Tomohiro Hashimoto
RealX3D: A Physically-Degraded 3D Benchmark for Multi-view Visual Restoration and Reconstruction
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:We introduce RealX3D, a real-capture benchmark for multi-view visual restoration and 3D reconstruction under diverse physical degradations. RealX3D groups corruptions into four families, including illumination, scattering, occlusion, and blurring, and captures each at multiple severity levels using a unified acquisition protocol that yields pixel-aligned LQ/GT views. Each scene includes high-resolution capture, RAW images, and dense laser scans, from which we derive world-scale meshes and metric depth. Benchmarking a broad range of optimization-based and feed-forward methods shows substantial degradation in reconstruction quality under physical corruptions, underscoring the fragility of current multi-view pipelines in real-world challenging environments.
DistML.js: Installation-free Distributed Deep Learning Framework for Web Browsers
Jul 01, 2024
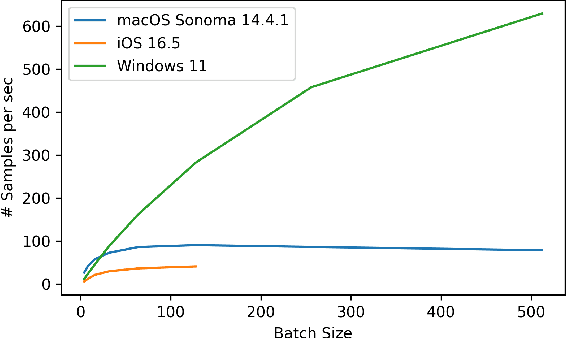
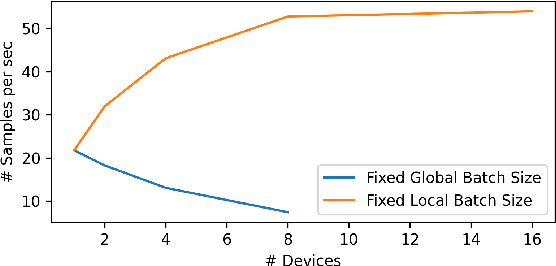
Abstract:We present "DistML.js", a library designed for training and inference of machine learning models within web browsers. Not only does DistML.js facilitate model training on local devices, but it also supports distributed learning through communication with servers. Its design and define-by-run API for deep learning model construction resemble PyTorch, thereby reducing the learning curve for prototyping. Matrix computations involved in model training and inference are executed on the backend utilizing WebGL, enabling high-speed calculations. We provide a comprehensive explanation of DistML.js's design, API, and implementation, alongside practical applications including data parallelism in learning. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/mil-tokyo/distmljs.
Advancing Large Multi-modal Models with Explicit Chain-of-Reasoning and Visual Question Generation
Jan 18, 2024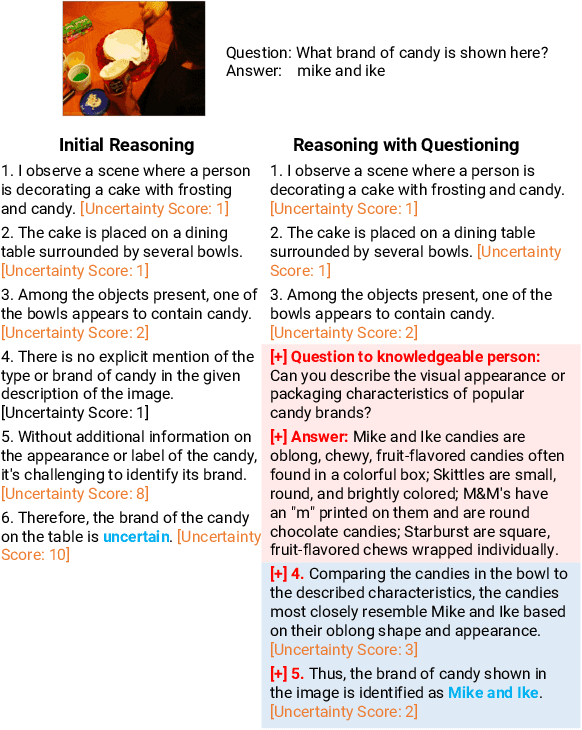
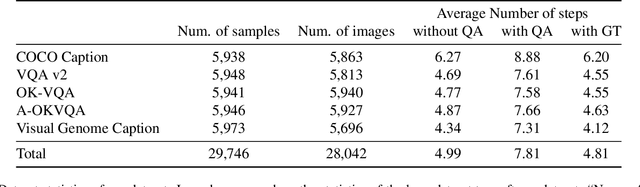

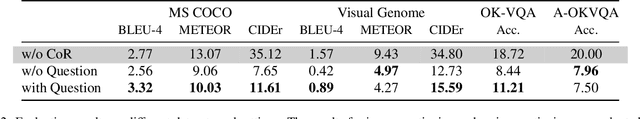
Abstract:The increasing demand for intelligent systems capable of interpreting and reasoning about visual content requires the development of Large Multi-Modal Models (LMMs) that are not only accurate but also have explicit reasoning capabilities. This paper presents a novel approach to imbue an LMM with the ability to conduct explicit reasoning based on visual content and textual instructions. We introduce a system that can ask a question to acquire necessary knowledge, thereby enhancing the robustness and explicability of the reasoning process. Our method comprises the development of a novel dataset generated by a Large Language Model (LLM), designed to promote chain-of-thought reasoning combined with a question-asking mechanism. We designed an LMM, which has high capabilities on region awareness to address the intricate requirements of image-text alignment. The model undergoes a three-stage training phase, starting with large-scale image-text alignment using a large-scale datasets, followed by instruction tuning, and fine-tuning with a focus on chain-of-thought reasoning. The results demonstrate a stride toward a more robust, accurate, and interpretable LMM, capable of reasoning explicitly and seeking information proactively when confronted with ambiguous visual input.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge