Qingyuan Cheng
Inference-Time Decontamination: Reusing Leaked Benchmarks for Large Language Model Evaluation
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:The training process of large language models (LLMs) often involves varying degrees of test data contamination. Although current LLMs are achieving increasingly better performance on various benchmarks, their performance in practical applications does not always match their benchmark results. Leakage of benchmarks can prevent the accurate assessment of LLMs' true performance. However, constructing new benchmarks is costly, labor-intensive and still carries the risk of leakage. Therefore, in this paper, we ask the question, Can we reuse these leaked benchmarks for LLM evaluation? We propose Inference-Time Decontamination (ITD) to address this issue by detecting and rewriting leaked samples without altering their difficulties. ITD can mitigate performance inflation caused by memorizing leaked benchmarks. Our proof-of-concept experiments demonstrate that ITD reduces inflated accuracy by 22.9% on GSM8K and 19.0% on MMLU. On MMLU, using Inference-time Decontamination can lead to a decrease in the results of Phi3 and Mistral by 6.7% and 3.6% respectively. We hope that ITD can provide more truthful evaluation results for large language models.
In-Memory Learning: A Declarative Learning Framework for Large Language Models
Mar 05, 2024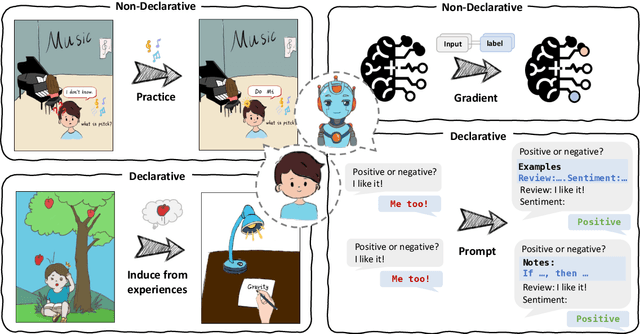



Abstract:The exploration of whether agents can align with their environment without relying on human-labeled data presents an intriguing research topic. Drawing inspiration from the alignment process observed in intelligent organisms, where declarative memory plays a pivotal role in summarizing past experiences, we propose a novel learning framework. The agents adeptly distill insights from past experiences, refining and updating existing notes to enhance their performance in the environment. This entire process transpires within the memory components and is implemented through natural language, so we character this framework as In-memory Learning. We also delve into the key features of benchmarks designed to evaluate the self-improvement process. Through systematic experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework and provide insights into this problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge