Ricardo Olivo
An Ultra-Compact Single FeFET Binary and Multi-Bit Associative Search Engine
Mar 15, 2022Abstract:Content addressable memory (CAM) is widely used in associative search tasks for its highly parallel pattern matching capability. To accommodate the increasingly complex and data-intensive pattern matching tasks, it is critical to keep improving the CAM density to enhance the performance and area efficiency. In this work, we demonstrate: i) a novel ultra-compact 1FeFET CAM design that enables parallel associative search and in-memory hamming distance calculation; ii) a multi-bit CAM for exact search using the same CAM cell; iii) compact device designs that integrate the series resistor current limiter into the intrinsic FeFET structure to turn the 1FeFET1R into an effective 1FeFET cell; iv) a successful 2-step search operation and a sufficient sensing margin of the proposed binary and multi-bit 1FeFET1R CAM array with sizes of practical interests in both experiments and simulations, given the existing unoptimized FeFET device variation; v) 89.9x speedup and 66.5x energy efficiency improvement over the state-of-the art alignment tools on GPU in accelerating genome pattern matching applications through the hyperdimensional computing paradigm.
In-Memory Nearest Neighbor Search with FeFET Multi-Bit Content-Addressable Memories
Nov 13, 2020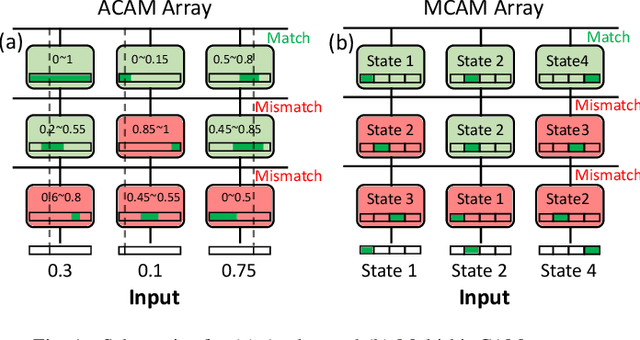
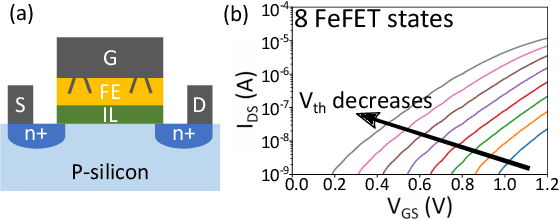
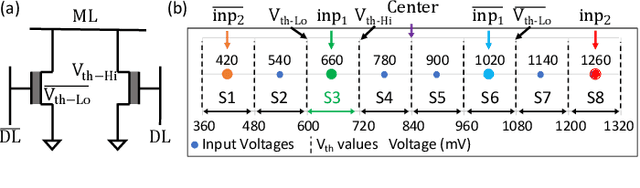
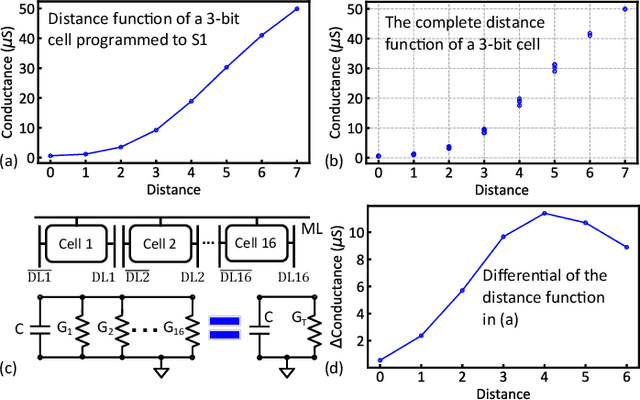
Abstract:Nearest neighbor (NN) search is an essential operation in many applications, such as one/few-shot learning and image classification. As such, fast and low-energy hardware support for accurate NN search is highly desirable. Ternary content-addressable memories (TCAMs) have been proposed to accelerate NN search for few-shot learning tasks by implementing $L_\infty$ and Hamming distance metrics, but they cannot achieve software-comparable accuracies. This paper proposes a novel distance function that can be natively evaluated with multi-bit content-addressable memories (MCAMs) based on ferroelectric FETs (FeFETs) to perform a single-step, in-memory NN search. Moreover, this approach achieves accuracies comparable to floating-point precision implementations in software for NN classification and one/few-shot learning tasks. As an example, the proposed method achieves a 98.34% accuracy for a 5-way, 5-shot classification task for the Omniglot dataset (only 0.8% lower than software-based implementations) with a 3-bit MCAM. This represents a 13% accuracy improvement over state-of-the-art TCAM-based implementations at iso-energy and iso-delay. The presented distance function is resilient to the effects of FeFET device-to-device variations. Furthermore, this work experimentally demonstrates a 2-bit implementation of FeFET MCAM using AND arrays from GLOBALFOUNDRIES to further validate proof of concept.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge