Penghang Liu
LLM-driven Imitation of Subrational Behavior : Illusion or Reality?
Feb 13, 2024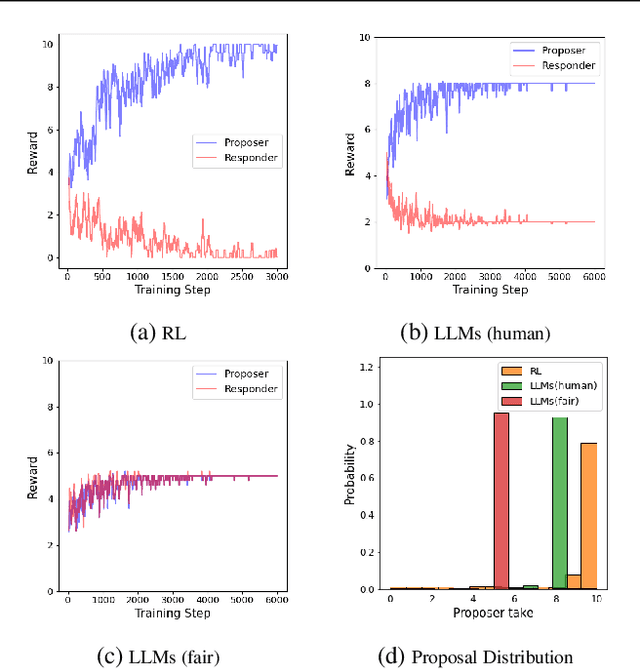
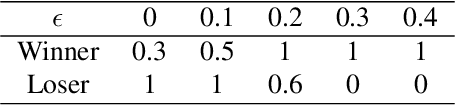
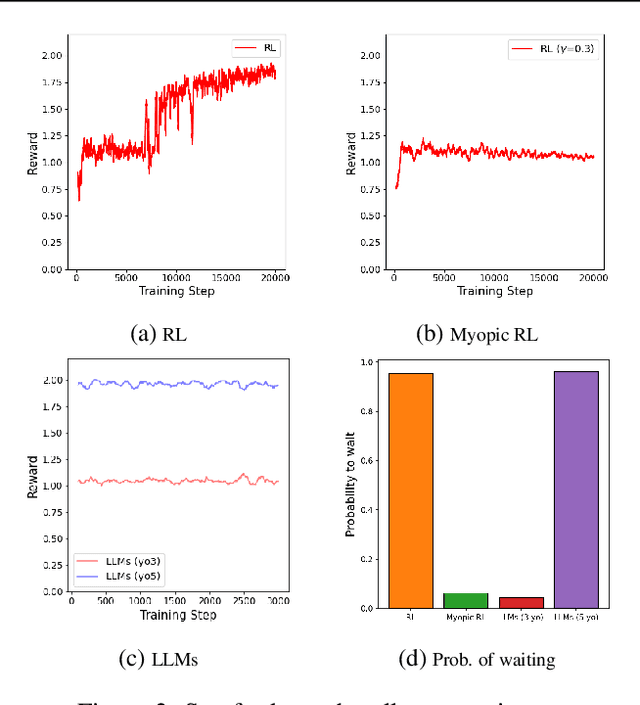

Abstract:Modeling subrational agents, such as humans or economic households, is inherently challenging due to the difficulty in calibrating reinforcement learning models or collecting data that involves human subjects. Existing work highlights the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to address complex reasoning tasks and mimic human communication, while simulation using LLMs as agents shows emergent social behaviors, potentially improving our comprehension of human conduct. In this paper, we propose to investigate the use of LLMs to generate synthetic human demonstrations, which are then used to learn subrational agent policies though Imitation Learning. We make an assumption that LLMs can be used as implicit computational models of humans, and propose a framework to use synthetic demonstrations derived from LLMs to model subrational behaviors that are characteristic of humans (e.g., myopic behavior or preference for risk aversion). We experimentally evaluate the ability of our framework to model sub-rationality through four simple scenarios, including the well-researched ultimatum game and marshmallow experiment. To gain confidence in our framework, we are able to replicate well-established findings from prior human studies associated with the above scenarios. We conclude by discussing the potential benefits, challenges and limitations of our framework.
Using Motif Transitions for Temporal Graph Generation
Jun 19, 2023Abstract:Graph generative models are highly important for sharing surrogate data and benchmarking purposes. Real-world complex systems often exhibit dynamic nature, where the interactions among nodes change over time in the form of a temporal network. Most temporal network generation models extend the static graph generation models by incorporating temporality in the generation process. More recently, temporal motifs are used to generate temporal networks with better success. However, existing models are often restricted to a small set of predefined motif patterns due to the high computational cost of counting temporal motifs. In this work, we develop a practical temporal graph generator, Motif Transition Model (MTM), to generate synthetic temporal networks with realistic global and local features. Our key idea is modeling the arrival of new events as temporal motif transition processes. We first calculate the transition properties from the input graph and then simulate the motif transition processes based on the transition probabilities and transition rates. We demonstrate that our model consistently outperforms the baselines with respect to preserving various global and local temporal graph statistics and runtime performance.
Temporal Motifs for Financial Networks: A Study on Mercari, JPMC, and Venmo Platforms
Jan 18, 2023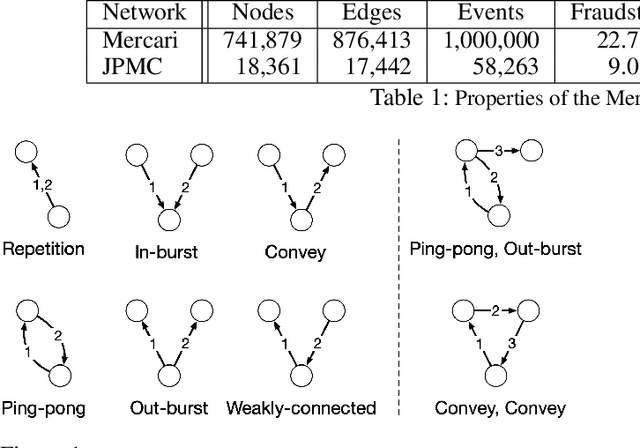

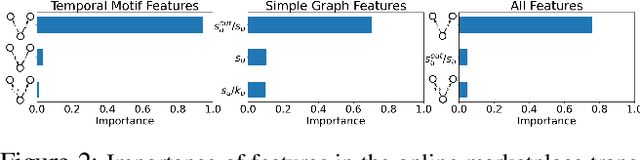
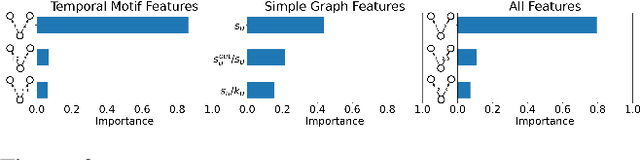
Abstract:Understanding the dynamics of financial transactions among people is critically important for various applications such as fraud detection. One important aspect of financial transaction networks is temporality. The order and repetition of transactions can offer new insights when considered within the graph structure. Temporal motifs, defined as a set of nodes that interact with each other in a short time period, are a promising tool in this context. In this work, we study three unique temporal financial networks: transactions in Mercari, an online marketplace, payments in a synthetic network generated by J.P. Morgan Chase, and payments and friendships among Venmo users. We consider the fraud detection problem on the Mercari and J.P. Morgan Chase networks, for which the ground truth is available. We show that temporal motifs offer superior performance than a previous method that considers simple graph features. For the Venmo network, we investigate the interplay between financial and social relations on three tasks: friendship prediction, vendor identification, and analysis of temporal cycles. For friendship prediction, temporal motifs yield better results than general heuristics, such as Jaccard and Adamic-Adar measures. We are also able to identify vendors with high accuracy and observe interesting patterns in rare motifs, like temporal cycles. We believe that the analysis, datasets, and lessons from this work will be beneficial for future research on financial transaction networks.
Biased or Limited: Modeling Sub-Rational Human Investors in Financial Markets
Oct 16, 2022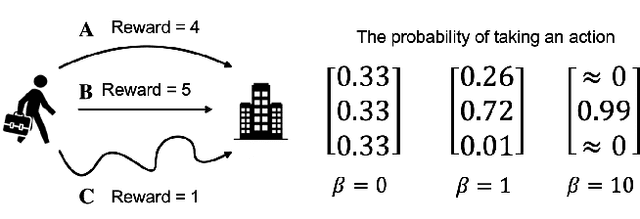
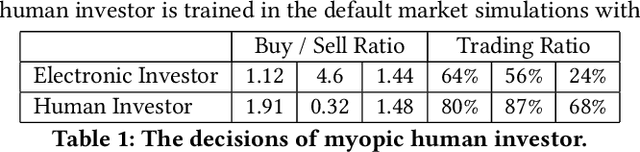
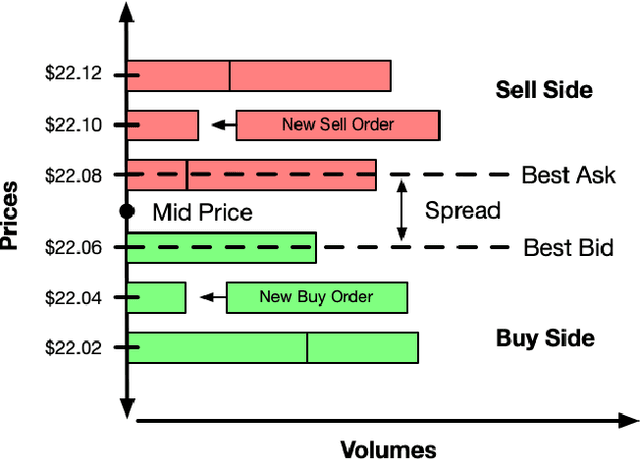
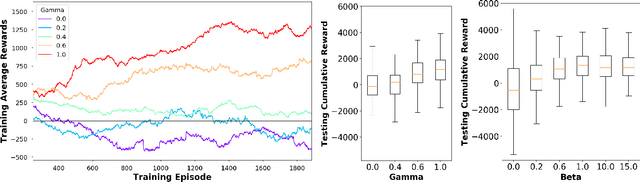
Abstract:Multi-agent market simulation is an effective tool to investigate the impact of various trading strategies in financial markets. One way of designing a trading agent in simulated markets is through reinforcement learning where the agent is trained to optimize its cumulative rewards (e.g., maximizing profits, minimizing risk, improving equitability). While the agent learns a rational policy that optimizes the reward function, in reality, human investors are sub-rational with their decisions often differing from the optimal. In this work, we model human sub-rationality as resulting from two possible causes: psychological bias and computational limitation. We first examine the relationship between investor profits and their degree of sub-rationality, and create hand-crafted market scenarios to intuitively explain the sub-rational human behaviors. Through experiments, we show that our models successfully capture human sub-rationality as observed in the behavioral finance literature. We also examine the impact of sub-rational human investors on market observables such as traded volumes, spread and volatility. We believe our work will benefit research in behavioral finance and provide a better understanding of human trading behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge