Qiyan Luo
Comparative Analysis of Advanced Feature Matching Algorithms in Challenging High Spatial Resolution Optical Satellite Stereo Scenarios
May 10, 2024



Abstract:Feature matching determines the orientation accuracy for the High Spatial Resolution (HSR) optical satellite stereos, subsequently impacting several significant applications such as 3D reconstruction and change detection. However, the matching of off-track HSR optical satellite stereos often encounters challenging conditions including wide-baseline observation, significant radiometric differences, multi-temporal changes, varying spatial resolutions, inconsistent spectral resolution, and diverse sensors. In this study, we evaluate various advanced feature matching algorithms for HSR optical satellite stereos. Utilizing a specially constructed dataset from five satellites across six challenging scenarios, HSROSS Dataset, we conduct a comparative analysis of four algorithms: the traditional SIFT, and deep-learning based methods including SuperPoint + SuperGlue, SuperPoint + LightGlue, and LoFTR. Our findings highlight overall superior performance of SuperPoint + LightGlue in balancing robustness, accuracy, distribution, and efficiency, showcasing its potential in complex HSR optical satellite scenarios.
SG-BEV: Satellite-Guided BEV Fusion for Cross-View Semantic Segmentation
Apr 03, 2024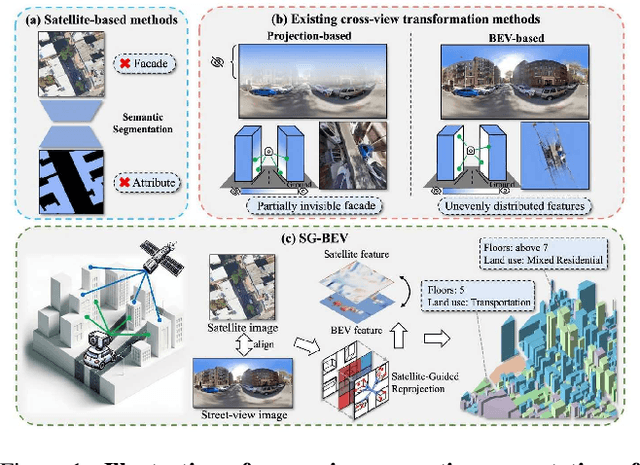

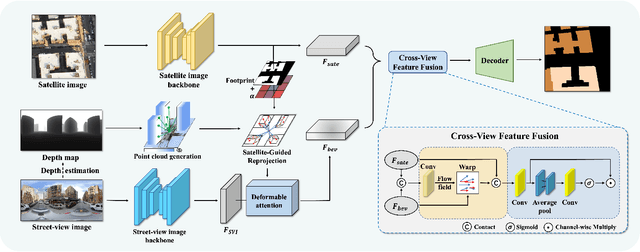

Abstract:This paper aims at achieving fine-grained building attribute segmentation in a cross-view scenario, i.e., using satellite and street-view image pairs. The main challenge lies in overcoming the significant perspective differences between street views and satellite views. In this work, we introduce SG-BEV, a novel approach for satellite-guided BEV fusion for cross-view semantic segmentation. To overcome the limitations of existing cross-view projection methods in capturing the complete building facade features, we innovatively incorporate Bird's Eye View (BEV) method to establish a spatially explicit mapping of street-view features. Moreover, we fully leverage the advantages of multiple perspectives by introducing a novel satellite-guided reprojection module, optimizing the uneven feature distribution issues associated with traditional BEV methods. Our method demonstrates significant improvements on four cross-view datasets collected from multiple cities, including New York, San Francisco, and Boston. On average across these datasets, our method achieves an increase in mIOU by 10.13% and 5.21% compared with the state-of-the-art satellite-based and cross-view methods. The code and datasets of this work will be released at https://github.com/yejy53/SG-BEV.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge