Quanyu Liao
Attacking Important Pixels for Anchor-free Detectors
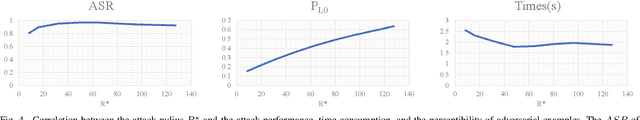
Jan 26, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks have been demonstrated to be vulnerable to adversarial attacks: subtle perturbation can completely change the prediction result. Existing adversarial attacks on object detection focus on attacking anchor-based detectors, which may not work well for anchor-free detectors. In this paper, we propose the first adversarial attack dedicated to anchor-free detectors. It is a category-wise attack that attacks important pixels of all instances of a category simultaneously. Our attack manifests in two forms, sparse category-wise attack (SCA) and dense category-wise attack (DCA), that minimize the $L_0$ and $L_\infty$ norm-based perturbations, respectively. For DCA, we present three variants, DCA-G, DCA-L, and DCA-S, that select a global region, a local region, and a semantic region, respectively, to attack. Our experiments on large-scale benchmark datasets including PascalVOC, MS-COCO, and MS-COCO Keypoints indicate that our proposed methods achieve state-of-the-art attack performance and transferability on both object detection and human pose estimation tasks.
Transferable Adversarial Examples for Anchor Free Object Detection
Jun 04, 2021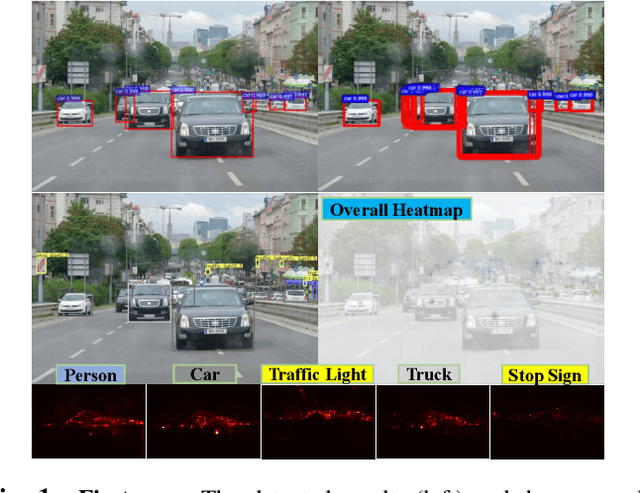
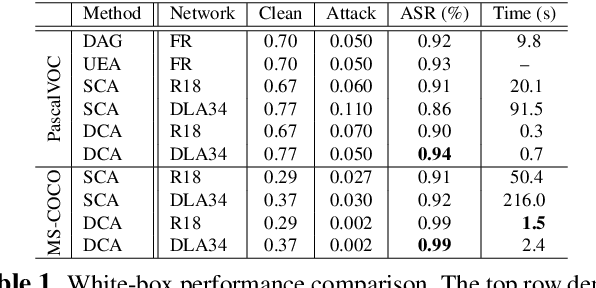
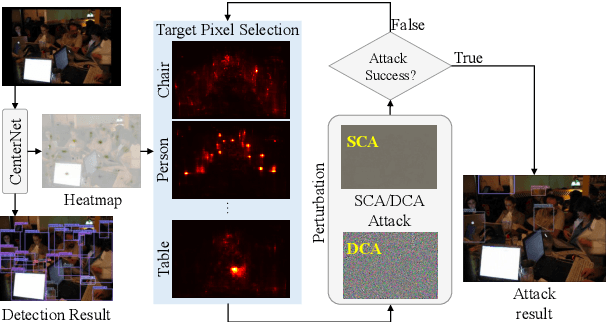
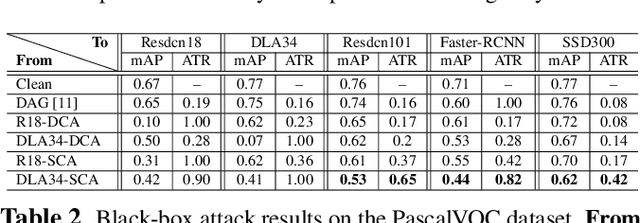
Abstract:Deep neural networks have been demonstrated to be vulnerable to adversarial attacks: subtle perturbation can completely change prediction result. The vulnerability has led to a surge of research in this direction, including adversarial attacks on object detection networks. However, previous studies are dedicated to attacking anchor-based object detectors. In this paper, we present the first adversarial attack on anchor-free object detectors. It conducts category-wise, instead of previously instance-wise, attacks on object detectors, and leverages high-level semantic information to efficiently generate transferable adversarial examples, which can also be transferred to attack other object detectors, even anchor-based detectors such as Faster R-CNN. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance and transferability.
Imperceptible Adversarial Examples for Fake Image Detection
Jun 03, 2021
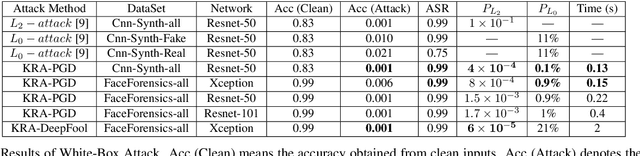
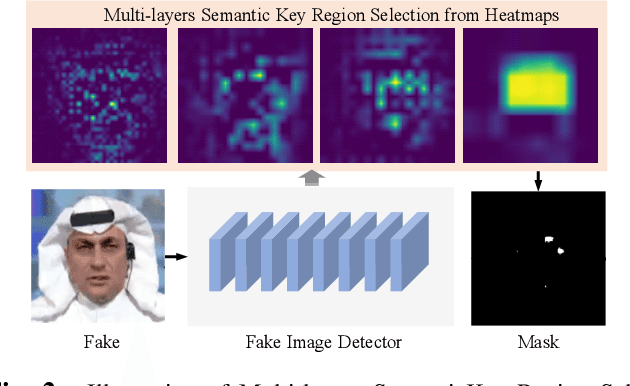
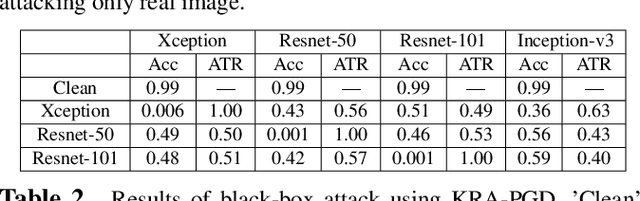
Abstract:Fooling people with highly realistic fake images generated with Deepfake or GANs brings a great social disturbance to our society. Many methods have been proposed to detect fake images, but they are vulnerable to adversarial perturbations -- intentionally designed noises that can lead to the wrong prediction. Existing methods of attacking fake image detectors usually generate adversarial perturbations to perturb almost the entire image. This is redundant and increases the perceptibility of perturbations. In this paper, we propose a novel method to disrupt the fake image detection by determining key pixels to a fake image detector and attacking only the key pixels, which results in the $L_0$ and the $L_2$ norms of adversarial perturbations much less than those of existing works. Experiments on two public datasets with three fake image detectors indicate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both white-box and black-box attacks.
Fast Local Attack: Generating Local Adversarial Examples for Object Detectors
Oct 27, 2020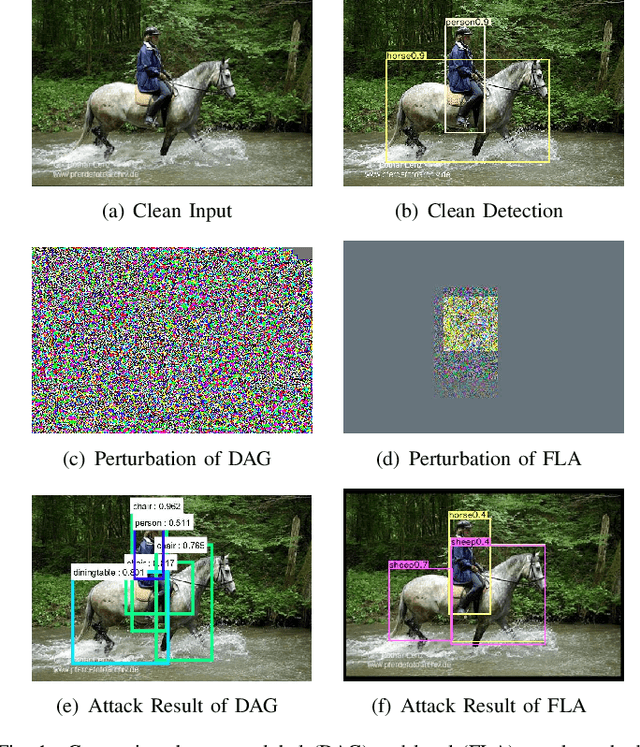

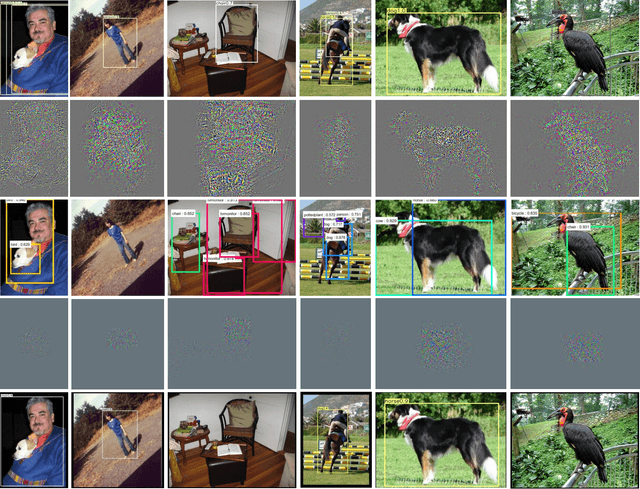
Abstract:The deep neural network is vulnerable to adversarial examples. Adding imperceptible adversarial perturbations to images is enough to make them fail. Most existing research focuses on attacking image classifiers or anchor-based object detectors, but they generate globally perturbation on the whole image, which is unnecessary. In our work, we leverage higher-level semantic information to generate high aggressive local perturbations for anchor-free object detectors. As a result, it is less computationally intensive and achieves a higher black-box attack as well as transferring attack performance. The adversarial examples generated by our method are not only capable of attacking anchor-free object detectors, but also able to be transferred to attack anchor-based object detector.
Category-wise Attack: Transferable Adversarial Examples for Anchor Free Object Detection
Feb 10, 2020



Abstract:Deep neural networks have been demonstrated to be vulnerable to adversarial attacks: sutle perturbations can completely change the classification results. Their vulnerability has led to a surge of research in this direction. However, most works dedicated to attacking anchor-based object detection models. In this work, we aim to present an effective and efficient algorithm to generate adversarial examples to attack anchor-free object models based on two approaches. First, we conduct category-wise instead of instance-wise attacks on the object detectors. Second, we leverage the high-level semantic information to generate the adversarial examples. Surprisingly, the generated adversarial examples it not only able to effectively attack the targeted anchor-free object detector but also to be transferred to attack other object detectors, even anchor-based detectors such as Faster R-CNN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge