Ramesh Raghunathan
KnowGraph: Knowledge-Enabled Anomaly Detection via Logical Reasoning on Graph Data
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Graph-based anomaly detection is pivotal in diverse security applications, such as fraud detection in transaction networks and intrusion detection for network traffic. Standard approaches, including Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), often struggle to generalize across shifting data distributions. Meanwhile, real-world domain knowledge is more stable and a common existing component of real-world detection strategies. To explicitly integrate such knowledge into data-driven models such as GCNs, we propose KnowGraph, which integrates domain knowledge with data-driven learning for enhanced graph-based anomaly detection. KnowGraph comprises two principal components: (1) a statistical learning component that utilizes a main model for the overarching detection task, augmented by multiple specialized knowledge models that predict domain-specific semantic entities; (2) a reasoning component that employs probabilistic graphical models to execute logical inferences based on model outputs, encoding domain knowledge through weighted first-order logic formulas. Extensive experiments on these large-scale real-world datasets show that KnowGraph consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in both transductive and inductive settings, achieving substantial gains in average precision when generalizing to completely unseen test graphs. Further ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed reasoning component in improving detection performance, especially under extreme class imbalance. These results highlight the potential of integrating domain knowledge into data-driven models for high-stakes, graph-based security applications.
BRIGHT -- Graph Neural Networks in Real-Time Fraud Detection
May 25, 2022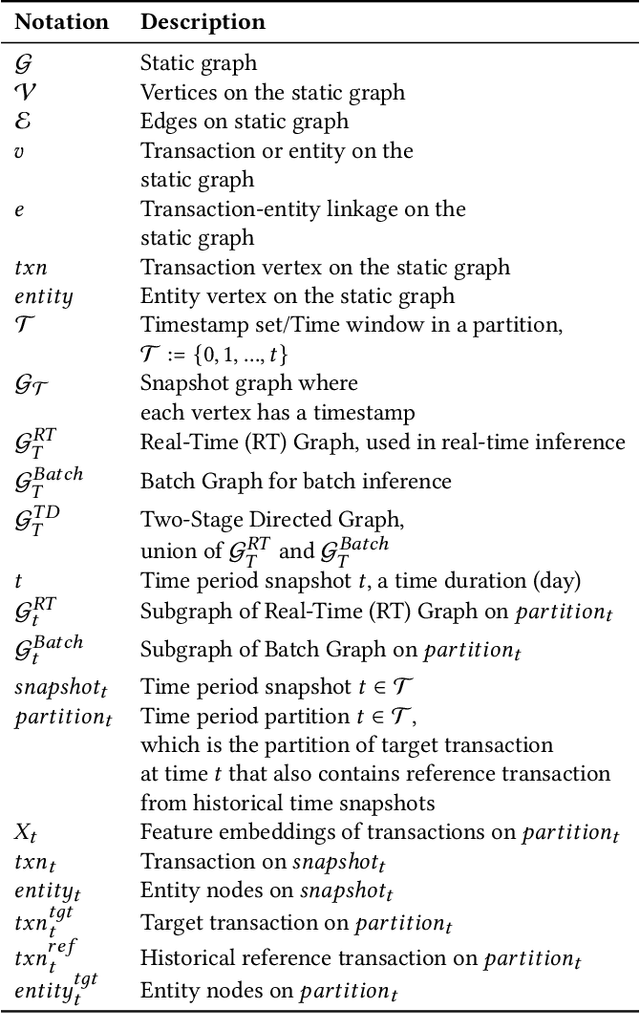
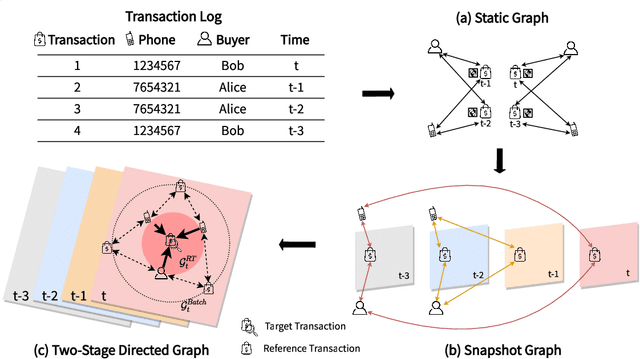
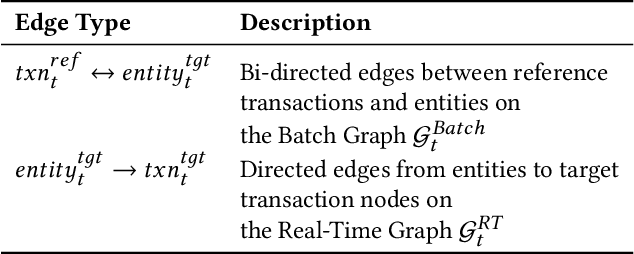
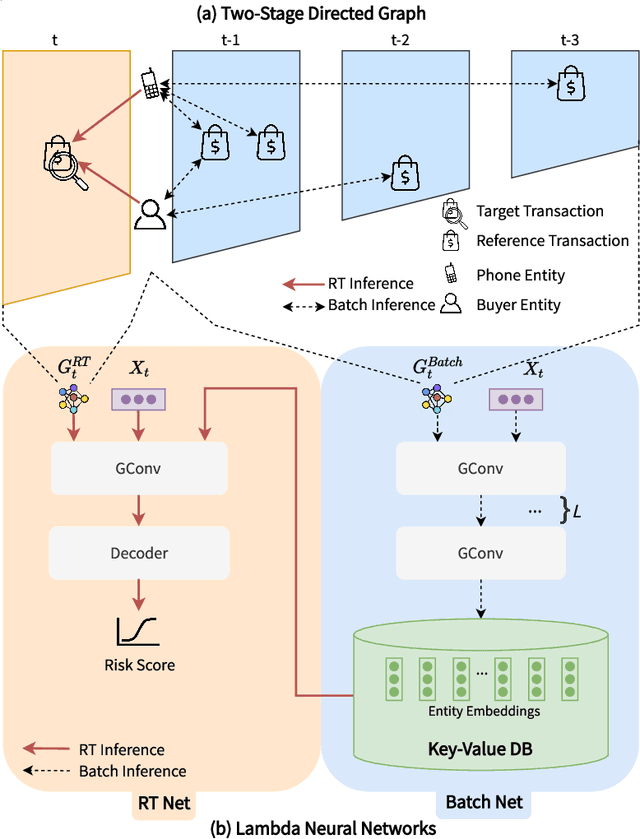
Abstract:Detecting fraudulent transactions is an essential component to control risk in e-commerce marketplaces. Apart from rule-based and machine learning filters that are already deployed in production, we want to enable efficient real-time inference with graph neural networks (GNNs), which is useful to catch multihop risk propagation in a transaction graph. However, two challenges arise in the implementation of GNNs in production. First, future information in a dynamic graph should not be considered in message passing to predict the past. Second, the latency of graph query and GNN model inference is usually up to hundreds of milliseconds, which is costly for some critical online services. To tackle these challenges, we propose a Batch and Real-time Inception GrapH Topology (BRIGHT) framework to conduct an end-to-end GNN learning that allows efficient online real-time inference. BRIGHT framework consists of a graph transformation module (Two-Stage Directed Graph) and a corresponding GNN architecture (Lambda Neural Network). The Two-Stage Directed Graph guarantees that the information passed through neighbors is only from the historical payment transactions. It consists of two subgraphs representing historical relationships and real-time links, respectively. The Lambda Neural Network decouples inference into two stages: batch inference of entity embeddings and real-time inference of transaction prediction. Our experiments show that BRIGHT outperforms the baseline models by >2\% in average w.r.t.~precision. Furthermore, BRIGHT is computationally efficient for real-time fraud detection. Regarding end-to-end performance (including neighbor query and inference), BRIGHT can reduce the P99 latency by >75\%. For the inference stage, our speedup is on average 7.8$\times$ compared to the traditional GNN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge