Qipeng Li
Snail-Radar: A large-scale diverse dataset for the evaluation of 4D-radar-based SLAM systems
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:4D radars are increasingly favored for odometry and mapping of autonomous systems due to their robustness in harsh weather and dynamic environments. Existing datasets, however, often cover limited areas and are typically captured using a single platform. To address this gap, we present a diverse large-scale dataset specifically designed for 4D radar-based localization and mapping. This dataset was gathered using three different platforms: a handheld device, an e-bike, and an SUV, under a variety of environmental conditions, including clear days, nighttime, and heavy rain. The data collection occurred from September 2023 to February 2024, encompassing diverse settings such as roads in a vegetated campus and tunnels on highways. Each route was traversed multiple times to facilitate place recognition evaluations. The sensor suite included a 3D lidar, 4D radars, stereo cameras, consumer-grade IMUs, and a GNSS/INS system. Sensor data packets were synchronized to GNSS time using a two-step process: a convex hull algorithm was applied to smooth host time jitter, and then odometry and correlation algorithms were used to correct constant time offsets. Extrinsic calibration between sensors was achieved through manual measurements and subsequent nonlinear optimization. The reference motion for the platforms was generated by registering lidar scans to a terrestrial laser scanner (TLS) point cloud map using a lidar inertial odometry (LIO) method in localization mode. Additionally, a data reversion technique was introduced to enable backward LIO processing. We believe this dataset will boost research in radar-based point cloud registration, odometry, mapping, and place recognition.
3D-SeqMOS: A Novel Sequential 3D Moving Object Segmentation in Autonomous Driving
Jul 18, 2023
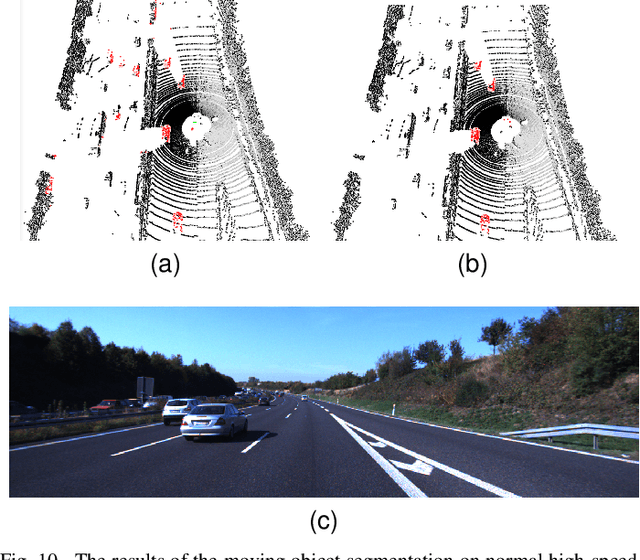
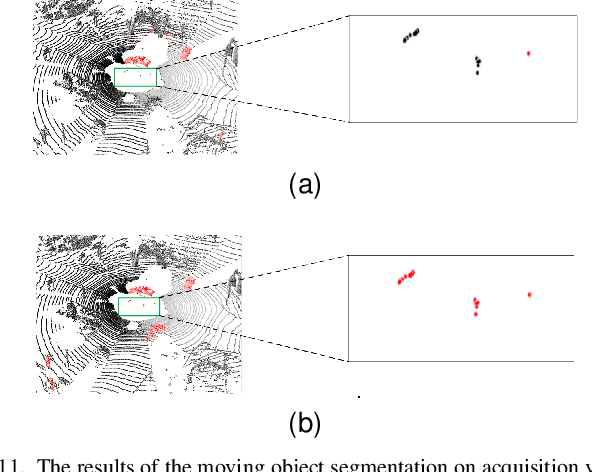
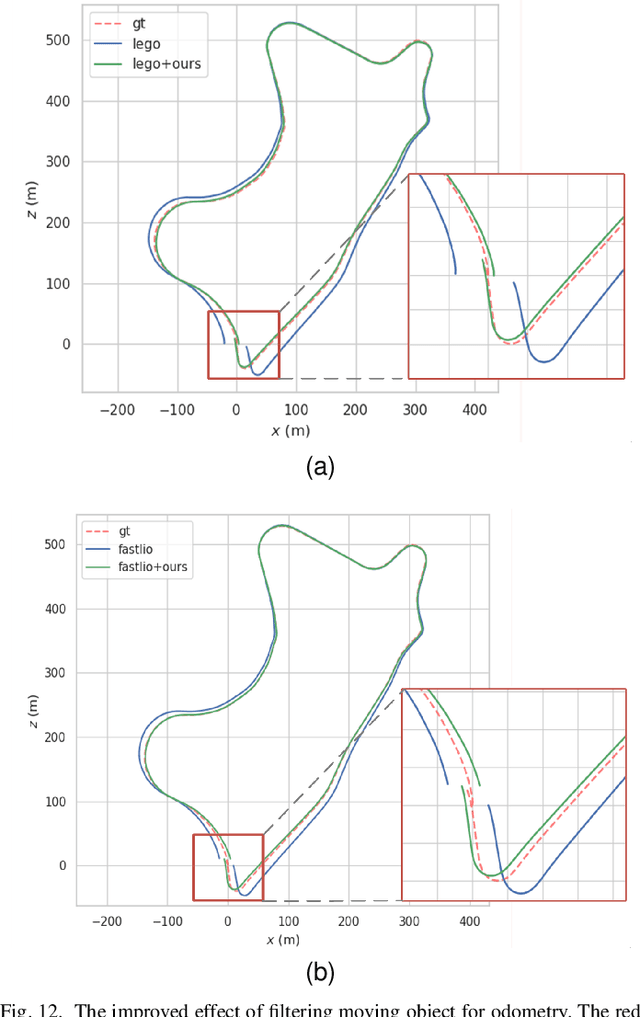
Abstract:For the SLAM system in robotics and autonomous driving, the accuracy of front-end odometry and back-end loop-closure detection determine the whole intelligent system performance. But the LiDAR-SLAM could be disturbed by current scene moving objects, resulting in drift errors and even loop-closure failure. Thus, the ability to detect and segment moving objects is essential for high-precision positioning and building a consistent map. In this paper, we address the problem of moving object segmentation from 3D LiDAR scans to improve the odometry and loop-closure accuracy of SLAM. We propose a novel 3D Sequential Moving-Object-Segmentation (3D-SeqMOS) method that can accurately segment the scene into moving and static objects, such as moving and static cars. Different from the existing projected-image method, we process the raw 3D point cloud and build a 3D convolution neural network for MOS task. In addition, to make full use of the spatio-temporal information of point cloud, we propose a point cloud residual mechanism using the spatial features of current scan and the temporal features of previous residual scans. Besides, we build a complete SLAM framework to verify the effectiveness and accuracy of 3D-SeqMOS. Experiments on SemanticKITTI dataset show that our proposed 3D-SeqMOS method can effectively detect moving objects and improve the accuracy of LiDAR odometry and loop-closure detection. The test results show our 3D-SeqMOS outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 12.4%. We extend the proposed method to the SemanticKITTI: Moving Object Segmentation competition and achieve the 2nd in the leaderboard, showing its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge