Rem Hida
Social Bias Evaluation for Large Language Models Requires Prompt Variations
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:Warning: This paper contains examples of stereotypes and biases. Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit considerable social biases, and various studies have tried to evaluate and mitigate these biases accurately. Previous studies use downstream tasks as prompts to examine the degree of social biases for evaluation and mitigation. While LLMs' output highly depends on prompts, previous studies evaluating and mitigating bias have often relied on a limited variety of prompts. In this paper, we investigate the sensitivity of LLMs when changing prompt variations (task instruction and prompt, few-shot examples, debias-prompt) by analyzing task performance and social bias of LLMs. Our experimental results reveal that LLMs are highly sensitive to prompts to the extent that the ranking of LLMs fluctuates when comparing models for task performance and social bias. Additionally, we show that LLMs have tradeoffs between performance and social bias caused by the prompts. Less bias from prompt setting may result in reduced performance. Moreover, the ambiguity of instances is one of the reasons for this sensitivity to prompts in advanced LLMs, leading to various outputs. We recommend using diverse prompts, as in this study, to compare the effects of prompts on social bias in LLMs.
Evaluation of Instruction-Following Ability for Large Language Models on Story-Ending Generation
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Instruction-tuned Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable performance across various benchmark tasks. While providing instructions to LLMs for guiding their generations is user-friendly, assessing their instruction-following capabilities is still unclarified due to a lack of evaluation metrics. In this paper, we focus on evaluating the instruction-following ability of LLMs in the context of story-ending generation, which requires diverse and context-specific instructions. We propose an automatic evaluation pipeline that utilizes a machine reading comprehension (MRC) model to determine whether the generated story-ending reflects instruction. Our findings demonstrate that our proposed metric aligns with human evaluation. Furthermore, our experiments confirm that recent open-source LLMs can achieve instruction-following performance close to GPT-3.5, as assessed through automatic evaluation.
Polyphone disambiguation and accent prediction using pre-trained language models in Japanese TTS front-end
Jan 24, 2022



Abstract:Although end-to-end text-to-speech (TTS) models can generate natural speech, challenges still remain when it comes to estimating sentence-level phonetic and prosodic information from raw text in Japanese TTS systems. In this paper, we propose a method for polyphone disambiguation (PD) and accent prediction (AP). The proposed method incorporates explicit features extracted from morphological analysis and implicit features extracted from pre-trained language models (PLMs). We use BERT and Flair embeddings as implicit features and examine how to combine them with explicit features. Our objective evaluation results showed that the proposed method improved the accuracy by 5.7 points in PD and 6.0 points in AP. Moreover, the perceptual listening test results confirmed that a TTS system employing our proposed model as a front-end achieved a mean opinion score close to that of synthesized speech with ground-truth pronunciation and accent in terms of naturalness.
Dynamic and Static Topic Model for Analyzing Time-Series Document Collections
May 06, 2018
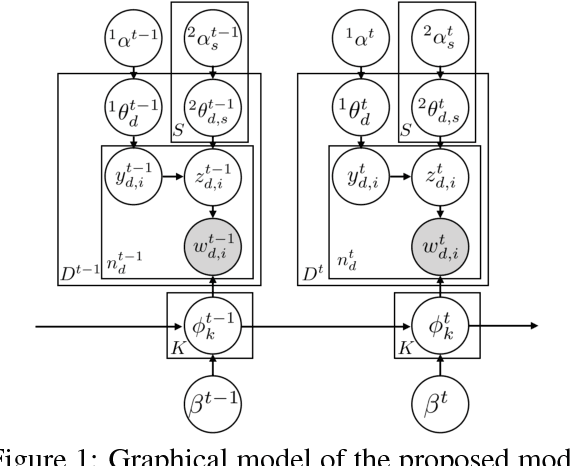
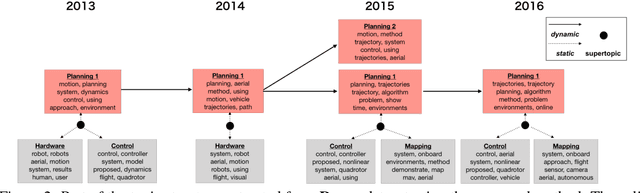
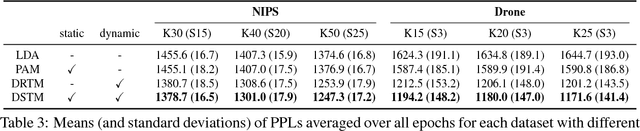
Abstract:For extracting meaningful topics from texts, their structures should be considered properly. In this paper, we aim to analyze structured time-series documents such as a collection of news articles and a series of scientific papers, wherein topics evolve along time depending on multiple topics in the past and are also related to each other at each time. To this end, we propose a dynamic and static topic model, which simultaneously considers the dynamic structures of the temporal topic evolution and the static structures of the topic hierarchy at each time. We show the results of experiments on collections of scientific papers, in which the proposed method outperformed conventional models. Moreover, we show an example of extracted topic structures, which we found helpful for analyzing research activities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge