Po-Yu Huang
VisualWebArena: Evaluating Multimodal Agents on Realistic Visual Web Tasks
Jan 24, 2024
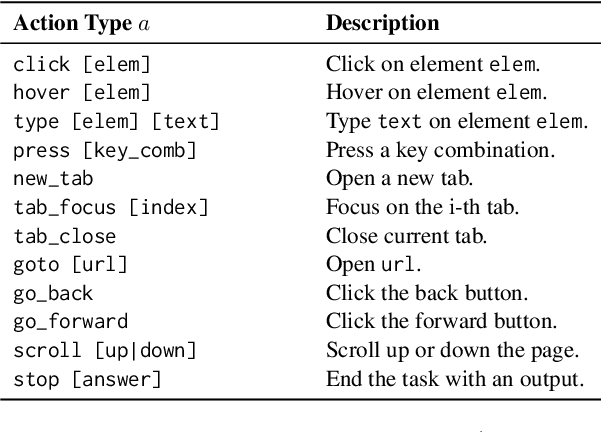


Abstract:Autonomous agents capable of planning, reasoning, and executing actions on the web offer a promising avenue for automating computer tasks. However, the majority of existing benchmarks primarily focus on text-based agents, neglecting many natural tasks that require visual information to effectively solve. Given that most computer interfaces cater to human perception, visual information often augments textual data in ways that text-only models struggle to harness effectively. To bridge this gap, we introduce VisualWebArena, a benchmark designed to assess the performance of multimodal web agents on realistic \textit{visually grounded tasks}. VisualWebArena comprises of a set of diverse and complex web-based tasks that evaluate various capabilities of autonomous multimodal agents. To perform on this benchmark, agents need to accurately process image-text inputs, interpret natural language instructions, and execute actions on websites to accomplish user-defined objectives. We conduct an extensive evaluation of state-of-the-art LLM-based autonomous agents, including several multimodal models. Through extensive quantitative and qualitative analysis, we identify several limitations of text-only LLM agents, and reveal gaps in the capabilities of state-of-the-art multimodal language agents. VisualWebArena provides a framework for evaluating multimodal autonomous language agents, and offers insights towards building stronger autonomous agents for the web. Our code, baseline models, and data is publicly available at https://jykoh.com/vwa.
Efficient Uncertainty Estimation for Semantic Segmentation in Videos
Jul 29, 2018
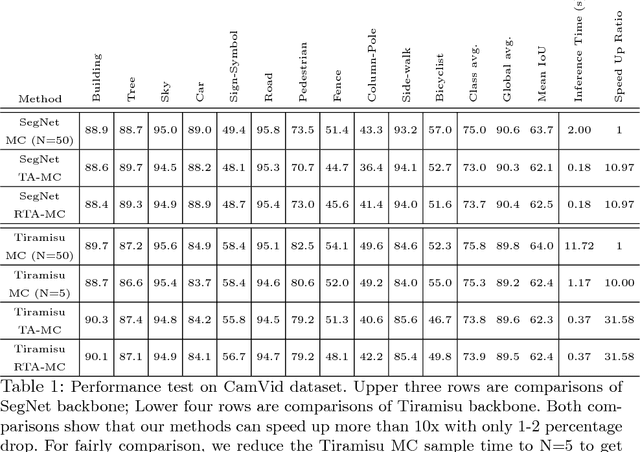
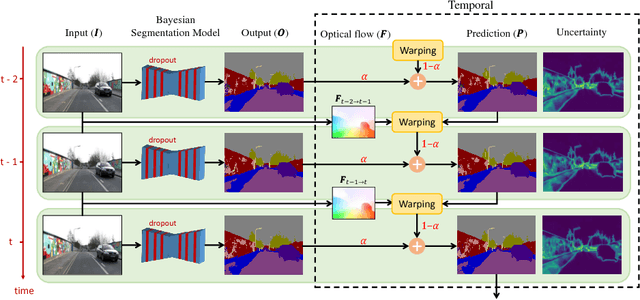

Abstract:Uncertainty estimation in deep learning becomes more important recently. A deep learning model can't be applied in real applications if we don't know whether the model is certain about the decision or not. Some literature proposes the Bayesian neural network which can estimate the uncertainty by Monte Carlo Dropout (MC dropout). However, MC dropout needs to forward the model $N$ times which results in $N$ times slower. For real-time applications such as a self-driving car system, which needs to obtain the prediction and the uncertainty as fast as possible, so that MC dropout becomes impractical. In this work, we propose the region-based temporal aggregation (RTA) method which leverages the temporal information in videos to simulate the sampling procedure. Our RTA method with Tiramisu backbone is 10x faster than the MC dropout with Tiramisu backbone ($N=5$). Furthermore, the uncertainty estimation obtained by our RTA method is comparable to MC dropout's uncertainty estimation on pixel-level and frame-level metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge