Peter W. Eklund
PIE-QG: Paraphrased Information Extraction for Unsupervised Question Generation from Small Corpora
Jan 03, 2023



Abstract:Supervised Question Answering systems (QA systems) rely on domain-specific human-labeled data for training. Unsupervised QA systems generate their own question-answer training pairs, typically using secondary knowledge sources to achieve this outcome. Our approach (called PIE-QG) uses Open Information Extraction (OpenIE) to generate synthetic training questions from paraphrased passages and uses the question-answer pairs as training data for a language model for a state-of-the-art QA system based on BERT. Triples in the form of <subject, predicate, object> are extracted from each passage, and questions are formed with subjects (or objects) and predicates while objects (or subjects) are considered as answers. Experimenting on five extractive QA datasets demonstrates that our technique achieves on-par performance with existing state-of-the-art QA systems with the benefit of being trained on an order of magnitude fewer documents and without any recourse to external reference data sources.
An Efficient and Reliable Asynchronous Federated Learning Scheme for Smart Public Transportation
Aug 30, 2022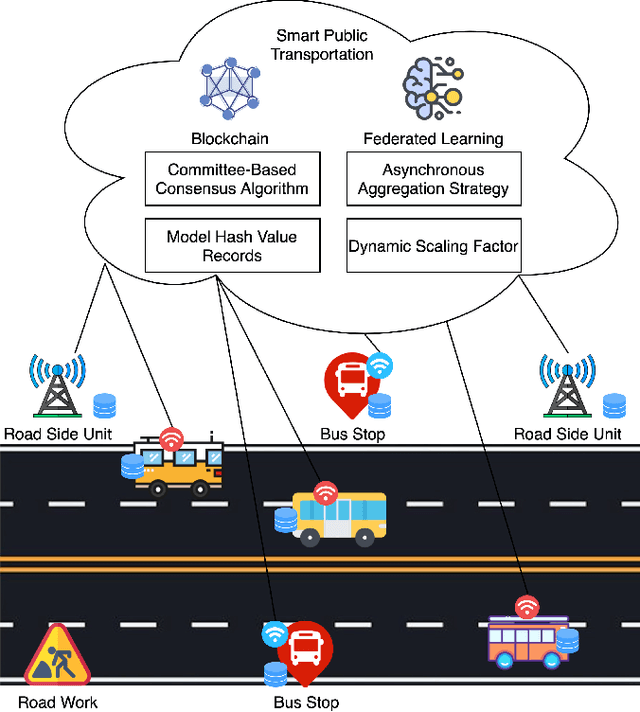
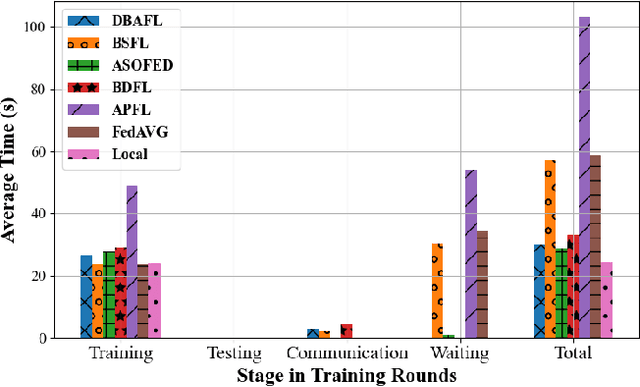
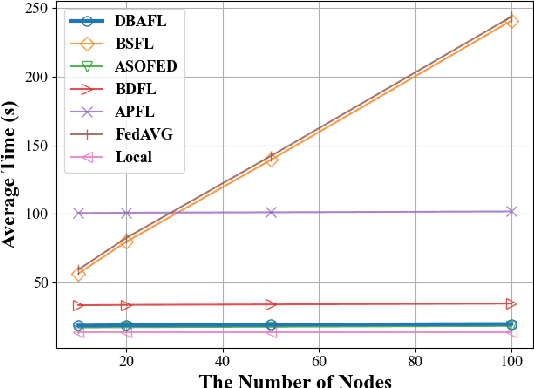
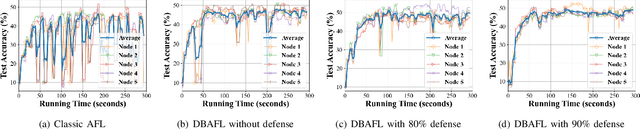
Abstract:Since the traffic conditions change over time, machine learning models that predict traffic flows must be updated continuously and efficiently in smart public transportation. Federated learning (FL) is a distributed machine learning scheme that allows buses to receive model updates without waiting for model training on the cloud. However, FL is vulnerable to poisoning or DDoS attacks since buses travel in public. Some work introduces blockchain to improve reliability, but the additional latency from the consensus process reduces the efficiency of FL. Asynchronous Federated Learning (AFL) is a scheme that reduces the latency of aggregation to improve efficiency, but the learning performance is unstable due to unreasonably weighted local models. To address the above challenges, this paper offers a blockchain-based asynchronous federated learning scheme with a dynamic scaling factor (DBAFL). Specifically, the novel committee-based consensus algorithm for blockchain improves reliability at the lowest possible cost of time. Meanwhile, the devised dynamic scaling factor allows AFL to assign reasonable weights to stale local models. Extensive experiments conducted on heterogeneous devices validate outperformed learning performance, efficiency, and reliability of DBAFL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge