Perfecto Herrera
Personalized musically induced emotions of not-so-popular Colombian music
Dec 09, 2021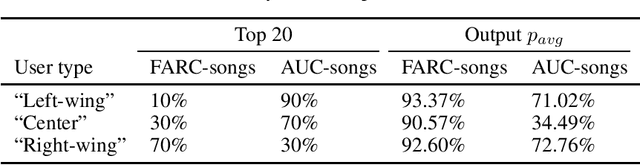
Abstract:This work presents an initial proof of concept of how Music Emotion Recognition (MER) systems could be intentionally biased with respect to annotations of musically induced emotions in a political context. In specific, we analyze traditional Colombian music containing politically charged lyrics of two types: (1) vallenatos and social songs from the "left-wing" guerrilla Fuerzas Armadas Revolucionarias de Colombia (FARC) and (2) corridos from the "right-wing" paramilitaries Autodefensas Unidas de Colombia (AUC). We train personalized machine learning models to predict induced emotions for three users with diverse political views - we aim at identifying the songs that may induce negative emotions for a particular user, such as anger and fear. To this extent, a user's emotion judgements could be interpreted as problematizing data - subjective emotional judgments could in turn be used to influence the user in a human-centered machine learning environment. In short, highly desired "emotion regulation" applications could potentially deviate to "emotion manipulation" - the recent discredit of emotion recognition technologies might transcend ethical issues of diversity and inclusion.
The emotions that we perceive in music: the influence of language and lyrics comprehension on agreement
Oct 25, 2019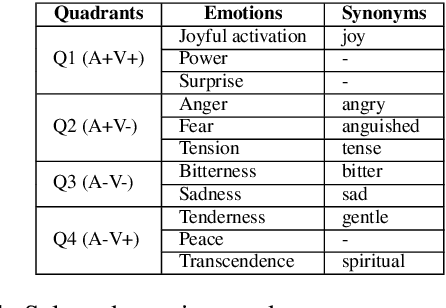
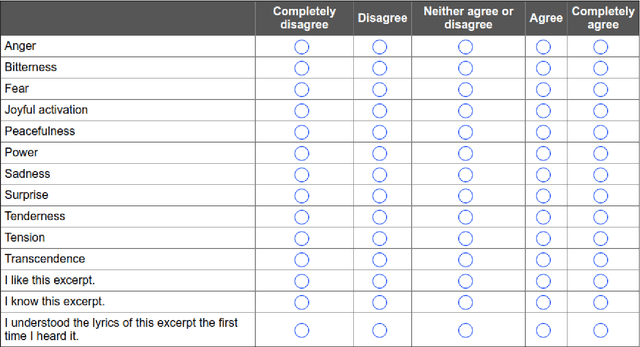
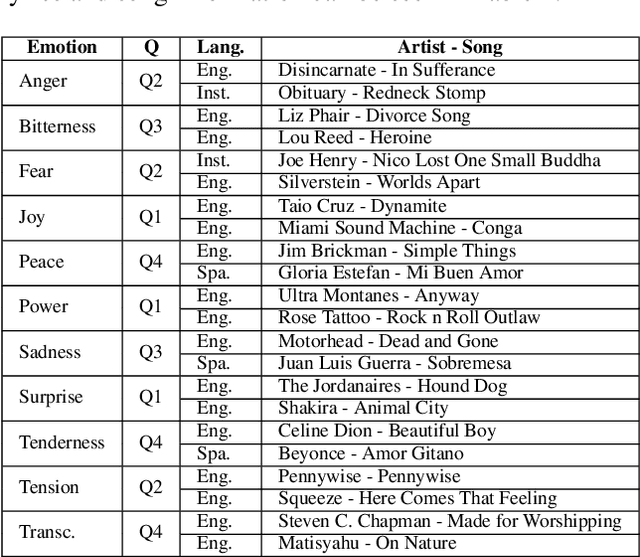
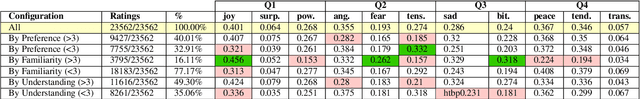
Abstract:In the present study, we address the relationship between the emotions perceived in pop and rock music (mainly in Euro-American styles with English lyrics) and the language spoken by the listener. Our goal is to understand the influence of lyrics comprehension on the perception of emotions and use this information to improve Music Emotion Recognition (MER) models. Two main research questions are addressed: 1. Are there differences and similarities between the emotions perceived in pop/rock music by listeners raised with different mother tongues? 2. Do personal characteristics have an influence on the perceived emotions for listeners of a given language? Personal characteristics include the listeners' general demographics, familiarity and preference for the fragments, and music sophistication. Our hypothesis is that inter-rater agreement (as defined by Krippendorff's alpha coefficient) from subjects is directly influenced by the comprehension of lyrics.
Assessing the impact of machine intelligence on human behaviour: an interdisciplinary endeavour
Jun 07, 2018
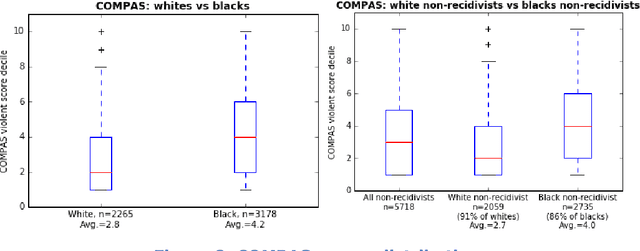
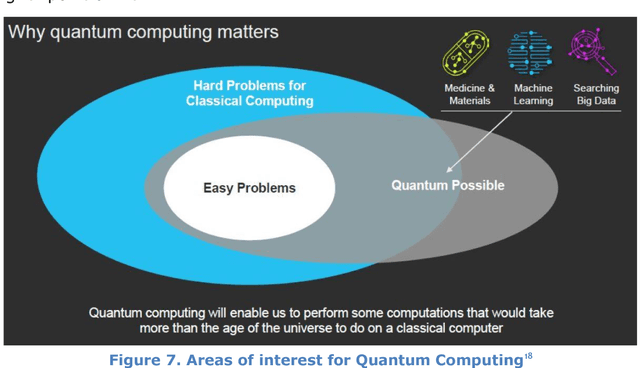
Abstract:This document contains the outcome of the first Human behaviour and machine intelligence (HUMAINT) workshop that took place 5-6 March 2018 in Barcelona, Spain. The workshop was organized in the context of a new research programme at the Centre for Advanced Studies, Joint Research Centre of the European Commission, which focuses on studying the potential impact of artificial intelligence on human behaviour. The workshop gathered an interdisciplinary group of experts to establish the state of the art research in the field and a list of future research challenges to be addressed on the topic of human and machine intelligence, algorithm's potential impact on human cognitive capabilities and decision making, and evaluation and regulation needs. The document is made of short position statements and identification of challenges provided by each expert, and incorporates the result of the discussions carried out during the workshop. In the conclusion section, we provide a list of emerging research topics and strategies to be addressed in the near future.
Characterization and exploitation of community structure in cover song networks
Sep 12, 2011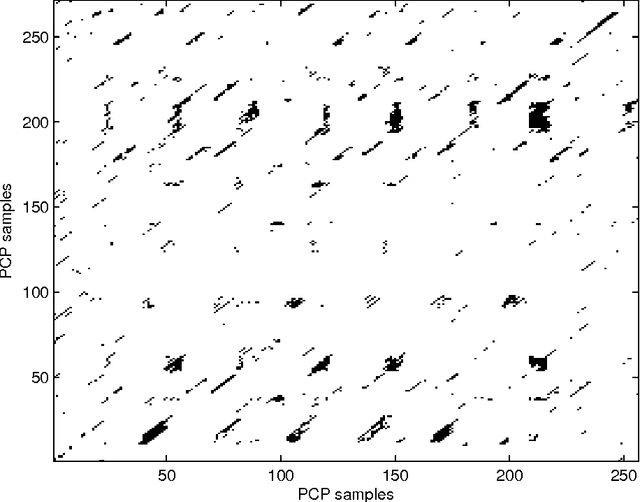

Abstract:The use of community detection algorithms is explored within the framework of cover song identification, i.e. the automatic detection of different audio renditions of the same underlying musical piece. Until now, this task has been posed as a typical query-by-example task, where one submits a query song and the system retrieves a list of possible matches ranked by their similarity to the query. In this work, we propose a new approach which uses song communities to provide more relevant answers to a given query. Starting from the output of a state-of-the-art system, songs are embedded in a complex weighted network whose links represent similarity (related musical content). Communities inside the network are then recognized as groups of covers and this information is used to enhance the results of the system. In particular, we show that this approach increases both the coherence and the accuracy of the system. Furthermore, we provide insight into the internal organization of individual cover song communities, showing that there is a tendency for the original song to be central within the community. We postulate that the methods and results presented here could be relevant to other query-by-example tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge