +/- 0.5 degrees. The average runtime of the single-view pose estimation was 0.7 +/- 0.2 seconds. The proposed method demonstrates accuracy similar to other state of the art systems which require optical tracking systems or multiple-view 2D/3D registrations with manual input. The errors reported on fragment poses and lateral center edge angles are within the margins required for accurate intraoperative evaluation of femoral head coverage.
Pelvis Surface Estimation From Partial CT for Computer-Aided Pelvic Osteotomies
Sep 23, 2019
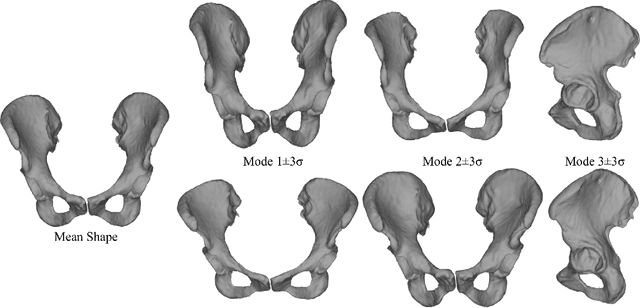
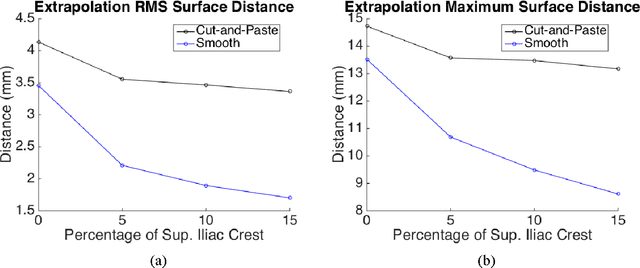
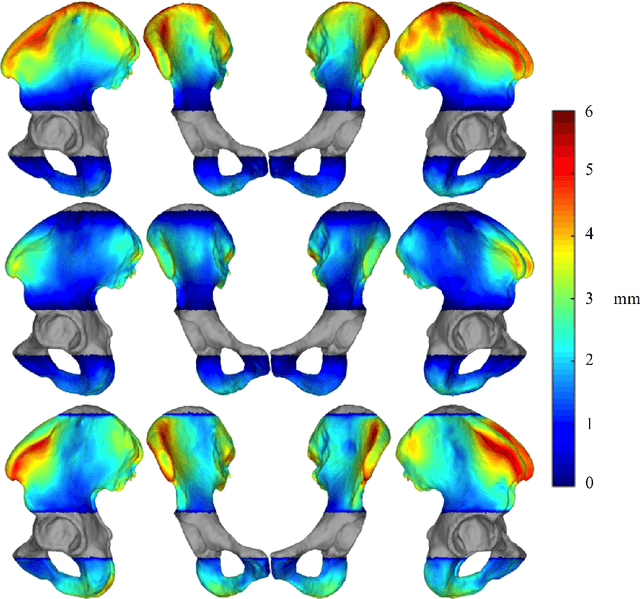
Abstract:Computer-aided surgical systems commonly use preoperative CT scans when performing pelvic osteotomies for intraoperative navigation. These systems have the potential to improve the safety and accuracy of pelvic osteotomies, however, exposing the patient to radiation is a significant drawback. In order to reduce radiation exposure, we propose a new smooth extrapolation method leveraging a partial pelvis CT and a statistical shape model (SSM) of the full pelvis in order to estimate a patient's complete pelvis. A SSM of normal, complete, female pelvis anatomy was created and evaluated from 42 subjects. A leave-one-out test was performed to characterise the inherent generalisation capability of the SSM. An additional leave-one-out test was conducted to measure performance of the smooth extrapolation method and an existing "cut-and-paste" extrapolation method. Unknown anatomy was simulated by keeping the axial slices of the patient's acetabulum intact and varying the amount of the superior iliac crest retained; from 0% to 15% of the total pelvis extent. The smooth technique showed an average improvement over the cut-and-paste method of 1.31 mm and 3.61 mm, in RMS and maximum surface error, respectively. With 5% of the iliac crest retained, the smoothly estimated surface had an RMS surface error of 2.21 mm, an improvement of 1.25 mm when retaining none of the iliac crest. This anatomical estimation method creates the possibility of a patient and surgeon benefiting from the use of a CAS system and simultaneously reducing the patient's radiation exposure.
* CAOS 2015 Extended Paper
Patch-Based Image Similarity for Intraoperative 2D/3D Pelvis Registration During Periacetabular Osteotomy
Sep 23, 2019



Abstract:Periacetabular osteotomy is a challenging surgical procedure for treating developmental hip dysplasia, providing greater coverage of the femoral head via relocation of a patient's acetabulum. Since fluoroscopic imaging is frequently used in the surgical workflow, computer-assisted X-Ray navigation of osteotomes and the relocated acetabular fragment should be feasible. We use intensity-based 2D/3D registration to estimate the pelvis pose with respect to fluoroscopic images, recover relative poses of multiple views, and triangulate landmarks which may be used for navigation. Existing similarity metrics are unable to consistently account for the inherent mismatch between the preoperative intact pelvis, and the intraoperative reality of a fractured pelvis. To mitigate the effect of this mismatch, we continuously estimate the relevance of each pixel to solving the registration and use these values as weightings in a patch-based similarity metric. Limiting computation to randomly selected subsets of patches results in faster runtimes than existing patch-based methods. A simulation study was conducted with random fragment shapes, relocations, and fluoroscopic views, and the proposed method achieved a 1.7 mm mean triangulation error over all landmarks, compared to mean errors of 3 mm and 2.8 mm for the non-patched and image-intensity-variance-weighted patch similarity metrics, respectively.
* Presented at MICCAI CLIP Workshop 2018
Smooth Extrapolation of Unknown Anatomy via Statistical Shape Models
Sep 23, 2019Abstract:Several methods to perform extrapolation of unknown anatomy were evaluated. The primary application is to enhance surgical procedures that may use partial medical images or medical images of incomplete anatomy. Le Fort-based, face-jaw-teeth transplant is one such procedure. From CT data of 36 skulls and 21 mandibles separate Statistical Shape Models of the anatomical surfaces were created. Using the Statistical Shape Models, incomplete surfaces were projected to obtain complete surface estimates. The surface estimates exhibit non-zero error in regions where the true surface is known; it is desirable to keep the true surface and seamlessly merge the estimated unknown surface. Existing extrapolation techniques produce non-smooth transitions from the true surface to the estimated surface, resulting in additional error and a less aesthetically pleasing result. The three extrapolation techniques evaluated were: copying and pasting of the surface estimate (non-smooth baseline), a feathering between the patient surface and surface estimate, and an estimate generated via a Thin Plate Spline trained from displacements between the surface estimate and corresponding vertices of the known patient surface. Feathering and Thin Plate Spline approaches both yielded smooth transitions. However, feathering corrupted known vertex values. Leave-one-out analyses were conducted, with 5% to 50% of known anatomy removed from the left-out patient and estimated via the proposed approaches. The Thin Plate Spline approach yielded smaller errors than the other two approaches, with an average vertex error improvement of 1.46 mm and 1.38 mm for the skull and mandible respectively, over the baseline approach.
* SPIE Medical Imaging Conference 2015 Paper
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge