Pengjie Liu
MUSE: Integrating Multi-Knowledge for Knowledge Graph Completion
Sep 26, 2024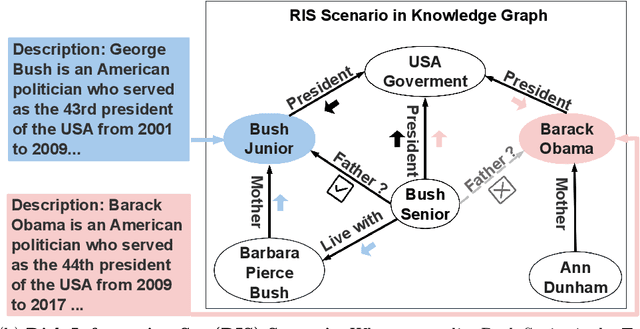
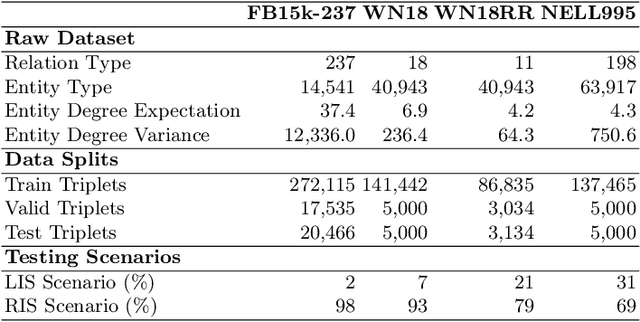
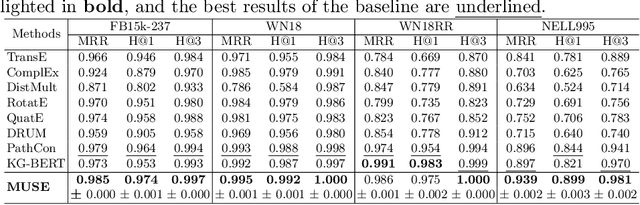
Abstract:Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC) aims to predict the missing [relation] part of (head entity)--[relation]->(tail entity) triplet. Most existing KGC methods focus on single features (e.g., relation types) or sub-graph aggregation. However, they do not fully explore the Knowledge Graph (KG) features and neglect the guidance of external semantic knowledge. To address these shortcomings, we propose a knowledge-aware reasoning model (MUSE), which designs a novel multi-knowledge representation learning mechanism for missing relation prediction. Our model develops a tailored embedding space through three parallel components: 1) Prior Knowledge Learning for enhancing the triplets' semantic representation by fine-tuning BERT; 2) Context Message Passing for enhancing the context messages of KG; 3) Relational Path Aggregation for enhancing the path representation from the head entity to the tail entity. The experimental results show that MUSE significantly outperforms other baselines on four public datasets, achieving over 5.50% H@1 improvement and 4.20% MRR improvement on the NELL995 dataset. The code and datasets will be released via https://github.com/SUSTech-TP/ADMA2024-MUSE.git.
SEMDR: A Semantic-Aware Dual Encoder Model for Legal Judgment Prediction with Legal Clue Tracing
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:Legal Judgment Prediction (LJP) aims to form legal judgments based on the criminal fact description. However, researchers struggle to classify confusing criminal cases, such as robbery and theft, which requires LJP models to distinguish the nuances between similar crimes. Existing methods usually design handcrafted features to pick up necessary semantic legal clues to make more accurate legal judgment predictions. In this paper, we propose a Semantic-Aware Dual Encoder Model (SEMDR), which designs a novel legal clue tracing mechanism to conduct fine-grained semantic reasoning between criminal facts and instruments. Our legal clue tracing mechanism is built from three reasoning levels: 1) Lexicon-Tracing, which aims to extract criminal facts from criminal descriptions; 2) Sentence Representation Learning, which contrastively trains language models to better represent confusing criminal facts; 3) Multi-Fact Reasoning, which builds a reasons graph to propagate semantic clues among fact nodes to capture the subtle difference among criminal facts. Our legal clue tracing mechanism helps SEMDR achieve state-of-the-art on the CAIL2018 dataset and shows its advance in few-shot scenarios. Our experiments show that SEMDR has a strong ability to learn more uniform and distinguished representations for criminal facts, which helps to make more accurate predictions on confusing criminal cases and reduces the model uncertainty during making judgments. All codes will be released via GitHub.
MUSE: Multi-Knowledge Passing on the Edges, Boosting Knowledge Graph Completion
Aug 09, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC) aims to predict the missing information in the (head entity)-[relation]-(tail entity) triplet. Deep Neural Networks have achieved significant progress in the relation prediction task. However, most existing KGC methods focus on single features (e.g., entity IDs) and sub-graph aggregation, which cannot fully explore all the features in the Knowledge Graph (KG), and neglect the external semantic knowledge injection. To address these problems, we propose MUSE, a knowledge-aware reasoning model to learn a tailored embedding space in three dimensions for missing relation prediction through a multi-knowledge representation learning mechanism. Our MUSE consists of three parallel components: 1) Prior Knowledge Learning for enhancing the triplets' semantic representation by fine-tuning BERT; 2) Context Message Passing for enhancing the context messages of KG; 3) Relational Path Aggregation for enhancing the path representation from the head entity to the tail entity. Our experimental results show that MUSE significantly outperforms other baselines on four public datasets, such as over 5.50% improvement in H@1 and 4.20% improvement in MRR on the NELL995 dataset. The code and all datasets will be released via https://github.com/NxxTGT/MUSE.
LegalDuet: Learning Effective Representations for Legal Judgment Prediction through a Dual-View Legal Clue Reasoning
Jan 27, 2024



Abstract:Most existing Legal Judgment Prediction (LJP) models focus on discovering the legal triggers in the criminal fact description. However, in real-world scenarios, a professional judge not only needs to assimilate the law case experience that thrives on past sentenced legal judgments but also depends on the professional legal grounded reasoning that learned from professional legal knowledge. In this paper, we propose a LegalDuet model, which pretrains language models to learn a tailored embedding space for making legal judgments. It proposes a dual-view legal clue reasoning mechanism, which derives from two reasoning chains of judges: 1) Law Case Reasoning, which makes legal judgments according to the judgment experiences learned from analogy/confusing legal cases; 2) Legal Ground Reasoning, which lies in matching the legal clues between criminal cases and legal decisions. Our experiments show that LegalDuet achieves state-of-the-art performance on the CAIL2018 dataset and outperforms baselines with about 4% improvements on average. Our dual-view reasoning based pretraining can capture critical legal clues to learn a tailored embedding space to distinguish criminal cases. It reduces LegalDuet's uncertainty during prediction and brings pretraining advances to the confusing/low frequent charges. All codes are available at https://github.com/NEUIR/LegalDuet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge