Rei Ito
Advancing Large Multi-modal Models with Explicit Chain-of-Reasoning and Visual Question Generation
Jan 18, 2024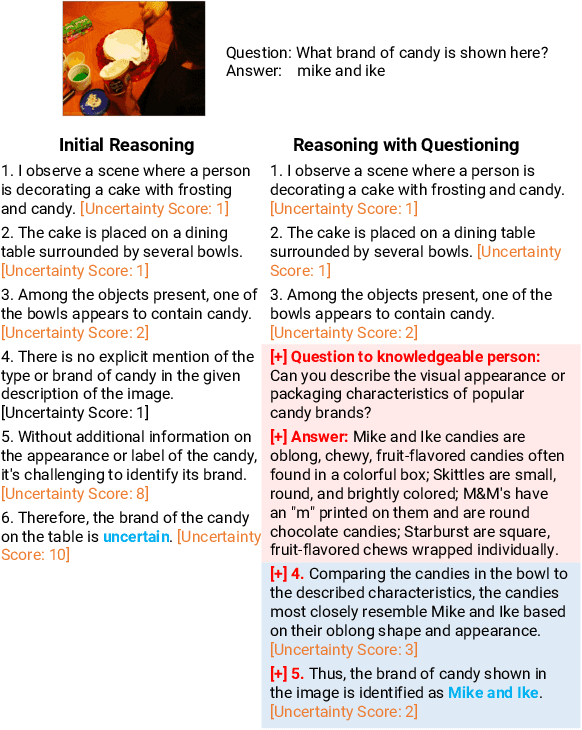
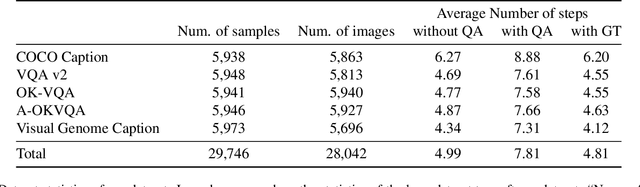

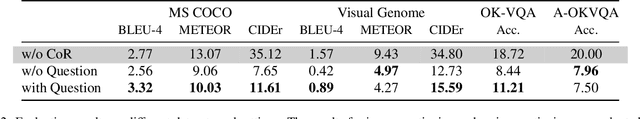
Abstract:The increasing demand for intelligent systems capable of interpreting and reasoning about visual content requires the development of Large Multi-Modal Models (LMMs) that are not only accurate but also have explicit reasoning capabilities. This paper presents a novel approach to imbue an LMM with the ability to conduct explicit reasoning based on visual content and textual instructions. We introduce a system that can ask a question to acquire necessary knowledge, thereby enhancing the robustness and explicability of the reasoning process. Our method comprises the development of a novel dataset generated by a Large Language Model (LLM), designed to promote chain-of-thought reasoning combined with a question-asking mechanism. We designed an LMM, which has high capabilities on region awareness to address the intricate requirements of image-text alignment. The model undergoes a three-stage training phase, starting with large-scale image-text alignment using a large-scale datasets, followed by instruction tuning, and fine-tuning with a focus on chain-of-thought reasoning. The results demonstrate a stride toward a more robust, accurate, and interpretable LMM, capable of reasoning explicitly and seeking information proactively when confronted with ambiguous visual input.
An On-Device Federated Learning Approach for Cooperative Anomaly Detection
Feb 27, 2020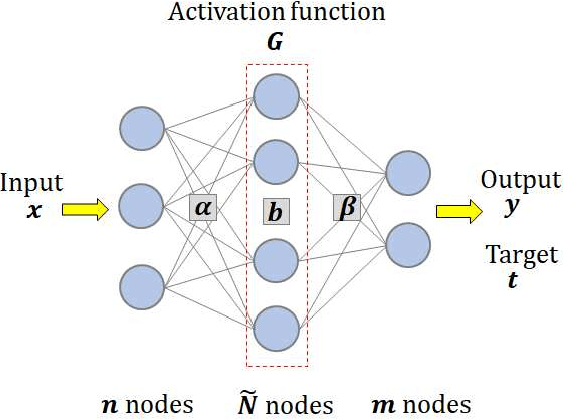
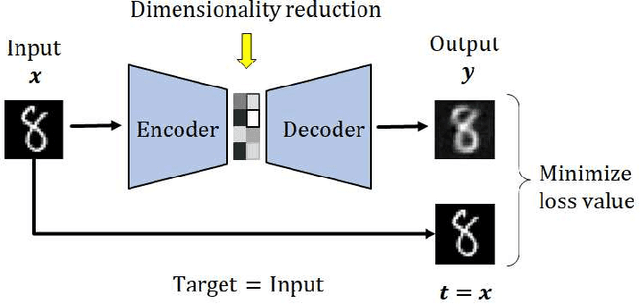
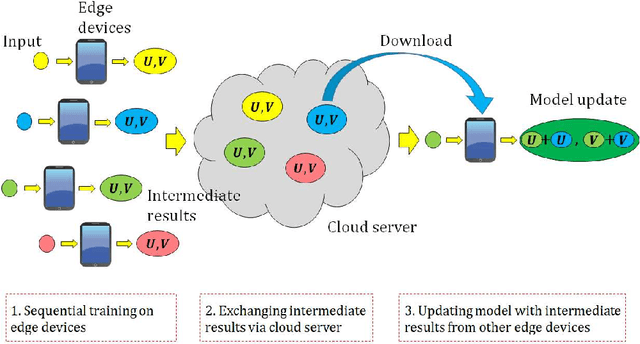
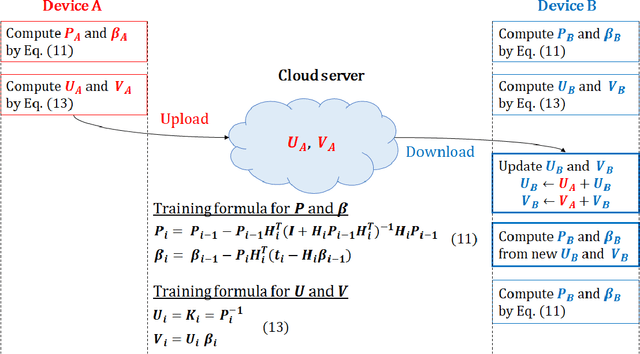
Abstract:Most edge AI focuses on prediction tasks on resource-limited edge devices, while the training is done at server machines, so retraining a model on the edge devices to reflect environmental changes is a complicated task. To follow such a concept drift, a neural-network based on-device learning approach is recently proposed, so that edge devices train incoming data at runtime to update their model. In this case, since a training is done at distributed edge devices, the issue is that only a limited amount of training data can be used for each edge device. To address this issue, one approach is a cooperative learning or federated learning, where edge devices exchange their trained results and update their model by using those collected from the other devices. In this paper, as an on-device learning algorithm, we focus on OS-ELM (Online Sequential Extreme Learning Machine) and combine it with Autoencoder for anomaly detection. We extend it for an on-device federated learning so that edge devices exchange their trained results and update their model by using those collected from the other edge devices. Experimental results using a driving dataset of cars demonstrate that the proposed on-device federated learning can produce more accurate model by combining trained results from multiple edge devices compared to a single model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge