Qing Cao
EchoNarrator: Generating natural text explanations for ejection fraction predictions
Oct 31, 2024Abstract:Ejection fraction (EF) of the left ventricle (LV) is considered as one of the most important measurements for diagnosing acute heart failure and can be estimated during cardiac ultrasound acquisition. While recent successes in deep learning research successfully estimate EF values, the proposed models often lack an explanation for the prediction. However, providing clear and intuitive explanations for clinical measurement predictions would increase the trust of cardiologists in these models. In this paper, we explore predicting EF measurements with Natural Language Explanation (NLE). We propose a model that in a single forward pass combines estimation of the LV contour over multiple frames, together with a set of modules and routines for computing various motion and shape attributes that are associated with ejection fraction. It then feeds the attributes into a large language model to generate text that helps to explain the network's outcome in a human-like manner. We provide experimental evaluation of our explanatory output, as well as EF prediction, and show that our model can provide EF comparable to state-of-the-art together with meaningful and accurate natural language explanation to the prediction. The project page can be found at https://github.com/guybenyosef/EchoNarrator .
Self-supervised Anomaly Detection Pretraining Enhances Long-tail ECG Diagnosis
Aug 30, 2024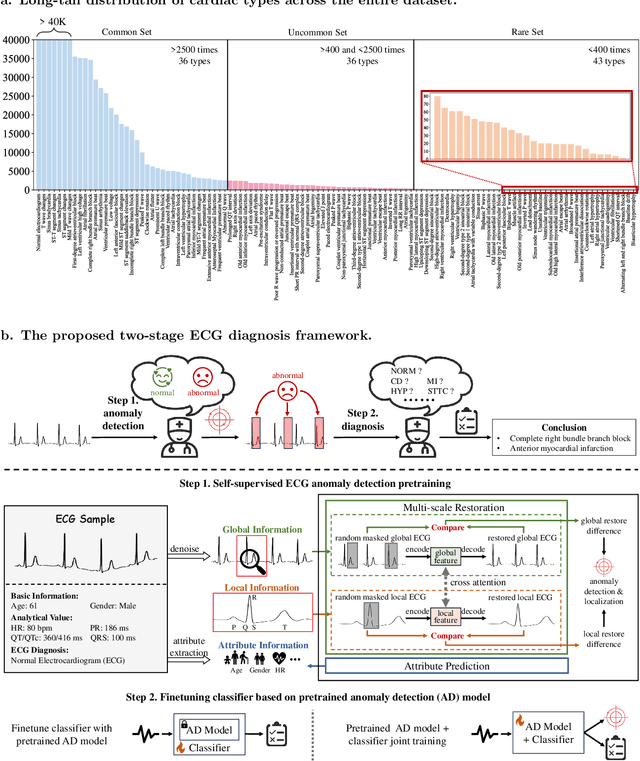
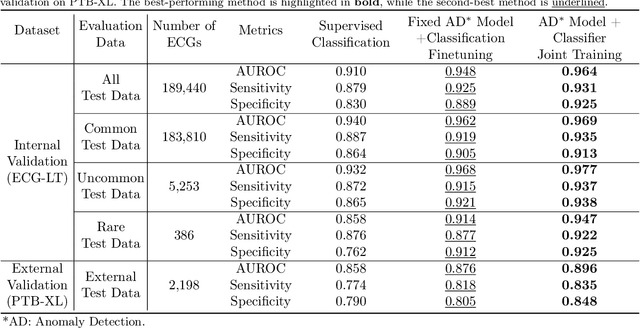
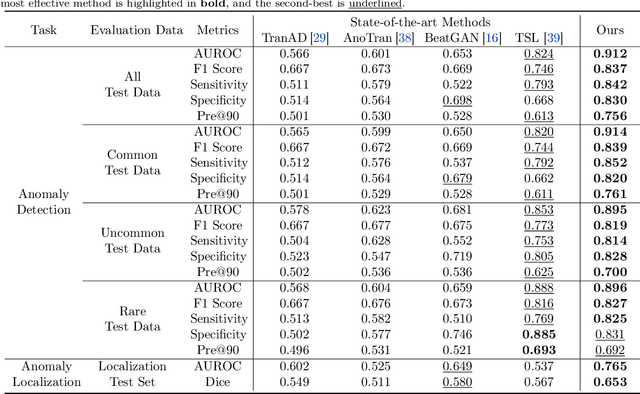
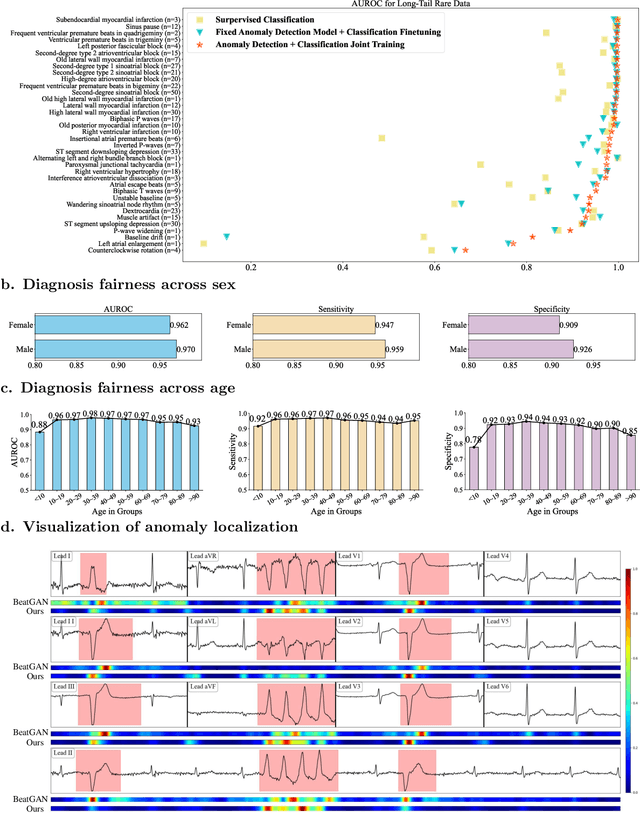
Abstract:Current computer-aided ECG diagnostic systems struggle with the underdetection of rare but critical cardiac anomalies due to the imbalanced nature of ECG datasets. This study introduces a novel approach using self-supervised anomaly detection pretraining to address this limitation. The anomaly detection model is specifically designed to detect and localize subtle deviations from normal cardiac patterns, capturing the nuanced details essential for accurate ECG interpretation. Validated on an extensive dataset of over one million ECG records from clinical practice, characterized by a long-tail distribution across 116 distinct categories, the anomaly detection-pretrained ECG diagnostic model has demonstrated a significant improvement in overall accuracy. Notably, our approach yielded a 94.7% AUROC, 92.2% sensitivity, and 92.5\% specificity for rare ECG types, significantly outperforming traditional methods and narrowing the performance gap with common ECG types. The integration of anomaly detection pretraining into ECG analysis represents a substantial contribution to the field, addressing the long-standing challenge of long-tail data distributions in clinical diagnostics. Furthermore, prospective validation in real-world clinical settings revealed that our AI-driven approach enhances diagnostic efficiency, precision, and completeness by 32%, 6.7%, and 11.8% respectively, when compared to standard practices. This advancement marks a pivotal step forward in the integration of AI within clinical cardiology, with particularly profound implications for emergency care, where rapid and accurate ECG interpretation is crucial. The contributions of this study not only push the boundaries of current ECG diagnostic capabilities but also lay the groundwork for more reliable and accessible cardiovascular care.
Anomaly Detection in Electrocardiograms: Advancing Clinical Diagnosis Through Self-Supervised Learning
Apr 07, 2024



Abstract:The electrocardiogram (ECG) is an essential tool for diagnosing heart disease, with computer-aided systems improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing healthcare costs. Despite advancements, existing systems often miss rare cardiac anomalies that could be precursors to serious, life-threatening issues or alterations in the cardiac macro/microstructure. We address this gap by focusing on self-supervised anomaly detection (AD), training exclusively on normal ECGs to recognize deviations indicating anomalies. We introduce a novel self-supervised learning framework for ECG AD, utilizing a vast dataset of normal ECGs to autonomously detect and localize cardiac anomalies. It proposes a novel masking and restoration technique alongside a multi-scale cross-attention module, enhancing the model's ability to integrate global and local signal features. The framework emphasizes accurate localization of anomalies within ECG signals, ensuring the method's clinical relevance and reliability. To reduce the impact of individual variability, the approach further incorporates crucial patient-specific information from ECG reports, such as age and gender, thus enabling accurate identification of a broad spectrum of cardiac anomalies, including rare ones. Utilizing an extensive dataset of 478,803 ECG graphic reports from real-world clinical practice, our method has demonstrated exceptional effectiveness in AD across all tested conditions, regardless of their frequency of occurrence, significantly outperforming existing models. It achieved superior performance metrics, including an AUROC of 91.2%, an F1 score of 83.7%, a sensitivity rate of 84.2%, a specificity of 83.0%, and a precision of 75.6% with a fixed recall rate of 90%. It has also demonstrated robust localization capabilities, with an AUROC of 76.5% and a Dice coefficient of 65.3% for anomaly localization.
Multi-scale Cross-restoration Framework for Electrocardiogram Anomaly Detection
Aug 03, 2023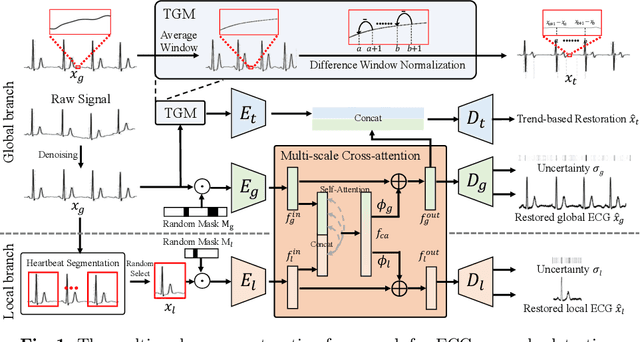
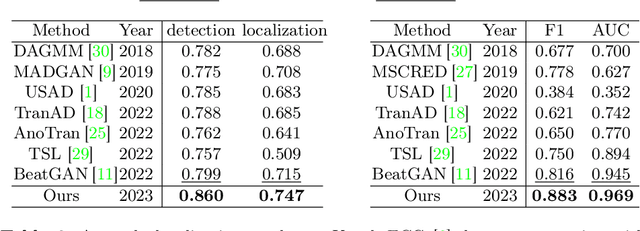
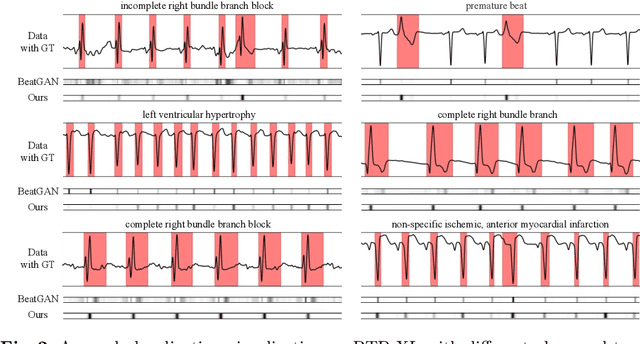
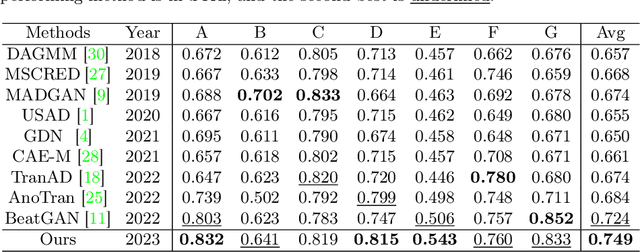
Abstract:Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a widely used diagnostic tool for detecting heart conditions. Rare cardiac diseases may be underdiagnosed using traditional ECG analysis, considering that no training dataset can exhaust all possible cardiac disorders. This paper proposes using anomaly detection to identify any unhealthy status, with normal ECGs solely for training. However, detecting anomalies in ECG can be challenging due to significant inter-individual differences and anomalies present in both global rhythm and local morphology. To address this challenge, this paper introduces a novel multi-scale cross-restoration framework for ECG anomaly detection and localization that considers both local and global ECG characteristics. The proposed framework employs a two-branch autoencoder to facilitate multi-scale feature learning through a masking and restoration process, with one branch focusing on global features from the entire ECG and the other on local features from heartbeat-level details, mimicking the diagnostic process of cardiologists. Anomalies are identified by their high restoration errors. To evaluate the performance on a large number of individuals, this paper introduces a new challenging benchmark with signal point-level ground truths annotated by experienced cardiologists. The proposed method demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on this benchmark and two other well-known ECG datasets. The benchmark dataset and source code are available at: \url{https://github.com/MediaBrain-SJTU/ECGAD}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge