Qinpei Zhao
Up-sampling-only and Adaptive Mesh-based GNN for Simulating Physical Systems
Sep 07, 2024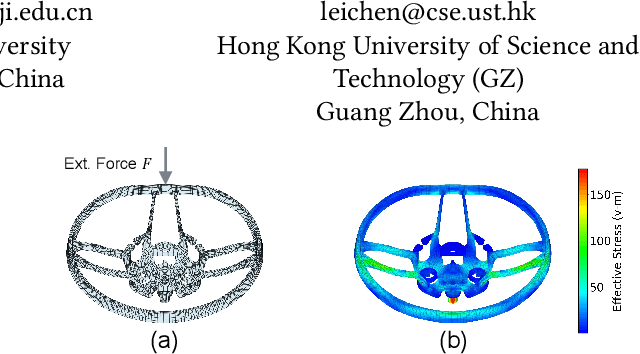
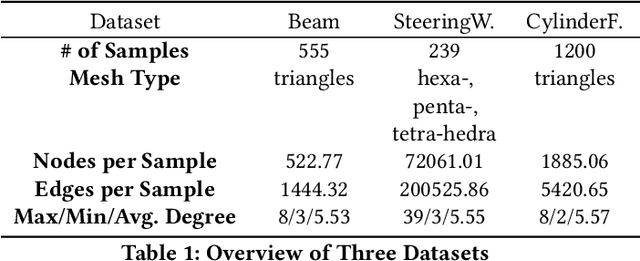
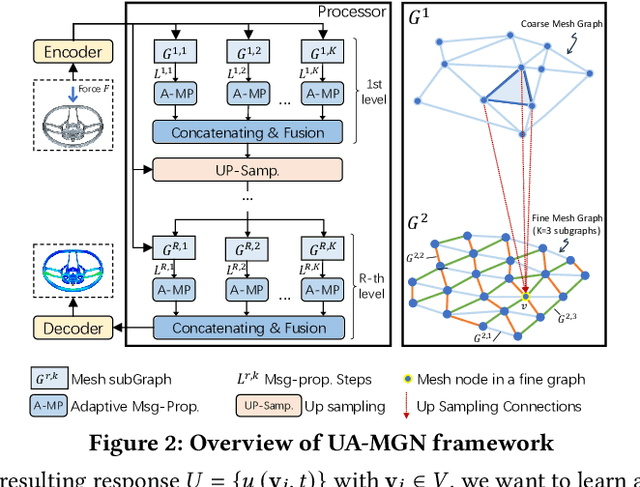
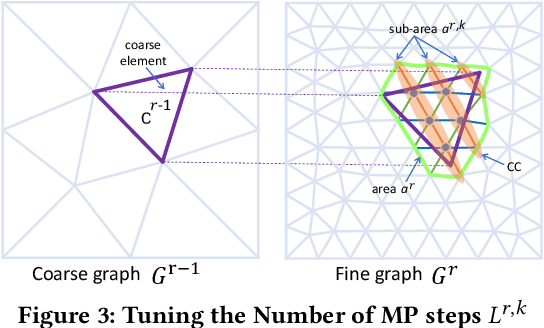
Abstract:Traditional simulation of complex mechanical systems relies on numerical solvers of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs), e.g., using the Finite Element Method (FEM). The FEM solvers frequently suffer from intensive computation cost and high running time. Recent graph neural network (GNN)-based simulation models can improve running time meanwhile with acceptable accuracy. Unfortunately, they are hard to tailor GNNs for complex mechanical systems, including such disadvantages as ineffective representation and inefficient message propagation (MP). To tackle these issues, in this paper, with the proposed Up-sampling-only and Adaptive MP techniques, we develop a novel hierarchical Mesh Graph Network, namely UA-MGN, for efficient and effective mechanical simulation. Evaluation on two synthetic and one real datasets demonstrates the superiority of the UA-MGN. For example, on the Beam dataset, compared to the state-of-the-art MS-MGN, UA-MGN leads to 40.99% lower errors but using only 43.48% fewer network parameters and 4.49% fewer floating point operations (FLOPs).
Abstractive Sentence Summarization with Guidance of Selective Multimodal Reference
Aug 11, 2021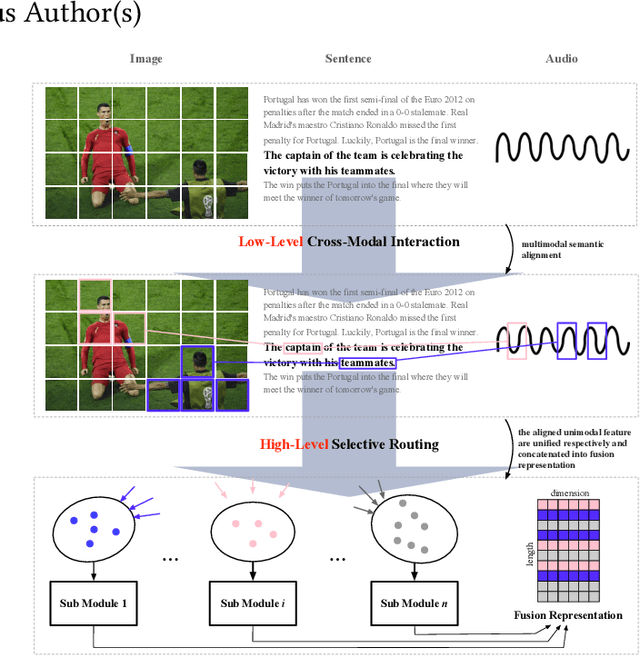
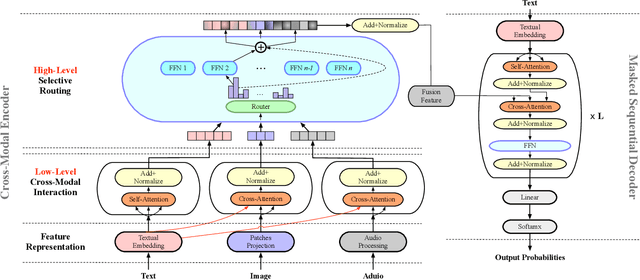
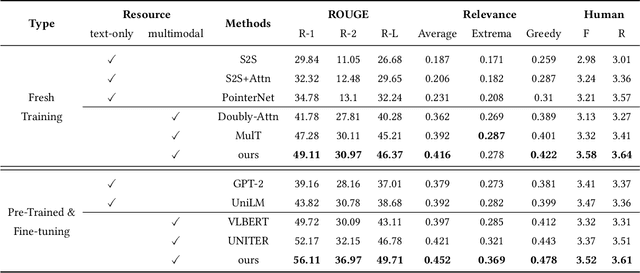
Abstract:Multimodal abstractive summarization with sentence output is to generate a textual summary given a multimodal triad -- sentence, image and audio, which has been proven to improve users satisfaction and convenient our life. Existing approaches mainly focus on the enhancement of multimodal fusion, while ignoring the unalignment among multiple inputs and the emphasis of different segments in feature, which has resulted in the superfluity of multimodal interaction. To alleviate these problems, we propose a Multimodal Hierarchical Selective Transformer (mhsf) model that considers reciprocal relationships among modalities (by low-level cross-modal interaction module) and respective characteristics within single fusion feature (by high-level selective routing module). In details, it firstly aligns the inputs from different sources and then adopts a divide and conquer strategy to highlight or de-emphasize multimodal fusion representation, which can be seen as a sparsely feed-forward model - different groups of parameters will be activated facing different segments in feature. We evaluate the generalism of proposed mhsf model with the pre-trained+fine-tuning and fresh training strategies. And Further experimental results on MSMO demonstrate that our model outperforms SOTA baselines in terms of ROUGE, relevance scores and human evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge