Raymond Chua
Deep RL Needs Deep Behavior Analysis: Exploring Implicit Planning by Model-Free Agents in Open-Ended Environments
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Understanding the behavior of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) agents -- particularly as task and agent sophistication increase -- requires more than simple comparison of reward curves, yet standard methods for behavioral analysis remain underdeveloped in DRL. We apply tools from neuroscience and ethology to study DRL agents in a novel, complex, partially observable environment, ForageWorld, designed to capture key aspects of real-world animal foraging -- including sparse, depleting resource patches, predator threats, and spatially extended arenas. We use this environment as a platform for applying joint behavioral and neural analysis to agents, revealing detailed, quantitatively grounded insights into agent strategies, memory, and planning. Contrary to common assumptions, we find that model-free RNN-based DRL agents can exhibit structured, planning-like behavior purely through emergent dynamics -- without requiring explicit memory modules or world models. Our results show that studying DRL agents like animals -- analyzing them with neuroethology-inspired tools that reveal structure in both behavior and neural dynamics -- uncovers rich structure in their learning dynamics that would otherwise remain invisible. We distill these tools into a general analysis framework linking core behavioral and representational features to diagnostic methods, which can be reused for a wide range of tasks and agents. As agents grow more complex and autonomous, bridging neuroscience, cognitive science, and AI will be essential -- not just for understanding their behavior, but for ensuring safe alignment and maximizing desirable behaviors that are hard to measure via reward. We show how this can be done by drawing on lessons from how biological intelligence is studied.
Learning Successor Features the Simple Way
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:In Deep Reinforcement Learning (RL), it is a challenge to learn representations that do not exhibit catastrophic forgetting or interference in non-stationary environments. Successor Features (SFs) offer a potential solution to this challenge. However, canonical techniques for learning SFs from pixel-level observations often lead to representation collapse, wherein representations degenerate and fail to capture meaningful variations in the data. More recent methods for learning SFs can avoid representation collapse, but they often involve complex losses and multiple learning phases, reducing their efficiency. We introduce a novel, simple method for learning SFs directly from pixels. Our approach uses a combination of a Temporal-difference (TD) loss and a reward prediction loss, which together capture the basic mathematical definition of SFs. We show that our approach matches or outperforms existing SF learning techniques in both 2D (Minigrid), 3D (Miniworld) mazes and Mujoco, for both single and continual learning scenarios. As well, our technique is efficient, and can reach higher levels of performance in less time than other approaches. Our work provides a new, streamlined technique for learning SFs directly from pixel observations, with no pretraining required.
Learning offline: memory replay in biological and artificial reinforcement learning
Sep 21, 2021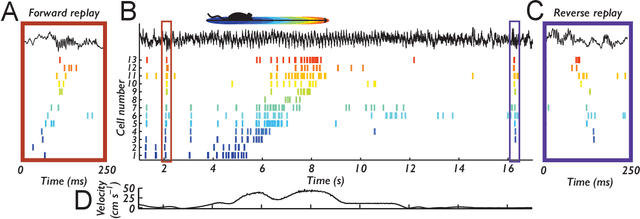
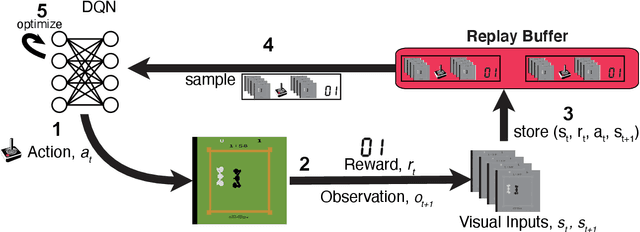
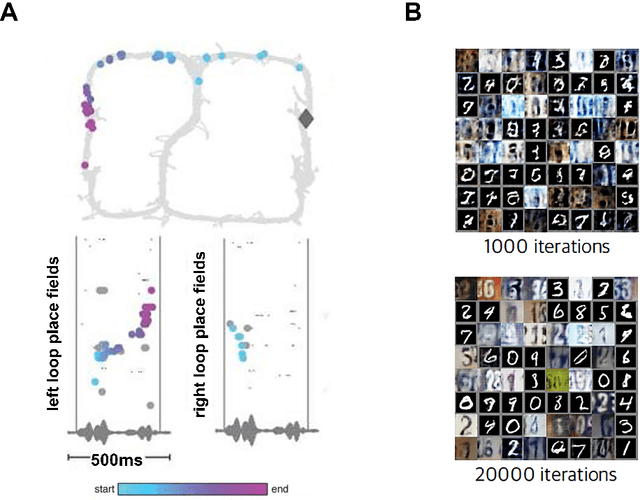
Abstract:Learning to act in an environment to maximise rewards is among the brain's key functions. This process has often been conceptualised within the framework of reinforcement learning, which has also gained prominence in machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) as a way to optimise decision-making. A common aspect of both biological and machine reinforcement learning is the reactivation of previously experienced episodes, referred to as replay. Replay is important for memory consolidation in biological neural networks, and is key to stabilising learning in deep neural networks. Here, we review recent developments concerning the functional roles of replay in the fields of neuroscience and AI. Complementary progress suggests how replay might support learning processes, including generalisation and continual learning, affording opportunities to transfer knowledge across the two fields to advance the understanding of biological and artificial learning and memory.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge