Pranam Chatterjee
Minimal-Action Discrete Schrödinger Bridge Matching for Peptide Sequence Design
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Generative modeling of peptide sequences requires navigating a discrete and highly constrained space in which many intermediate states are chemically implausible or unstable. Existing discrete diffusion and flow-based methods rely on reversing fixed corruption processes or following prescribed probability paths, which can force generation through low-likelihood regions and require countless sampling steps. We introduce Minimal-action discrete Schrödinger Bridge Matching (MadSBM), a rate-based generative framework for peptide design that formulates generation as a controlled continuous-time Markov process on the amino-acid edit graph. To yield probability trajectories that remain near high-likelihood sequence neighborhoods throughout generation, MadSBM 1) defines generation relative to a biologically informed reference process derived from pre-trained protein language model logits and 2) learns a time-dependent control field that biases transition rates to produce low-action transport paths from a masked prior to the data distribution. We finally introduce guidance to the MadSBM sampling procedure towards a specific functional objective, expanding the design space of therapeutic peptides; to our knowledge, this represents the first-ever application of discrete classifier guidance to Schrödinger bridge-based generative models.
Entangled Schrödinger Bridge Matching
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Simulating trajectories of multi-particle systems on complex energy landscapes is a central task in molecular dynamics (MD) and drug discovery, but remains challenging at scale due to computationally expensive and long simulations. Previous approaches leverage techniques such as flow or Schrödinger bridge matching to implicitly learn joint trajectories through data snapshots. However, many systems, including biomolecular systems and heterogeneous cell populations, undergo dynamic interactions that evolve over their trajectory and cannot be captured through static snapshots. To close this gap, we introduce Entangled Schrödinger Bridge Matching (EntangledSBM), a framework that learns the first- and second-order stochastic dynamics of interacting, multi-particle systems where the direction and magnitude of each particle's path depend dynamically on the paths of the other particles. We define the Entangled Schrödinger Bridge (EntangledSB) problem as solving a coupled system of bias forces that entangle particle velocities. We show that our framework accurately simulates heterogeneous cell populations under perturbations and rare transitions in high-dimensional biomolecular systems.
Branched Schrödinger Bridge Matching
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Predicting the intermediate trajectories between an initial and target distribution is a central problem in generative modeling. Existing approaches, such as flow matching and Schr\"odinger Bridge Matching, effectively learn mappings between two distributions by modeling a single stochastic path. However, these methods are inherently limited to unimodal transitions and cannot capture branched or divergent evolution from a common origin to multiple distinct outcomes. To address this, we introduce Branched Schr\"odinger Bridge Matching (BranchSBM), a novel framework that learns branched Schr\"odinger bridges. BranchSBM parameterizes multiple time-dependent velocity fields and growth processes, enabling the representation of population-level divergence into multiple terminal distributions. We show that BranchSBM is not only more expressive but also essential for tasks involving multi-path surface navigation, modeling cell fate bifurcations from homogeneous progenitor states, and simulating diverging cellular responses to perturbations.
Multi-Objective-Guided Discrete Flow Matching for Controllable Biological Sequence Design
May 14, 2025Abstract:Designing biological sequences that satisfy multiple, often conflicting, functional and biophysical criteria remains a central challenge in biomolecule engineering. While discrete flow matching models have recently shown promise for efficient sampling in high-dimensional sequence spaces, existing approaches address only single objectives or require continuous embeddings that can distort discrete distributions. We present Multi-Objective-Guided Discrete Flow Matching (MOG-DFM), a general framework to steer any pretrained discrete flow matching generator toward Pareto-efficient trade-offs across multiple scalar objectives. At each sampling step, MOG-DFM computes a hybrid rank-directional score for candidate transitions and applies an adaptive hypercone filter to enforce consistent multi-objective progression. We also trained two unconditional discrete flow matching models, PepDFM for diverse peptide generation and EnhancerDFM for functional enhancer DNA generation, as base generation models for MOG-DFM. We demonstrate MOG-DFM's effectiveness in generating peptide binders optimized across five properties (hemolysis, non-fouling, solubility, half-life, and binding affinity), and in designing DNA sequences with specific enhancer classes and DNA shapes. In total, MOG-DFM proves to be a powerful tool for multi-property-guided biomolecule sequence design.
Gumbel-Softmax Flow Matching with Straight-Through Guidance for Controllable Biological Sequence Generation
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Flow matching in the continuous simplex has emerged as a promising strategy for DNA sequence design, but struggles to scale to higher simplex dimensions required for peptide and protein generation. We introduce Gumbel-Softmax Flow and Score Matching, a generative framework on the simplex based on a novel Gumbel-Softmax interpolant with a time-dependent temperature. Using this interpolant, we introduce Gumbel-Softmax Flow Matching by deriving a parameterized velocity field that transports from smooth categorical distributions to distributions concentrated at a single vertex of the simplex. We alternatively present Gumbel-Softmax Score Matching which learns to regress the gradient of the probability density. Our framework enables high-quality, diverse generation and scales efficiently to higher-dimensional simplices. To enable training-free guidance, we propose Straight-Through Guided Flows (STGFlow), a classifier-based guidance method that leverages straight-through estimators to steer the unconditional velocity field toward optimal vertices of the simplex. STGFlow enables efficient inference-time guidance using classifiers pre-trained on clean sequences, and can be used with any discrete flow method. Together, these components form a robust framework for controllable de novo sequence generation. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in conditional DNA promoter design, sequence-only protein generation, and target-binding peptide design for rare disease treatment.
Path Planning for Masked Diffusion Model Sampling
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we investigate how the order in which tokens are unmasked during masked diffusion models (MDMs) inference affects generative quality. We derive an expanded evidence lower bound (ELBO) that introduces a planner, responsible for selecting which tokens to unmask at each step. Our analysis suggests that alternative unmasking strategies can improve generative performance. Based on these insights, we propose Path Planning (P2), a sampling framework that leverages pre-trained BERT or the denoiser itself to guide unmasking decisions. P2 generalizes all known MDM sampling strategies and enables significant improvements across diverse domains including language generation (in-context learning, code generation, story infilling, mathematical reasoning, reverse curse correction) and biological sequence generation (protein and RNA sequences).
PepTune: De Novo Generation of Therapeutic Peptides with Multi-Objective-Guided Discrete Diffusion
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Peptide therapeutics, a major class of medicines, have achieved remarkable success across diseases such as diabetes and cancer, with landmark examples such as GLP-1 receptor agonists revolutionizing the treatment of type-2 diabetes and obesity. Despite their success, designing peptides that satisfy multiple conflicting objectives, such as target binding affinity, solubility, and membrane permeability, remains a major challenge. Classical drug development and structure-based design are ineffective for such tasks, as they fail to optimize global functional properties critical for therapeutic efficacy. Existing generative frameworks are largely limited to continuous spaces, unconditioned outputs, or single-objective guidance, making them unsuitable for discrete sequence optimization across multiple properties. To address this, we present PepTune, a multi-objective discrete diffusion model for the simultaneous generation and optimization of therapeutic peptide SMILES. Built on the Masked Discrete Language Model (MDLM) framework, PepTune ensures valid peptide structures with state-dependent masking schedules and penalty-based objectives. To guide the diffusion process, we propose a Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS)-based strategy that balances exploration and exploitation to iteratively refine Pareto-optimal sequences. MCTS integrates classifier-based rewards with search-tree expansion, overcoming gradient estimation challenges and data sparsity inherent to discrete spaces. Using PepTune, we generate diverse, chemically-modified peptides optimized for multiple therapeutic properties, including target binding affinity, membrane permeability, solubility, hemolysis, and non-fouling characteristics on various disease-relevant targets. In total, our results demonstrate that MCTS-guided discrete diffusion is a powerful and modular approach for multi-objective sequence design in discrete state spaces.
Steering Masked Discrete Diffusion Models via Discrete Denoising Posterior Prediction
Oct 10, 2024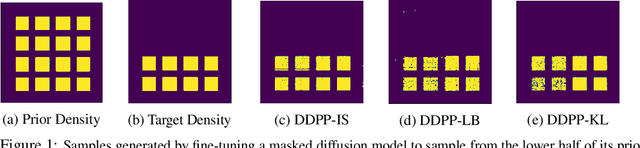
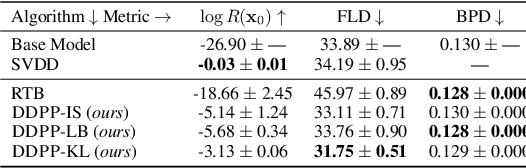
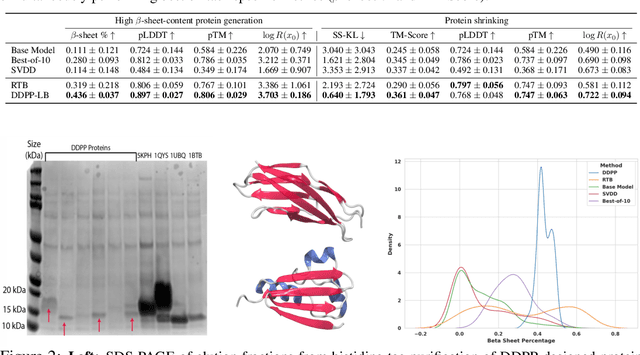
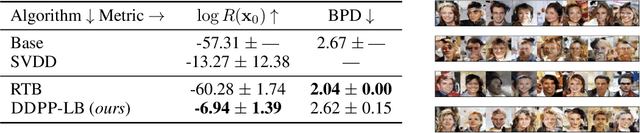
Abstract:Generative modeling of discrete data underlies important applications spanning text-based agents like ChatGPT to the design of the very building blocks of life in protein sequences. However, application domains need to exert control over the generated data by steering the generative process - typically via RLHF - to satisfy a specified property, reward, or affinity metric. In this paper, we study the problem of steering Masked Diffusion Models (MDMs), a recent class of discrete diffusion models that offer a compelling alternative to traditional autoregressive models. We introduce Discrete Denoising Posterior Prediction (DDPP), a novel framework that casts the task of steering pre-trained MDMs as a problem of probabilistic inference by learning to sample from a target Bayesian posterior. Our DDPP framework leads to a family of three novel objectives that are all simulation-free, and thus scalable while applying to general non-differentiable reward functions. Empirically, we instantiate DDPP by steering MDMs to perform class-conditional pixel-level image modeling, RLHF-based alignment of MDMs using text-based rewards, and finetuning protein language models to generate more diverse secondary structures and shorter proteins. We substantiate our designs via wet-lab validation, where we observe transient expression of reward-optimized protein sequences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge