Qinyu Wang
Stability as a Liability:Systematic Breakdown of Linguistic Structure in LLMs
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Training stability is typically regarded as a prerequisite for reliable optimization in large language models. In this work, we analyze how stabilizing training dynamics affects the induced generation distribution. We show that under standard maximum likelihood training, stable parameter trajectories lead stationary solutions to approximately minimize the forward KL divergence to the empirical distribution, while implicitly reducing generative entropy. As a consequence, the learned model can concentrate probability mass on a limited subset of empirical modes, exhibiting systematic degeneration despite smooth loss convergence. We empirically validate this effect using a controlled feedback-based training framework that stabilizes internal generation statistics, observing consistent low-entropy outputs and repetitive behavior across architectures and random seeds. It indicates that optimization stability and generative expressivity are not inherently aligned, and that stability alone is an insufficient indicator of generative quality.
GNN-Enabled Optimization of Placement and Transmission Design for UAV Communications
Oct 03, 2024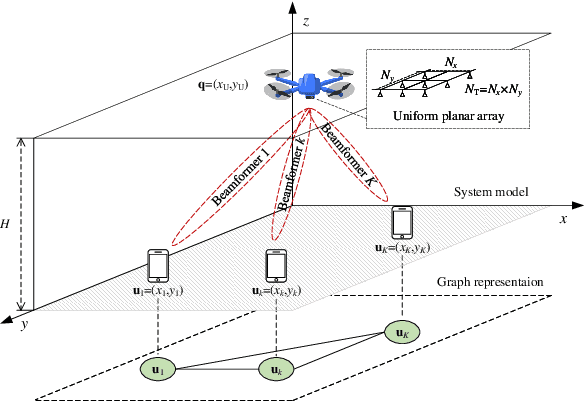
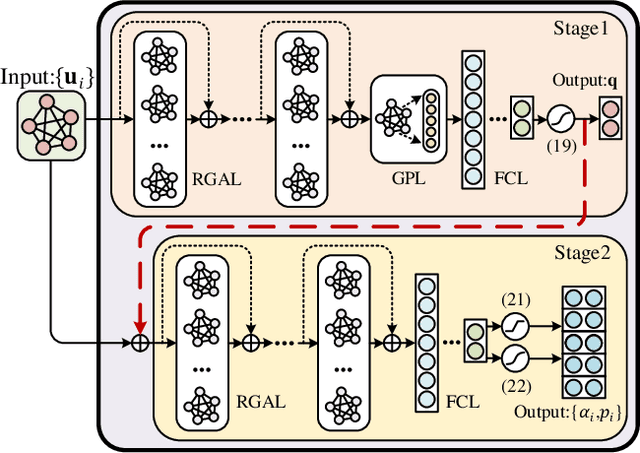
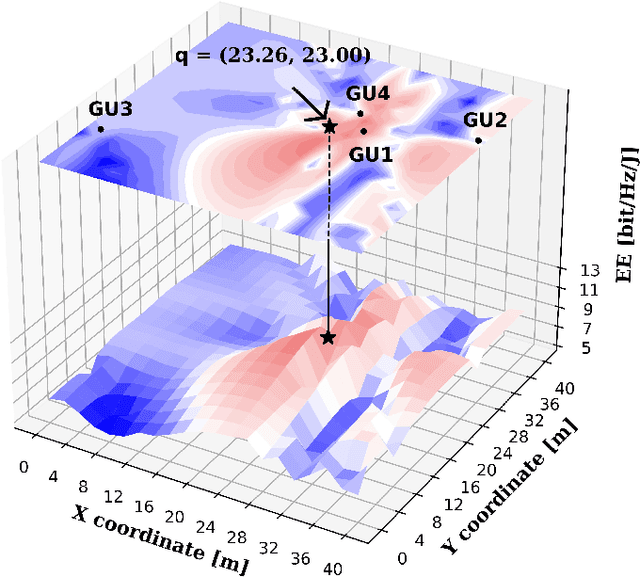
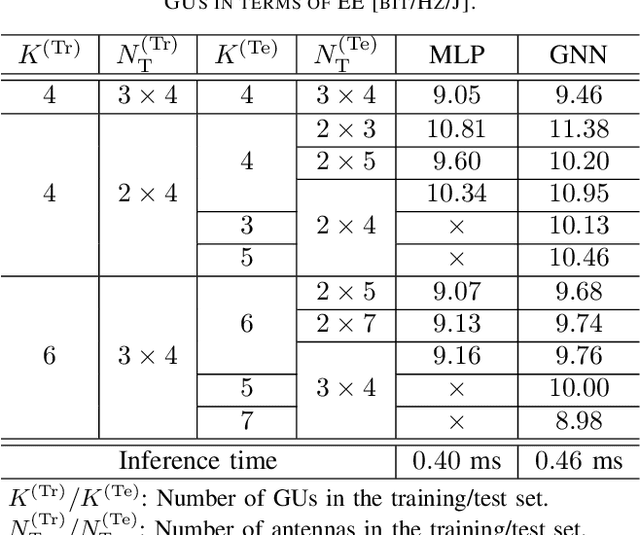
Abstract:This paper applies graph neural networks (GNN) in UAV communications to optimize the placement and transmission design. We consider a multiple-user multiple-input-single-output UAV communication system where a UAV intends to find a placement to hover and serve users with maximum energy efficiency (EE). To facilitate the GNN-based learning, we adopt the hybrid maximum ratio transmission and zero forcing scheme to design the beamforming vectors and a feature augment is implemented by manually setting edge features. Furthermore, we propose a two-stage GNN-based model where the first stage and the second stage yield the placement and the transmission design, respectively. The two stages are connected via a residual and their learnable weights are jointly optimized by via unsupervised learning. Numerical results illustrate the effectiveness and validate the scalability to both UAV antennas and users of the proposed model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge