Recommender Systems Based on Generative Adversarial Networks: A Problem-Driven Perspective
Paper and Code
Mar 05, 2020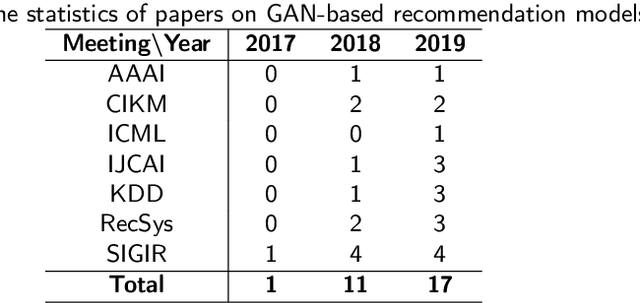

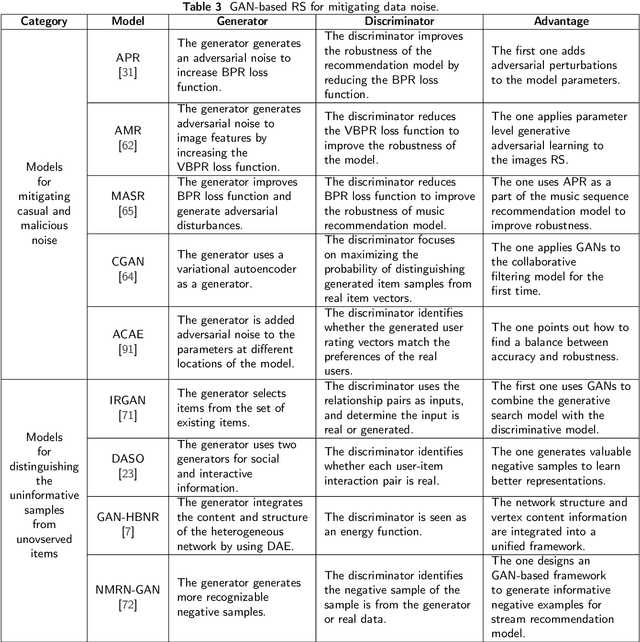
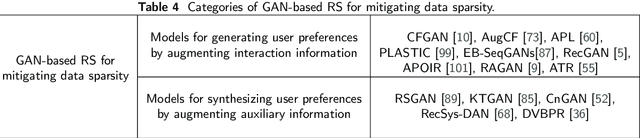
Recommender systems (RS) play a very important role in various aspects of people's online life. Many companies leverage RS to help users discover new and favored items. Despite their empirical success, these systems still suffer from two main problems: data noise and data sparsity. In recent years, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have received a surge of interests in many fields because of their great potential to learn complex real data distribution, and they also provide new means to mitigate the aforementioned problems of RS. Particularly, owing to adversarial learning, the problem of data noise can be handled by adding adversarial perturbations or forcing discriminators to tell the informative and uninformative data examples apart. As for the mitigation of data sparsity issue, the GAN-based models are able to replicate the real distribution of the user-item interactions and augment the available data. To gain a comprehensive understanding of these GAN-based recommendation models, we provide a retrospective of these studies and organize them from a problem-driven perspective. Specifically, we propose a taxonomy of these models, along with a detailed description of them and their advantages. Finally, we elaborate on several open issues and expand on current trends in the GAN-based RS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge