Rajith Vidanaarachchi
Semantic Segmentation using Vision Transformers: A survey
May 05, 2023Abstract:Semantic segmentation has a broad range of applications in a variety of domains including land coverage analysis, autonomous driving, and medical image analysis. Convolutional neural networks (CNN) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) provide the architecture models for semantic segmentation. Even though ViTs have proven success in image classification, they cannot be directly applied to dense prediction tasks such as image segmentation and object detection since ViT is not a general purpose backbone due to its patch partitioning scheme. In this survey, we discuss some of the different ViT architectures that can be used for semantic segmentation and how their evolution managed the above-stated challenge. The rise of ViT and its performance with a high success rate motivated the community to slowly replace the traditional convolutional neural networks in various computer vision tasks. This survey aims to review and compare the performances of ViT architectures designed for semantic segmentation using benchmarking datasets. This will be worthwhile for the community to yield knowledge regarding the implementations carried out in semantic segmentation and to discover more efficient methodologies using ViTs.
Urban feature analysis from aerial remote sensing imagery using self-supervised and semi-supervised computer vision
Aug 17, 2022
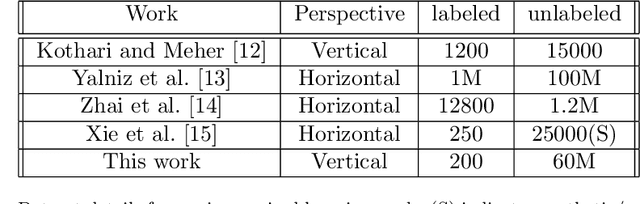
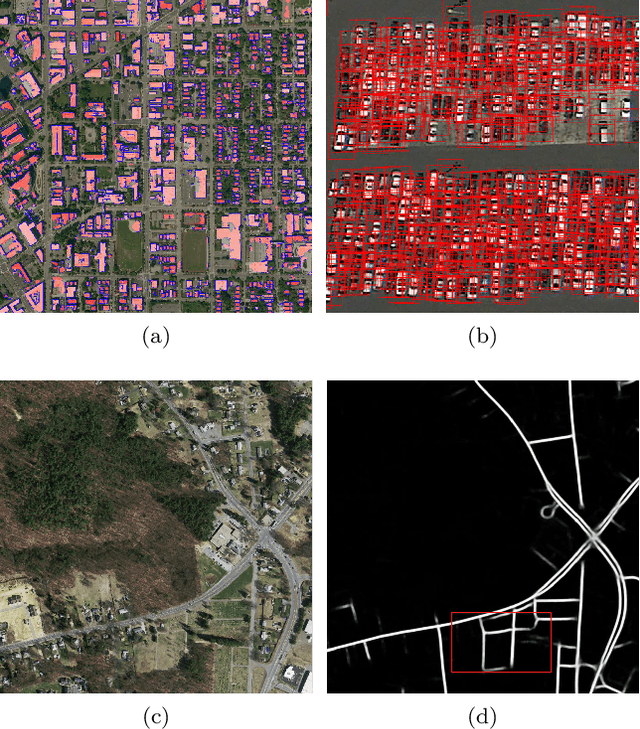
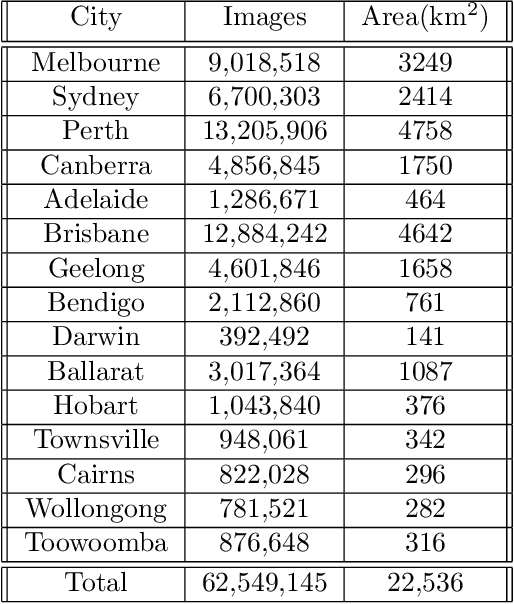
Abstract:Analysis of overhead imagery using computer vision is a problem that has received considerable attention in academic literature. Most techniques that operate in this space are both highly specialised and require expensive manual annotation of large datasets. These problems are addressed here through the development of a more generic framework, incorporating advances in representation learning which allows for more flexibility in analysing new categories of imagery with limited labeled data. First, a robust representation of an unlabeled aerial imagery dataset was created based on the momentum contrast mechanism. This was subsequently specialised for different tasks by building accurate classifiers with as few as 200 labeled images. The successful low-level detection of urban infrastructure evolution over a 10-year period from 60 million unlabeled images, exemplifies the substantial potential of our approach to advance quantitative urban research.
DALLE-URBAN: Capturing the urban design expertise of large text to image transformers
Aug 03, 2022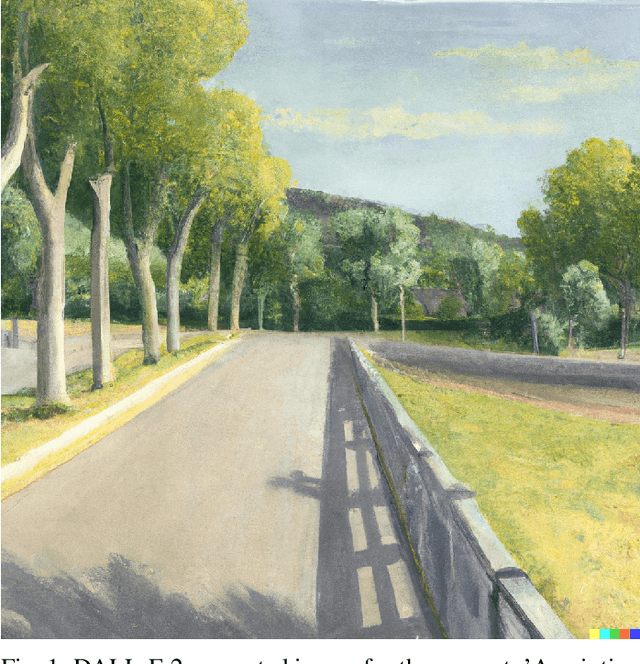
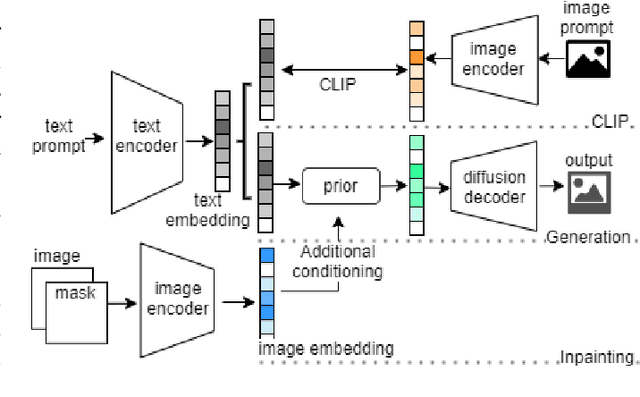
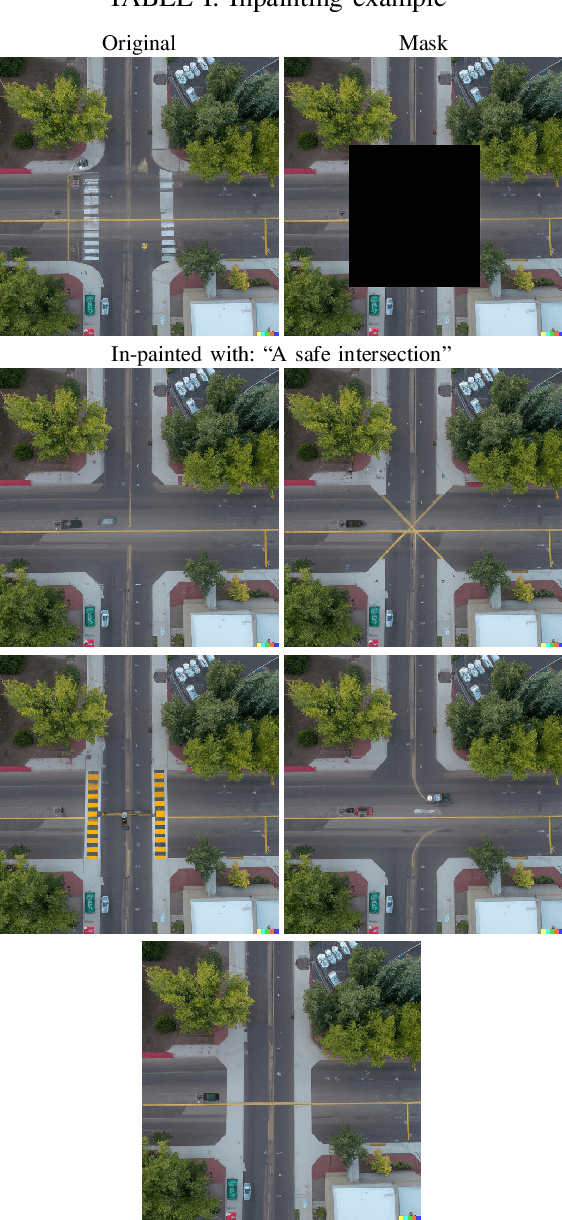
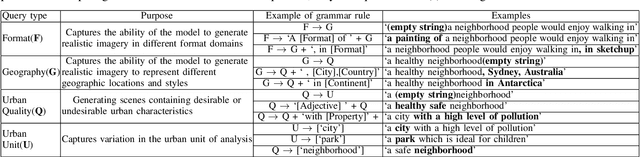
Abstract:Automatically converting text descriptions into images using transformer architectures has recently received considerable attention. Such advances have implications for many applied design disciplines across fashion, art, architecture, urban planning, landscape design and the future tools available to such disciplines. However, a detailed analysis capturing the capabilities of such models, specifically with a focus on the built environment, has not been performed to date. In this work, we investigate the capabilities and biases of such text-to-image methods as it applies to the built environment in detail. We use a systematic grammar to generate queries related to the built environment and evaluate resulting generated images. We generate 1020 different images and find that text to image transformers are robust at generating realistic images across different domains for this use-case. Generated imagery can be found at the github: https://github.com/sachith500/DALLEURBAN
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge