Rajendra Ugrani
ChunkWise LoRA: Adaptive Sequence Partitioning for Memory-Efficient Low-Rank Adaptation and Accelerated LLM Inference
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in low-rank adaptation (LoRA) have enabled efficient fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) with minimal additional parameters. However, existing LoRA methods apply static rank configurations uniformly across all input tokens, ignoring variation in token complexity and computational requirements. In this work, we propose ChunkWise LoRA, a dynamic and adaptive approach that partitions sequences into variable-length chunks based on token complexity and assigns each chunk a tailored low-rank configuration. Our system introduces a runtime scheduler that estimates token difficulty, performs adaptive chunking, and selects per-chunk LoRA rank and scaling using a rank-ladder mechanism. To preserve output consistency, we further introduce a boundary-safe composition module and integrate policy-driven KV-cache strategies. Experiments on benchmark datasets such as Wikitext-103 and SQuAD demonstrate that ChunkWise LoRA achieves up to 34\% lower latency and 38% memory reduction compared to baseline LoRA, while maintaining or improving task performance metrics like BLEU, EM, and perplexity. The proposed framework remains fully compatible with existing transformer architectures and inference frameworks, providing a practical solution for real-world deployment of parameter-efficient LLMs.
Iterative Data Programming for Expanding Text Classification Corpora
Feb 04, 2020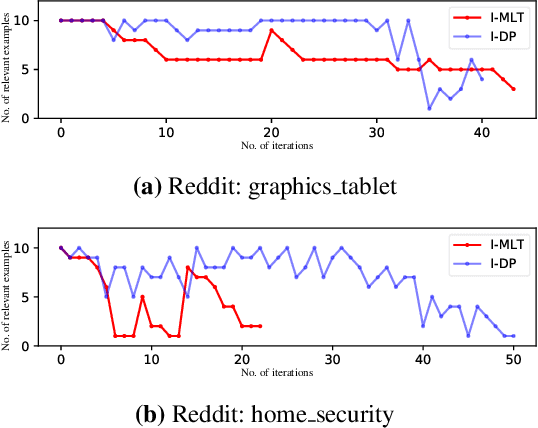
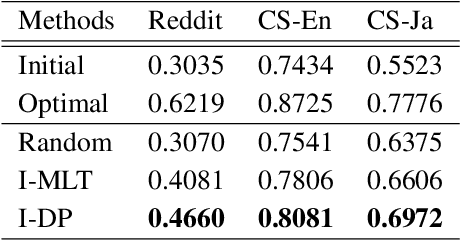
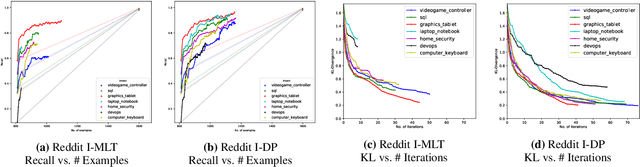
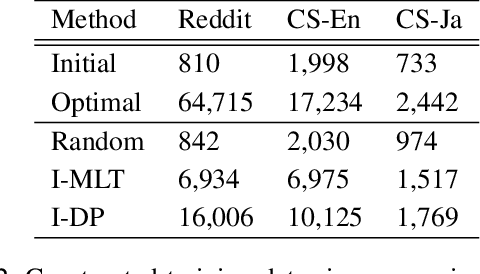
Abstract:Real-world text classification tasks often require many labeled training examples that are expensive to obtain. Recent advancements in machine teaching, specifically the data programming paradigm, facilitate the creation of training data sets quickly via a general framework for building weak models, also known as labeling functions, and denoising them through ensemble learning techniques. We present a fast, simple data programming method for augmenting text data sets by generating neighborhood-based weak models with minimal supervision. Furthermore, our method employs an iterative procedure to identify sparsely distributed examples from large volumes of unlabeled data. The iterative data programming techniques improve newer weak models as more labeled data is confirmed with human-in-loop. We show empirical results on sentence classification tasks, including those from a task of improving intent recognition in conversational agents.
Bootstrapping Conversational Agents With Weak Supervision
Dec 14, 2018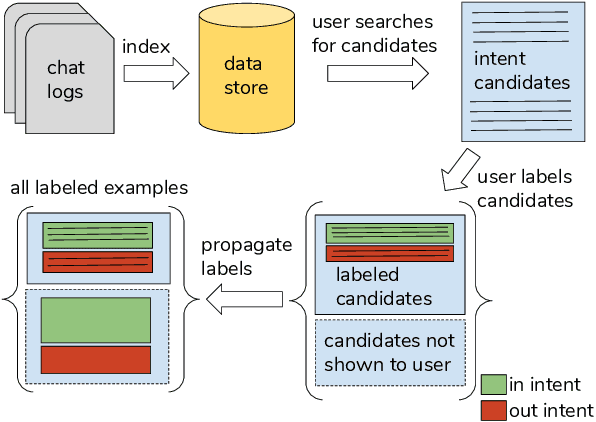
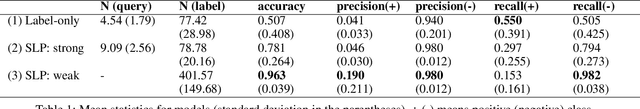
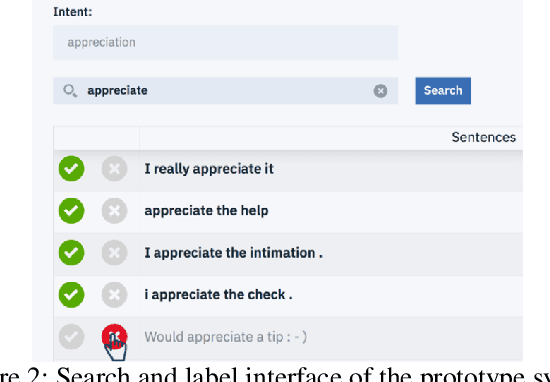
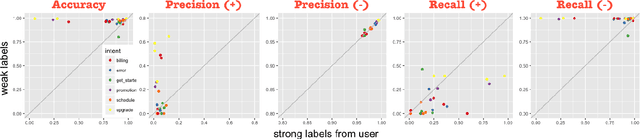
Abstract:Many conversational agents in the market today follow a standard bot development framework which requires training intent classifiers to recognize user input. The need to create a proper set of training examples is often the bottleneck in the development process. In many occasions agent developers have access to historical chat logs that can provide a good quantity as well as coverage of training examples. However, the cost of labeling them with tens to hundreds of intents often prohibits taking full advantage of these chat logs. In this paper, we present a framework called \textit{search, label, and propagate} (SLP) for bootstrapping intents from existing chat logs using weak supervision. The framework reduces hours to days of labeling effort down to minutes of work by using a search engine to find examples, then relies on a data programming approach to automatically expand the labels. We report on a user study that shows positive user feedback for this new approach to build conversational agents, and demonstrates the effectiveness of using data programming for auto-labeling. While the system is developed for training conversational agents, the framework has broader application in significantly reducing labeling effort for training text classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge