Rafiqul Islam
Mob-based cattle weight gain forecasting using ML models
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Forecasting mob based cattle weight gain (MB CWG) may benefit large livestock farms, allowing farmers to refine their feeding strategies, make educated breeding choices, and reduce risks linked to climate variability and market fluctuations. In this paper, a novel technique termed MB CWG is proposed to forecast the one month advanced weight gain of herd based cattle using historical data collected from the Charles Sturt University Farm. This research employs a Random Forest (RF) model, comparing its performance against Support Vector Regression (SVR) and Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) models for monthly weight gain prediction. Four datasets were used to evaluate the performance of models, using 756 sample data from 108 herd-based cattle, along with weather data (rainfall and temperature) influencing CWG. The RF model performs better than the SVR and LSTM models across all datasets, achieving an R^2 of 0.973, RMSE of 0.040, and MAE of 0.033 when both weather and age factors were included. The results indicate that including both weather and age factors significantly improves the accuracy of weight gain predictions, with the RF model outperforming the SVR and LSTM models in all scenarios. These findings demonstrate the potential of RF as a robust tool for forecasting cattle weight gain in variable conditions, highlighting the influence of age and climatic factors on herd based weight trends. This study has also developed an innovative automated pre processing tool to generate a benchmark dataset for MB CWG predictive models. The tool is publicly available on GitHub and can assist in preparing datasets for current and future analytical research..
RLSA-PFL: Robust Lightweight Secure Aggregation with Model Inconsistency Detection in Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) allows users to collaboratively train a global machine learning model by sharing local model only, without exposing their private data to a central server. This distributed learning is particularly appealing in scenarios where data privacy is crucial, and it has garnered substantial attention from both industry and academia. However, studies have revealed privacy vulnerabilities in FL, where adversaries can potentially infer sensitive information from the shared model parameters. In this paper, we present an efficient masking-based secure aggregation scheme utilizing lightweight cryptographic primitives to mitigate privacy risks. Our scheme offers several advantages over existing methods. First, it requires only a single setup phase for the entire FL training session, significantly reducing communication overhead. Second, it minimizes user-side overhead by eliminating the need for user-to-user interactions, utilizing an intermediate server layer and a lightweight key negotiation method. Third, the scheme is highly resilient to user dropouts, and the users can join at any FL round. Fourth, it can detect and defend against malicious server activities, including recently discovered model inconsistency attacks. Finally, our scheme ensures security in both semi-honest and malicious settings. We provide security analysis to formally prove the robustness of our approach. Furthermore, we implemented an end-to-end prototype of our scheme. We conducted comprehensive experiments and comparisons, which show that it outperforms existing solutions in terms of communication and computation overhead, functionality, and security.
Learning-based estimation of cattle weight gain and its influencing factors
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Many cattle farmers still depend on manual methods to measure the live weight gain of cattle at set intervals, which is time consuming, labour intensive, and stressful for both the animals and handlers. A remote and autonomous monitoring system using machine learning (ML) or deep learning (DL) can provide a more efficient and less invasive method and also predictive capabilities for future cattle weight gain (CWG). This system allows continuous monitoring and estimation of individual cattle live weight gain, growth rates and weight fluctuations considering various factors like environmental conditions, genetic predispositions, feed availability, movement patterns and behaviour. Several researchers have explored the efficiency of estimating CWG using ML and DL algorithms. However, estimating CWG suffers from a lack of consistency in its application. Moreover, ML or DL can provide weight gain estimations based on several features that vary in existing research. Additionally, previous studies have encountered various data related challenges when estimating CWG. This paper presents a comprehensive investigation in estimating CWG using advanced ML techniques based on research articles (between 2004 and 2024). This study investigates the current tools, methods, and features used in CWG estimation, as well as their strengths and weaknesses. The findings highlight the significance of using advanced ML approaches in CWG estimation and its critical influence on factors. Furthermore, this study identifies potential research gaps and provides research direction on CWG prediction, which serves as a reference for future research in this area.
CL3: A Collaborative Learning Framework for the Medical Data Ensuring Data Privacy in the Hyperconnected Environment
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:In a hyperconnected environment, medical institutions are particularly concerned with data privacy when sharing and transmitting sensitive patient information due to the risk of data breaches, where malicious actors could intercept sensitive information. A collaborative learning framework, including transfer, federated, and incremental learning, can generate efficient, secure, and scalable models while requiring less computation, maintaining patient data privacy, and ensuring an up-to-date model. This study aims to address the detection of COVID-19 using chest X-ray images through a proposed collaborative learning framework called CL3. Initially, transfer learning is employed, leveraging knowledge from a pre-trained model as the starting global model. Local models from different medical institutes are then integrated, and a new global model is constructed to adapt to any data drift observed in the local models. Additionally, incremental learning is considered, allowing continuous adaptation to new medical data without forgetting previously learned information. Experimental results demonstrate that the CL3 framework achieved a global accuracy of 89.99\% when using Xception with a batch size of 16 after being trained for six federated communication rounds.
Melanoma Skin Cancer and Nevus Mole Classification using Intensity Value Estimation with Convolutional Neural Network
Sep 30, 2022



Abstract:Melanoma skin cancer is one of the most dangerous and life-threatening cancer. Exposure to ultraviolet rays may damage the skin cell's DNA, which causes melanoma skin cancer. However, it is difficult to detect and classify melanoma and nevus mole at the immature stages. In this work, an automatic deep learning system is developed based on the intensity value estimation with a convolutional neural network model (CNN) to detect and classify melanoma and nevus mole more accurately. Since intensity levels are the most distinctive features for object or region of interest identification, the high-intensity pixel values are selected from the extracted lesion images. Incorporating those high-intensity features into the CNN improves the overall performance of the proposed model than the state-of-the-art methods for detecting melanoma skin cancer. To evaluate the system, we used 5-fold cross-validation. Experimental results show that a superior percentage of accuracy (92.58%), sensitivity (93.76%), specificity (91.56%), and precision (90.68%) are achieved.
Dependable Intrusion Detection System for IoT: A Deep Transfer Learning-based Approach
Apr 11, 2022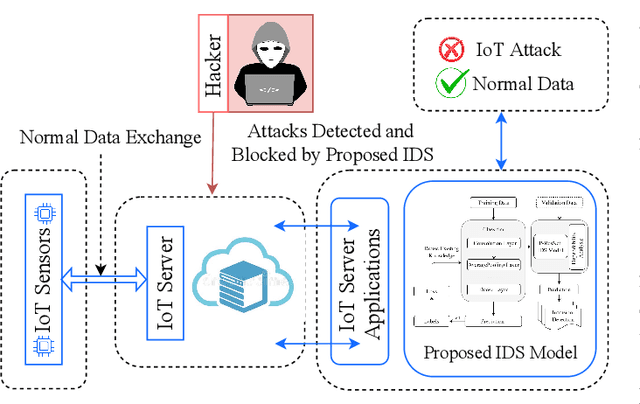
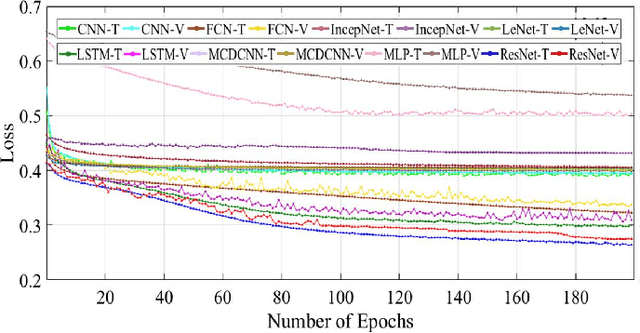
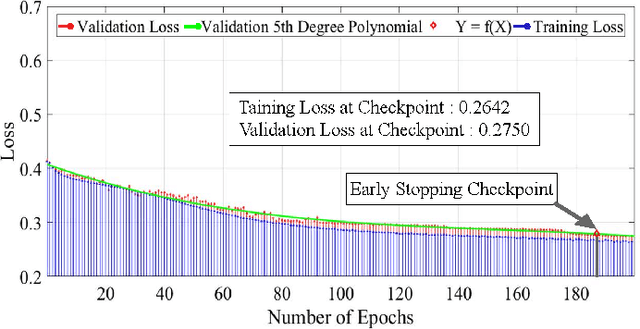
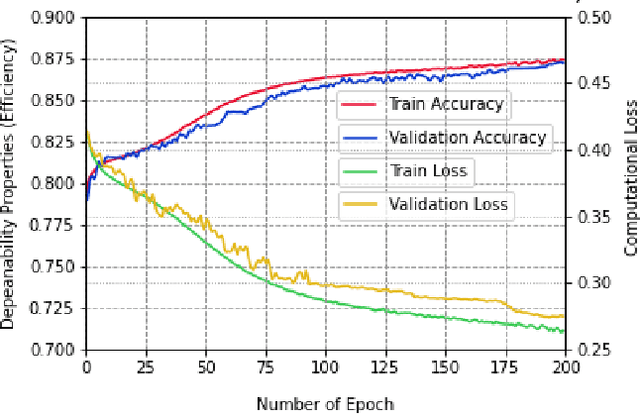
Abstract:Security concerns for IoT applications have been alarming because of their widespread use in different enterprise systems. The potential threats to these applications are constantly emerging and changing, and therefore, sophisticated and dependable defense solutions are necessary against such threats. With the rapid development of IoT networks and evolving threat types, the traditional machine learning-based IDS must update to cope with the security requirements of the current sustainable IoT environment. In recent years, deep learning, and deep transfer learning have progressed and experienced great success in different fields and have emerged as a potential solution for dependable network intrusion detection. However, new and emerging challenges have arisen related to the accuracy, efficiency, scalability, and dependability of the traditional IDS in a heterogeneous IoT setup. This manuscript proposes a deep transfer learning-based dependable IDS model that outperforms several existing approaches. The unique contributions include effective attribute selection, which is best suited to identify normal and attack scenarios for a small amount of labeled data, designing a dependable deep transfer learning-based ResNet model, and evaluating considering real-world data. To this end, a comprehensive experimental performance evaluation has been conducted. Extensive analysis and performance evaluation show that the proposed model is robust, more efficient, and has demonstrated better performance, ensuring dependability.
* 12 pages, 13 Figures, 4 tables IEEE Transaction
A Systematic Literature Review on Blockchain Enabled Federated Learning Framework for Internet of Vehicles
Mar 10, 2022
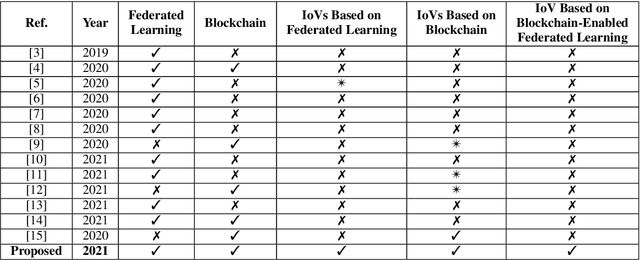
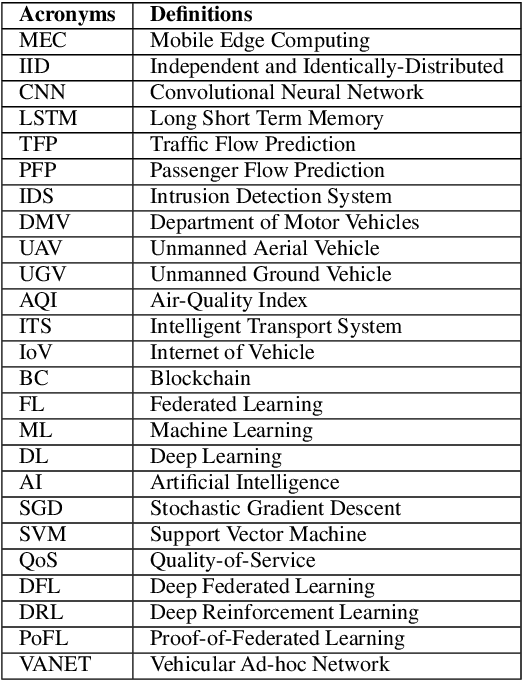
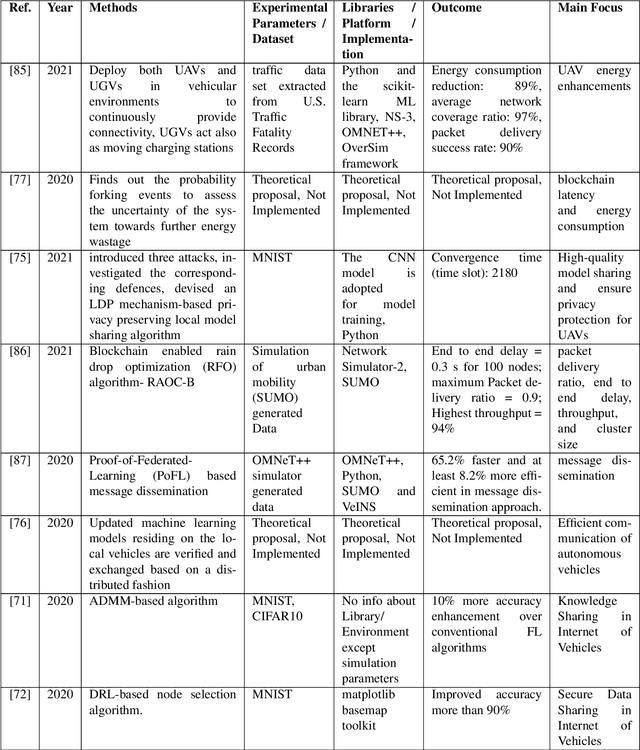
Abstract:While the convergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques with improved information technology systems ensured enormous benefits to the Internet of Vehicles (IoVs) systems, it also introduced an increased amount of security and privacy threats. To ensure the security of IoVs data, privacy preservation methodologies have gained significant attention in the literature. However, these strategies also need specific adjustments and modifications to cope with the advances in IoVs design. In the interim, Federated Learning (FL) has been proven as an emerging idea to protect IoVs data privacy and security. On the other hand, Blockchain technology is showing prominent possibilities with secured, dispersed, and auditable data recording and sharing schemes. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey on the application and implementation of Blockchain-Enabled Federated Learning frameworks for IoVs. Besides, probable issues, challenges, solutions, and future research directions for BC-Enabled FL frameworks for IoVs are also presented. This survey can further be used as the basis for developing modern BC-Enabled FL solutions to resolve different data privacy issues and scenarios of IoVs.
Detecting Malicious URLs of COVID-19 Pandemic using ML technologies
Sep 19, 2020



Abstract:Throughout the COVID-19 outbreak, malicious attacks have become more pervasive and damaging than ever. Malicious intruders have been responsible for most cybercrimes committed recently and are the cause for a growing number of cyber threats, including identity and IP thefts, financial crimes, and cyber-attacks to critical infrastructures. Machine learning (ML) has proven itself as a prominent field of study over the past decade by solving many highly complex and sophisticated real-world problems. This paper proposes an ML-based classification technique to detect the growing number of malicious URLs, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, which is currently considered a threat to IT users. We have used a large volume of Open Source data and preprocessed it using our developed tool to generate feature vectors and we trained the ML model using the apprehensive malicious threat weight. Our ML model has been tested, with and without entropy to forecast the threatening factors of COVID-19 URLs. The empirical evidence proves our methods to be a promising mechanism to mitigate COVID-19 related threats early in the attack lifecycle.
BanglaLekha-Isolated: A Comprehensive Bangla Handwritten Character Dataset
Feb 22, 2017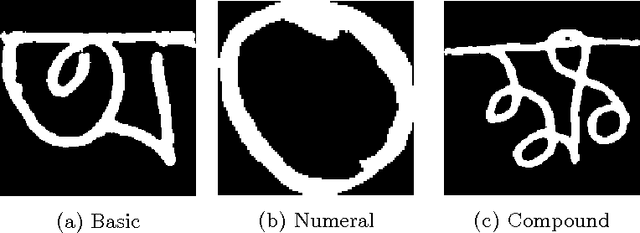
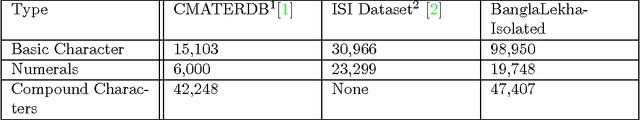
Abstract:Bangla handwriting recognition is becoming a very important issue nowadays. It is potentially a very important task specially for Bangla speaking population of Bangladesh and West Bengal. By keeping that in our mind we are introducing a comprehensive Bangla handwritten character dataset named BanglaLekha-Isolated. This dataset contains Bangla handwritten numerals, basic characters and compound characters. This dataset was collected from multiple geographical location within Bangladesh and includes sample collected from a variety of aged groups. This dataset can also be used for other classification problems i.e: gender, age, district. This is the largest dataset on Bangla handwritten characters yet.
An approach of IR-Based short-range correspondence systems for swarm robot balanced requisitions and communications
Aug 11, 2016


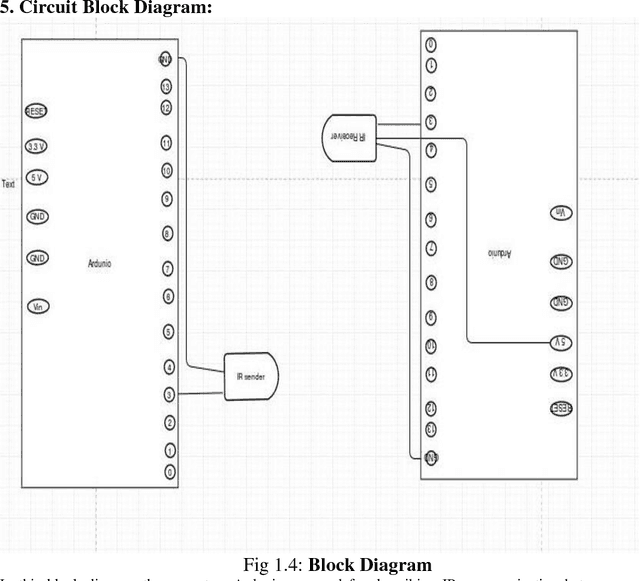
Abstract:This paper exhibits a short-run correspondence method appropriate for swarm versatile robots application. Infrared is utilized for transmitting and accepting information and obstruction location. The infrared correspondence code based swarm signaling is utilized for an independent versatile robot communication system in this research. A code based signaling system is developed for transmitting information between different entities of robot. The reflected infrared sign is additionally utilized for separation estimation for obstruction evasion. Investigation of robot demonstrates the possibility of utilizing infrared signs to get a solid nearby correspondence between swarm portable robots. This paper exhibits a basic decentralized control for swarm of self-collecting robots. Every robot in the code based swarm signaling is completely self-governing and controlled utilizing a conduct based methodology with just infrared-based nearby detecting and correspondences. The viability of the methodology has been checked with simulation, for a set of swarm robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge