Qiujie Xie
AutoFigure: Generating and Refining Publication-Ready Scientific Illustrations
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:High-quality scientific illustrations are crucial for effectively communicating complex scientific and technical concepts, yet their manual creation remains a well-recognized bottleneck in both academia and industry. We present FigureBench, the first large-scale benchmark for generating scientific illustrations from long-form scientific texts. It contains 3,300 high-quality scientific text-figure pairs, covering diverse text-to-illustration tasks from scientific papers, surveys, blogs, and textbooks. Moreover, we propose AutoFigure, the first agentic framework that automatically generates high-quality scientific illustrations based on long-form scientific text. Specifically, before rendering the final result, AutoFigure engages in extensive thinking, recombination, and validation to produce a layout that is both structurally sound and aesthetically refined, outputting a scientific illustration that achieves both structural completeness and aesthetic appeal. Leveraging the high-quality data from FigureBench, we conduct extensive experiments to test the performance of AutoFigure against various baseline methods. The results demonstrate that AutoFigure consistently surpasses all baseline methods, producing publication-ready scientific illustrations. The code, dataset and huggingface space are released in https://github.com/ResearAI/AutoFigure.
DeepScientist: Advancing Frontier-Pushing Scientific Findings Progressively
Sep 30, 2025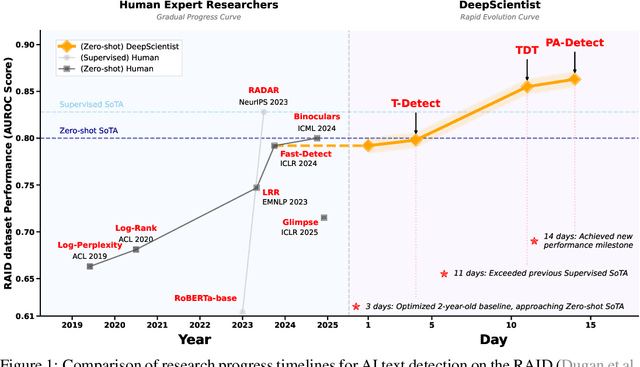
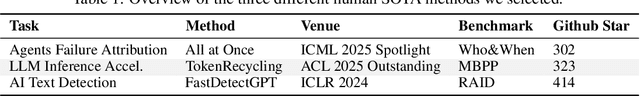
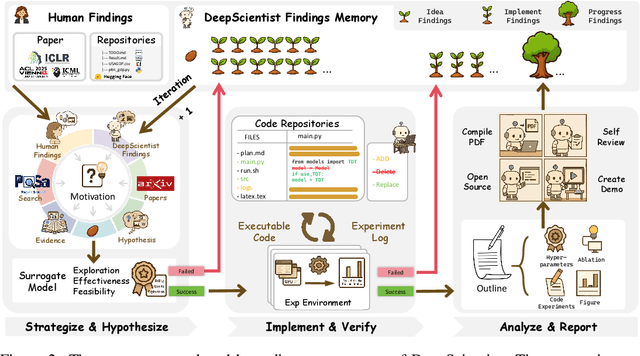
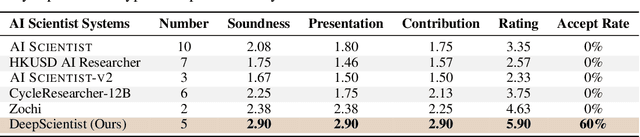
Abstract:While previous AI Scientist systems can generate novel findings, they often lack the focus to produce scientifically valuable contributions that address pressing human-defined challenges. We introduce DeepScientist, a system designed to overcome this by conducting goal-oriented, fully autonomous scientific discovery over month-long timelines. It formalizes discovery as a Bayesian Optimization problem, operationalized through a hierarchical evaluation process consisting of "hypothesize, verify, and analyze". Leveraging a cumulative Findings Memory, this loop intelligently balances the exploration of novel hypotheses with exploitation, selectively promoting the most promising findings to higher-fidelity levels of validation. Consuming over 20,000 GPU hours, the system generated about 5,000 unique scientific ideas and experimentally validated approximately 1100 of them, ultimately surpassing human-designed state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on three frontier AI tasks by 183.7\%, 1.9\%, and 7.9\%. This work provides the first large-scale evidence of an AI achieving discoveries that progressively surpass human SOTA on scientific tasks, producing valuable findings that genuinely push the frontier of scientific discovery. To facilitate further research into this process, we will open-source all experimental logs and system code at https://github.com/ResearAI/DeepScientist/.
Triple Path Enhanced Neural Architecture Search for Multimodal Fake News Detection
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Multimodal fake news detection has become one of the most crucial issues on social media platforms. Although existing methods have achieved advanced performance, two main challenges persist: (1) Under-performed multimodal news information fusion due to model architecture solidification, and (2) weak generalization ability on partial-modality contained fake news. To meet these challenges, we propose a novel and flexible triple path enhanced neural architecture search model MUSE. MUSE includes two dynamic paths for detecting partial-modality contained fake news and a static path for exploiting potential multimodal correlations. Experimental results show that MUSE achieves stable performance improvement over the baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge