Ritu Tiwari
Multilingual Machine Translation with Quantum Encoder Decoder Attention-based Convolutional Variational Circuits
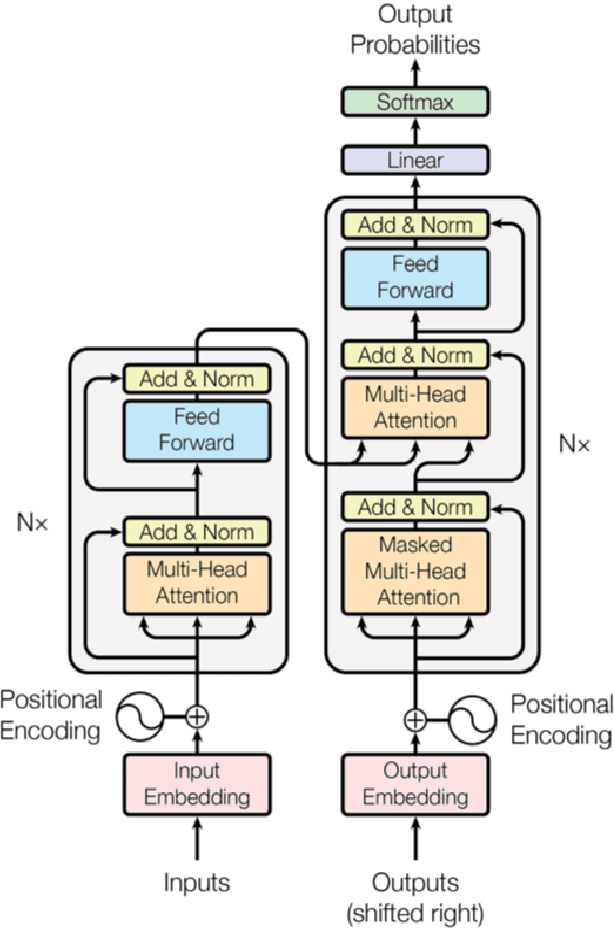
May 14, 2025Abstract:Cloud-based multilingual translation services like Google Translate and Microsoft Translator achieve state-of-the-art translation capabilities. These services inherently use large multilingual language models such as GRU, LSTM, BERT, GPT, T5, or similar encoder-decoder architectures with attention mechanisms as the backbone. Also, new age natural language systems, for instance ChatGPT and DeepSeek, have established huge potential in multiple tasks in natural language processing. At the same time, they also possess outstanding multilingual translation capabilities. However, these models use the classical computing realm as a backend. QEDACVC (Quantum Encoder Decoder Attention-based Convolutional Variational Circuits) is an alternate solution that explores the quantum computing realm instead of the classical computing realm to study and demonstrate multilingual machine translation. QEDACVC introduces the quantum encoder-decoder architecture that simulates and runs on quantum computing hardware via quantum convolution, quantum pooling, quantum variational circuit, and quantum attention as software alterations. QEDACVC achieves an Accuracy of 82% when trained on the OPUS dataset for English, French, German, and Hindi corpora for multilingual translations.
Three Dimensional Route Planning for Multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles using Salp Swarm Algorithm
Dec 18, 2019



Abstract:Route planning for multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) is a series of translation and rotational steps from a given start location to the destination goal location. The goal of the route planning problem is to determine the most optimal route avoiding any collisions with the obstacles present in the environment. Route planning is an NP-hard optimization problem. In this paper, a newly proposed Salp Swarm Algorithm (SSA) is used, and its performance is compared with deterministic and other Nature-Inspired Algorithms (NIAs). The results illustrate that SSA outperforms all the other meta-heuristic algorithms in route planning for multiple UAVs in a 3D environment. The proposed approach improves the average cost and overall time by 1.25% and 6.035% respectively when compared to recently reported data. Route planning is involved in many real-life applications like robot navigation, self-driving car, autonomous UAV for search and rescue operations in dangerous ground-zero situations, civilian surveillance, military combat and even commercial services like package delivery by drones.
Feature Engineering Combined with 1 D Convolutional Neural Network for Improved Mortality Prediction
Dec 08, 2019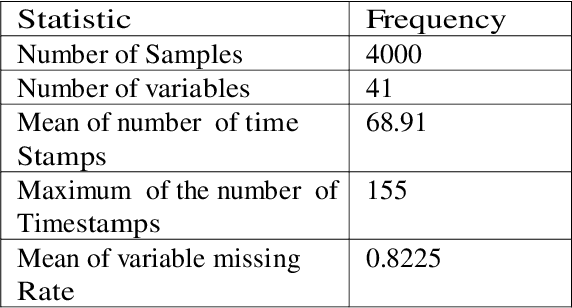
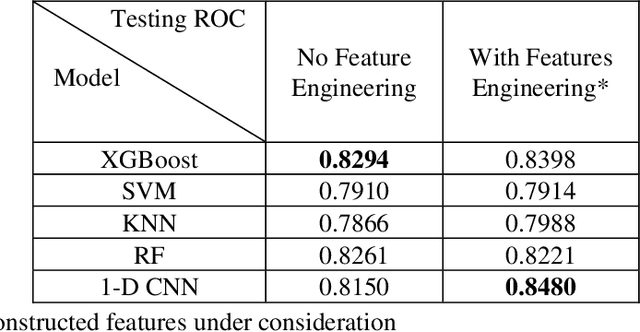
Abstract:The intensive care units (ICUs) are responsible for generating a wealth of useful data in the form of Electronic Health Record (EHR). This data allows for the development of a prediction tool with perfect knowledge backing. We aimed to build a mortality prediction model on 2012 Physionet Challenge mortality prediction database of 4000 patients admitted in ICU. The challenges in the dataset, such as high dimensionality, imbalanced distribution, and missing values were tackled with analytical methods and tools via feature engineering and new variable construction. The objective of the research is to utilize the relations among the clinical variables and construct new variables which would establish the effectiveness of 1-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network (1- D CNN) with constructed features. Its performance with the traditional machine learning algorithms like XGBoost classifier, Support Vector Machine (SVM), K-Neighbours Classifier (K-NN), and Random Forest Classifier (RF) is compared for Area Under Curve (AUC). The investigation reveals the best AUC of 0.848 using 1-D CNN model.
Robot navigation and target capturing using nature-inspired approaches in a dynamic environment
Nov 06, 2019



Abstract:Path Planning and target searching in a three-dimensional environment is a challenging task in the field of robotics. It is an optimization problem as the path from source to destination has to be optimal. This paper aims to generate a collision-free trajectory in a dynamic environment. The path planning problem has sought to be of extreme importance in the military, search and rescue missions and in life-saving tasks. During its operation, the unmanned air vehicle operates in a hostile environment, and faster replanning is needed to reach the target as optimally as possible. This paper presents a novel approach of hierarchical planning using multiresolution abstract levels for faster replanning. Economic constraints like path length, total path planning time and the number of turns are taken into consideration that mandate the use of cost functions. Experimental results show that the hierarchical version of GSO gives better performance compared to the BBO, IWO and their hierarchical versions.
Self-attention based end-to-end Hindi-English Neural Machine Translation
Sep 21, 2019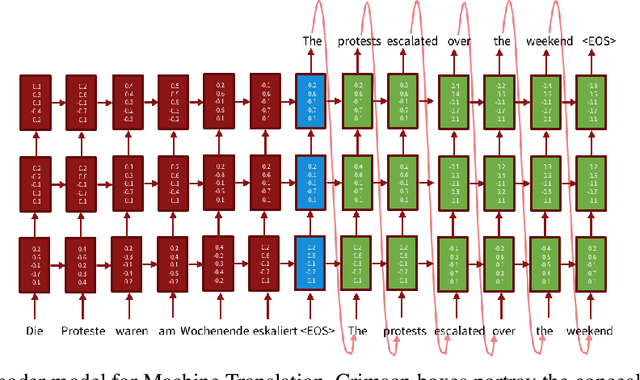
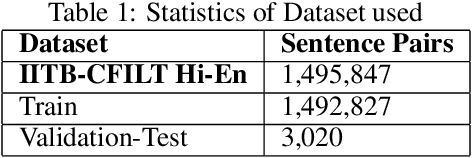

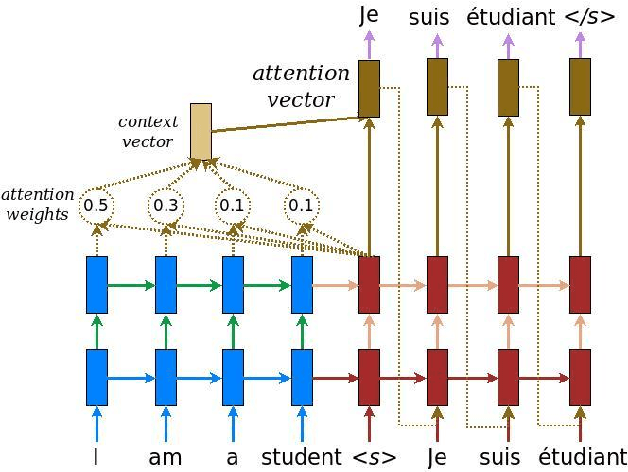
Abstract:Machine Translation (MT) is a zone of concentrate in Natural Language processing which manages the programmed interpretation of human language, starting with one language then onto the next by the PC. Having a rich research history spreading over about three decades, Machine interpretation is a standout amongst the most looked for after region of research in the computational linguistics network. As a piece of this current ace's proposal, the fundamental center examines the Deep-learning based strategies that have gained critical ground as of late and turning into the de facto strategy in MT. We would like to point out the recent advances that have been put forward in the field of Neural Translation models, different domains under which NMT has replaced conventional SMT models and would also like to mention future avenues in the field. Consequently, we propose an end-to-end self-attention transformer network for Neural Machine Translation, trained on Hindi-English parallel corpus and compare the model's efficiency with other state of art models like encoder-decoder and attention-based encoder-decoder neural models on the basis of BLEU. We conclude this paper with a comparative analysis of the three proposed models.
Machine Translation : From Statistical to modern Deep-learning practices
Dec 11, 2018
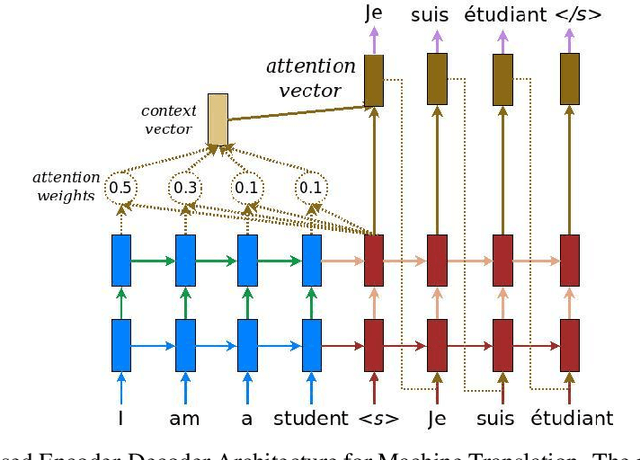
Abstract:Machine translation (MT) is an area of study in Natural Language processing which deals with the automatic translation of human language, from one language to another by the computer. Having a rich research history spanning nearly three decades, Machine translation is one of the most sought after area of research in the linguistics and computational community. In this paper, we investigate the models based on deep learning that have achieved substantial progress in recent years and becoming the prominent method in MT. We shall discuss the two main deep-learning based Machine Translation methods, one at component or domain level which leverages deep learning models to enhance the efficacy of Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) and end-to-end deep learning models in MT which uses neural networks to find correspondence between the source and target languages using the encoder-decoder architecture. We conclude this paper by providing a time line of the major research problems solved by the researchers and also provide a comprehensive overview of present areas of research in Neural Machine Translation.
Offline Handwriting Recognition using Genetic Algorithm
Apr 19, 2010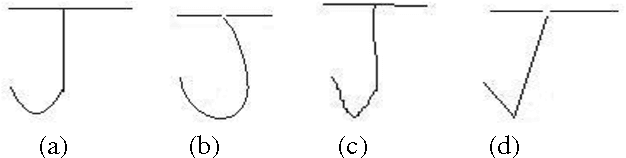
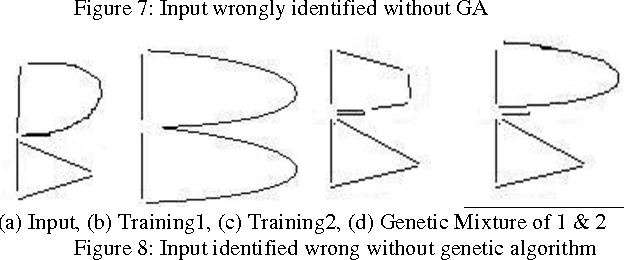
Abstract:Handwriting Recognition enables a person to scribble something on a piece of paper and then convert it into text. If we look into the practical reality there are enumerable styles in which a character may be written. These styles can be self combined to generate more styles. Even if a small child knows the basic styles a character can be written, he would be able to recognize characters written in styles intermediate between them or formed by their mixture. This motivates the use of Genetic Algorithms for the problem. In order to prove this, we made a pool of images of characters. We converted them to graphs. The graph of every character was intermixed to generate styles intermediate between the styles of parent character. Character recognition involved the matching of the graph generated from the unknown character image with the graphs generated by mixing. Using this method we received an accuracy of 98.44%.
* International Journal of Computer Science Issues at http://ijcsi.org/articles/Offline-Handwriting-Recognition-using-Genetic-Algorithm.php
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge