Qirui Sun
Ada-adapter:Fast Few-shot Style Personlization of Diffusion Model with Pre-trained Image Encoder
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:Fine-tuning advanced diffusion models for high-quality image stylization usually requires large training datasets and substantial computational resources, hindering their practical applicability. We propose Ada-Adapter, a novel framework for few-shot style personalization of diffusion models. Ada-Adapter leverages off-the-shelf diffusion models and pre-trained image feature encoders to learn a compact style representation from a limited set of source images. Our method enables efficient zero-shot style transfer utilizing a single reference image. Furthermore, with a small number of source images (three to five are sufficient) and a few minutes of fine-tuning, our method can capture intricate style details and conceptual characteristics, generating high-fidelity stylized images that align well with the provided text prompts. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on various artistic styles, including flat art, 3D rendering, and logo design. Our experimental results show that Ada-Adapter outperforms existing zero-shot and few-shot stylization methods in terms of output quality, diversity, and training efficiency.
BMPQ: Bit-Gradient Sensitivity Driven Mixed-Precision Quantization of DNNs from Scratch
Dec 24, 2021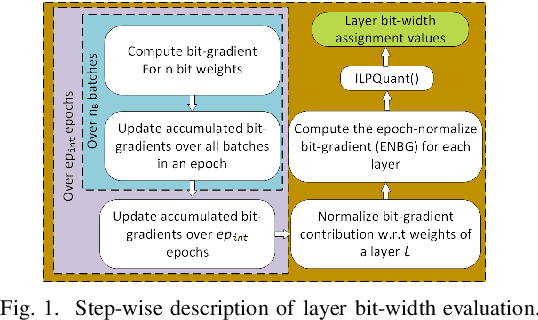
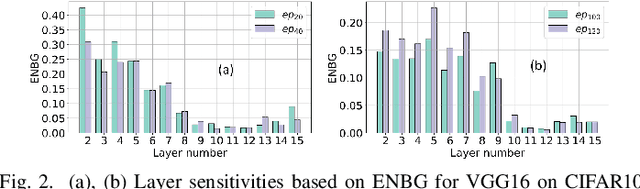
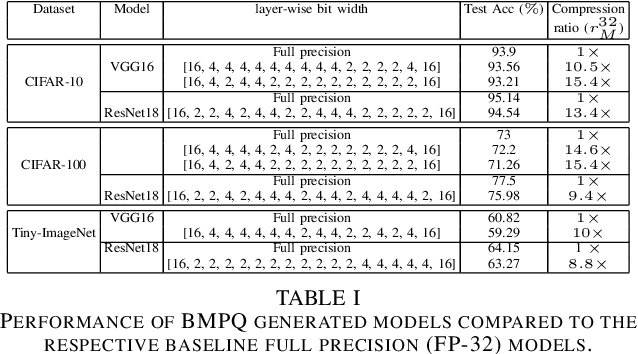
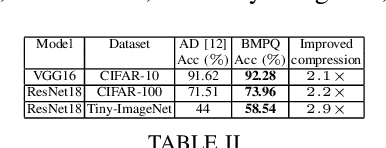
Abstract:Large DNNs with mixed-precision quantization can achieve ultra-high compression while retaining high classification performance. However, because of the challenges in finding an accurate metric that can guide the optimization process, these methods either sacrifice significant performance compared to the 32-bit floating-point (FP-32) baseline or rely on a compute-expensive, iterative training policy that requires the availability of a pre-trained baseline. To address this issue, this paper presents BMPQ, a training method that uses bit gradients to analyze layer sensitivities and yield mixed-precision quantized models. BMPQ requires a single training iteration but does not need a pre-trained baseline. It uses an integer linear program (ILP) to dynamically adjust the precision of layers during training, subject to a fixed hardware budget. To evaluate the efficacy of BMPQ, we conduct extensive experiments with VGG16 and ResNet18 on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and Tiny-ImageNet datasets. Compared to the baseline FP-32 models, BMPQ can yield models that have 15.4x fewer parameter bits with a negligible drop in accuracy. Compared to the SOTA "during training", mixed-precision training scheme, our models are 2.1x, 2.2x, and 2.9x smaller, on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and Tiny-ImageNet, respectively, with an improved accuracy of up to 14.54%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge