Peipei Zhao
Exploration of Class Center for Fine-Grained Visual Classification
Jul 05, 2024Abstract:Different from large-scale classification tasks, fine-grained visual classification is a challenging task due to two critical problems: 1) evident intra-class variances and subtle inter-class differences, and 2) overfitting owing to fewer training samples in datasets. Most existing methods extract key features to reduce intra-class variances, but pay no attention to subtle inter-class differences in fine-grained visual classification. To address this issue, we propose a loss function named exploration of class center, which consists of a multiple class-center constraint and a class-center label generation. This loss function fully utilizes the information of the class center from the perspective of features and labels. From the feature perspective, the multiple class-center constraint pulls samples closer to the target class center, and pushes samples away from the most similar nontarget class center. Thus, the constraint reduces intra-class variances and enlarges inter-class differences. From the label perspective, the class-center label generation utilizes classcenter distributions to generate soft labels to alleviate overfitting. Our method can be easily integrated with existing fine-grained visual classification approaches as a loss function, to further boost excellent performance with only slight training costs. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate consistent improvements achieved by our method on four widely-used fine-grained visual classification datasets. In particular, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the FGVC-Aircraft and CUB-200-2011 datasets.
Self-distillation with Batch Knowledge Ensembling Improves ImageNet Classification
Apr 27, 2021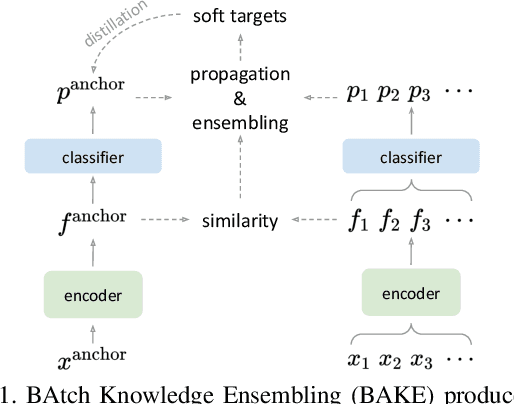
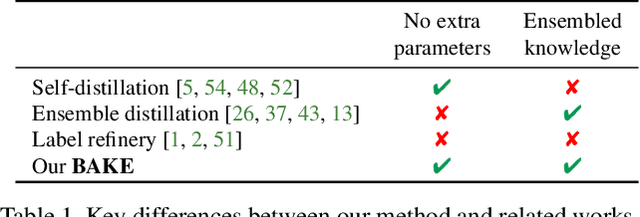
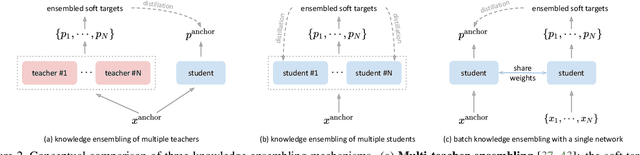
Abstract:The recent studies of knowledge distillation have discovered that ensembling the "dark knowledge" from multiple teachers or students contributes to creating better soft targets for training, but at the cost of significantly more computations and/or parameters. In this work, we present BAtch Knowledge Ensembling (BAKE) to produce refined soft targets for anchor images by propagating and ensembling the knowledge of the other samples in the same mini-batch. Specifically, for each sample of interest, the propagation of knowledge is weighted in accordance with the inter-sample affinities, which are estimated on-the-fly with the current network. The propagated knowledge can then be ensembled to form a better soft target for distillation. In this way, our BAKE framework achieves online knowledge ensembling across multiple samples with only a single network. It requires minimal computational and memory overhead compared to existing knowledge ensembling methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the lightweight yet effective BAKE consistently boosts the classification performance of various architectures on multiple datasets, e.g., a significant +1.2% gain of ResNet-50 on ImageNet with only +3.7% computational overhead and zero additional parameters. BAKE does not only improve the vanilla baselines, but also surpasses the single-network state-of-the-arts on all the benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge