Qiaoben Bao
LOREN: Logic Enhanced Neural Reasoning for Fact Verification
Dec 25, 2020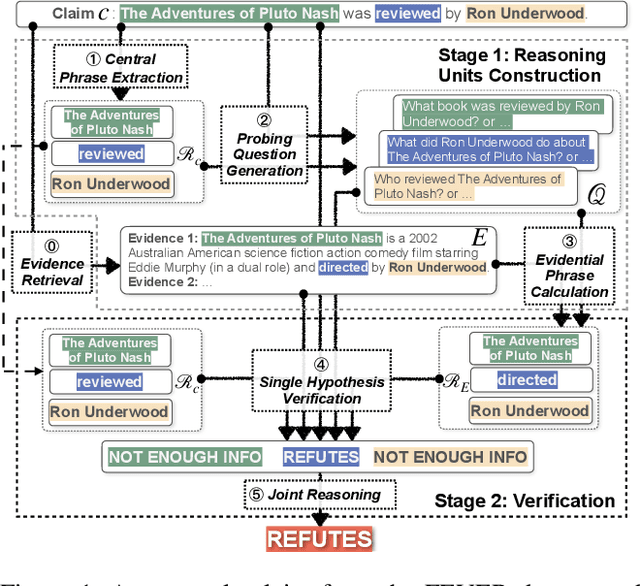
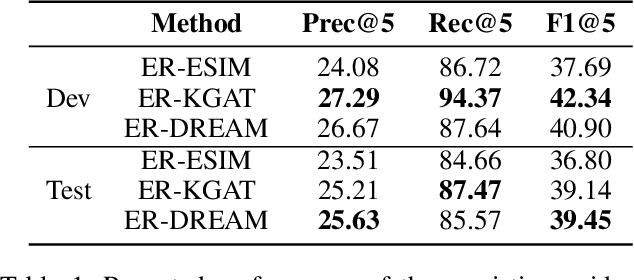
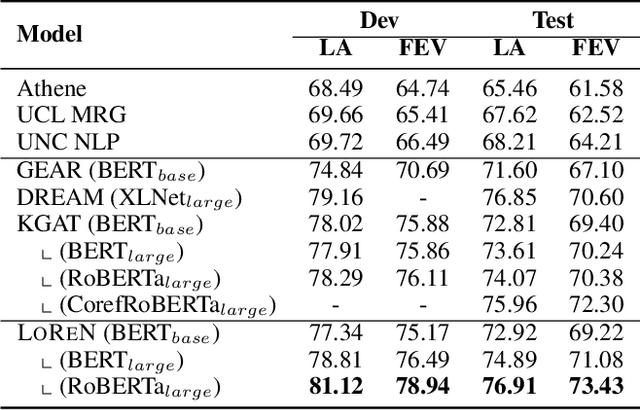

Abstract:Given a natural language statement, how to verify whether it is supported, refuted, or unknown according to a large-scale knowledge source like Wikipedia? Existing neural-network-based methods often regard a sentence as a whole. While we argue that it is beneficial to decompose a statement into multiple verifiable logical points. In this paper, we propose LOREN, a novel approach for fact verification that integrates both Logic guided Reasoning and Neural inference. The key insight of LOREN is that it decomposes a statement into multiple reasoning units around the central phrases. Instead of directly validating a single reasoning unit, LOREN turns it into a question-answering task and calculates the confidence of every single hypothesis using neural networks in the embedding space. They are aggregated to make a final prediction using a neural joint reasoner guided by a set of three-valued logic rules. LOREN enjoys the additional merit of interpretability -- it is easy to explain how it reaches certain results with intermediate results and why it makes mistakes. We evaluate LOREN on FEVER, a public benchmark for fact verification. Experiments show that our proposed LOREN outperforms other previously published methods and achieves 73.43% of the FEVER score.
Complex Relation Extraction: Challenges and Opportunities
Dec 09, 2020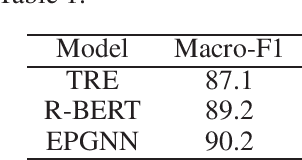

Abstract:Relation extraction aims to identify the target relations of entities in texts. Relation extraction is very important for knowledge base construction and text understanding. Traditional binary relation extraction, including supervised, semi-supervised and distant supervised ones, has been extensively studied and significant results are achieved. In recent years, many complex relation extraction tasks, i.e., the variants of simple binary relation extraction, are proposed to meet the complex applications in practice. However, there is no literature to fully investigate and summarize these complex relation extraction works so far. In this paper, we first report the recent progress in traditional simple binary relation extraction. Then we summarize the existing complex relation extraction tasks and present the definition, recent progress, challenges and opportunities for each task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge