Qingyu Xiong
SWGCN: Synergy Weighted Graph Convolutional Network for Multi-Behavior Recommendation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Multi-behavior recommendation paradigms have emerged to capture diverse user activities, forecasting primary conversions (e.g., purchases) by leveraging secondary signals like browsing history. However, current graph-based methods often overlook cross-behavioral synergistic signals and fine-grained intensity of individual actions. Motivated by the need to overcome these shortcomings, we introduce Synergy Weighted Graph Convolutional Network (SWGCN). SWGCN introduces two novel components: a Target Preference Weigher, which adaptively assigns weights to user-item interactions within each behavior, and a Synergy Alignment Task, which guides its training by leveraging an Auxiliary Preference Valuator. This task prioritizes interactions from synergistic signals that more accurately reflect user preferences. The performance of our model is rigorously evaluated through comprehensive tests on three open-source datasets, specifically Taobao, IJCAI, and Beibei. On the Taobao dataset, SWGCN yields relative gains of 112.49% and 156.36% in terms of Hit Ratio (HR) and Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG), respectively. It also yields consistent gains on IJCAI and Beibei, confirming its robustness and generalizability across various datasets. Our implementation is open-sourced and can be accessed via https://github.com/FangdChen/SWGCN.
Predictive and Contrastive: Dual-Auxiliary Learning for Recommendation
Mar 08, 2022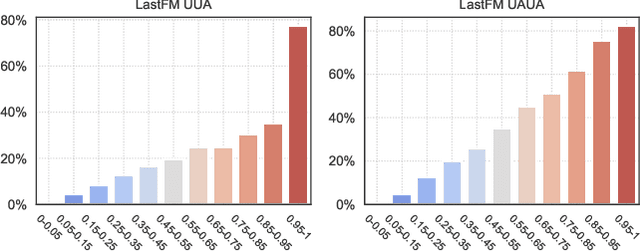
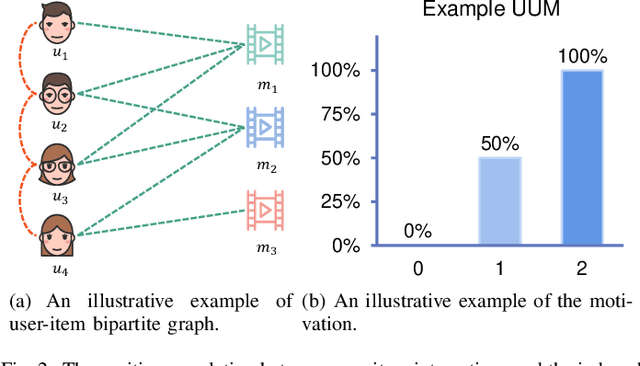
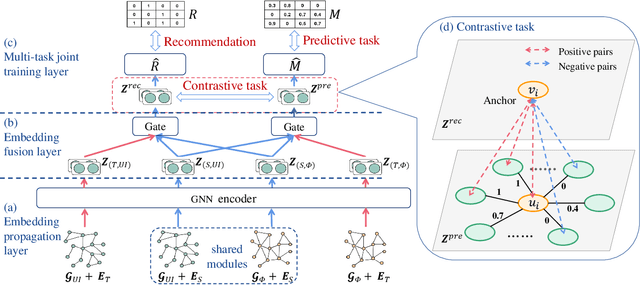
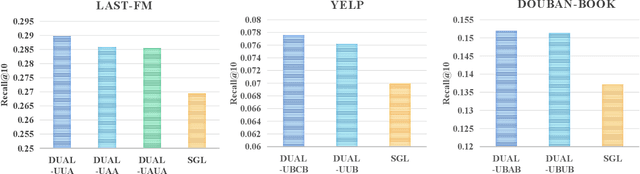
Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) recently has achieved outstanding success on recommendation. By setting up an auxiliary task (either predictive or contrastive), SSL can discover supervisory signals from the raw data without human annotation, which greatly mitigates the problem of sparse user-item interactions. However, most SSL-based recommendation models rely on general-purpose auxiliary tasks, e.g., maximizing correspondence between node representations learned from the original and perturbed interaction graphs, which are explicitly irrelevant to the recommendation task. Accordingly, the rich semantics reflected by social relationships and item categories, which lie in the recommendation data-based heterogeneous graphs, are not fully exploited. To explore recommendation-specific auxiliary tasks, we first quantitatively analyze the heterogeneous interaction data and find a strong positive correlation between the interactions and the number of user-item paths induced by meta-paths. Based on the finding, we design two auxiliary tasks that are tightly coupled with the target task (one is predictive and the other one is contrastive) towards connecting recommendation with the self-supervision signals hiding in the positive correlation. Finally, a model-agnostic DUal-Auxiliary Learning (DUAL) framework which unifies the SSL and recommendation tasks is developed. The extensive experiments conducted on three real-world datasets demonstrate that DUAL can significantly improve recommendation, reaching the state-of-the-art performance.
Recommender Systems Based on Generative Adversarial Networks: A Problem-Driven Perspective
Mar 05, 2020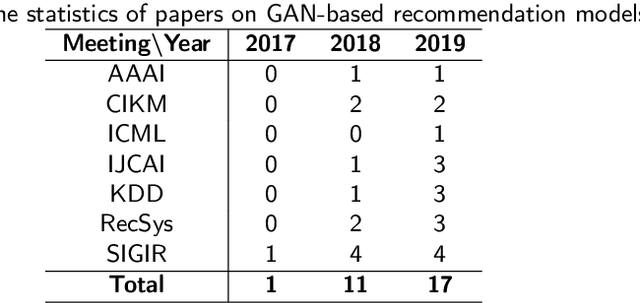

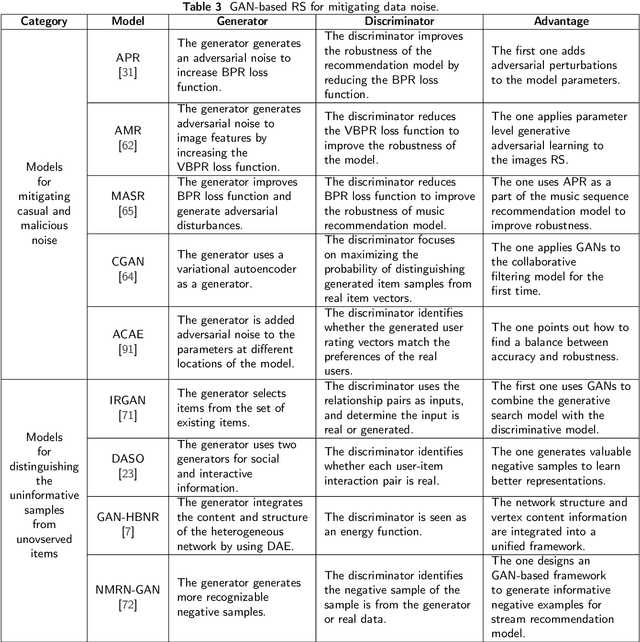
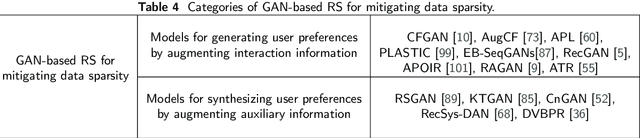
Abstract:Recommender systems (RS) play a very important role in various aspects of people's online life. Many companies leverage RS to help users discover new and favored items. Despite their empirical success, these systems still suffer from two main problems: data noise and data sparsity. In recent years, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have received a surge of interests in many fields because of their great potential to learn complex real data distribution, and they also provide new means to mitigate the aforementioned problems of RS. Particularly, owing to adversarial learning, the problem of data noise can be handled by adding adversarial perturbations or forcing discriminators to tell the informative and uninformative data examples apart. As for the mitigation of data sparsity issue, the GAN-based models are able to replicate the real distribution of the user-item interactions and augment the available data. To gain a comprehensive understanding of these GAN-based recommendation models, we provide a retrospective of these studies and organize them from a problem-driven perspective. Specifically, we propose a taxonomy of these models, along with a detailed description of them and their advantages. Finally, we elaborate on several open issues and expand on current trends in the GAN-based RS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge