Pavan Seshadri
SCOPE: Language Models as One-Time Teacher for Hierarchical Planning in Text Environments
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Long-term planning in complex, text-based environments presents significant challenges due to open-ended action spaces, ambiguous observations, and sparse feedback. Recent research suggests that large language models (LLMs) encode rich semantic knowledge about the world, which can be valuable for guiding agents in high-level reasoning and planning across both embodied and purely textual settings. However, existing approaches often depend heavily on querying LLMs during training and inference, making them computationally expensive and difficult to deploy efficiently. In addition, these methods typically employ a pretrained, unaltered LLM whose parameters remain fixed throughout training, providing no opportunity for adaptation to the target task. To address these limitations, we introduce SCOPE (Subgoal-COnditioned Pretraining for Efficient planning), a one-shot hierarchical planner that leverages LLM-generated subgoals only at initialization to pretrain a lightweight student model. Unlike prior approaches that distill LLM knowledge by repeatedly prompting the model to adaptively generate subgoals during training, our method derives subgoals directly from example trajectories. This design removes the need for repeated LLM queries, significantly improving efficiency, though at the cost of reduced explainability and potentially suboptimal subgoals. Despite their suboptimality, our results on the TextCraft environment show that LLM-generated subgoals can still serve as a strong starting point for hierarchical goal decomposition in text-based planning tasks. Compared to the LLM-based hierarchical agent ADaPT (Prasad et al., 2024), which achieves a 0.52 success rate, our method reaches 0.56 and reduces inference time from 164.4 seconds to just 3.0 seconds.
Uncertainty Estimation in the Real World: A Study on Music Emotion Recognition
Jan 20, 2025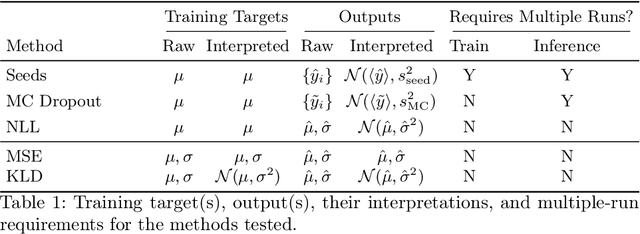
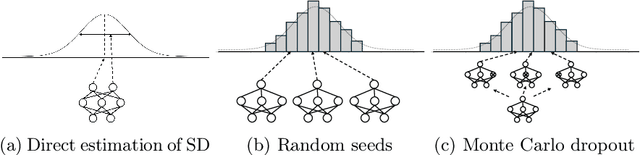
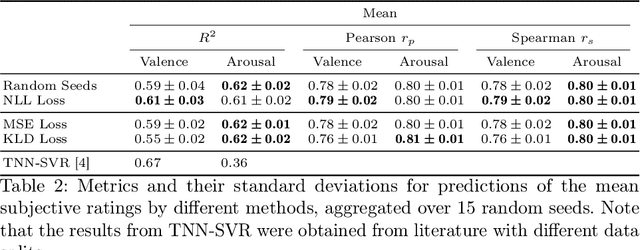
Abstract:Any data annotation for subjective tasks shows potential variations between individuals. This is particularly true for annotations of emotional responses to musical stimuli. While older approaches to music emotion recognition systems frequently addressed this uncertainty problem through probabilistic modeling, modern systems based on neural networks tend to ignore the variability and focus only on predicting central tendencies of human subjective responses. In this work, we explore several methods for estimating not only the central tendencies of the subjective responses to a musical stimulus, but also for estimating the uncertainty associated with these responses. In particular, we investigate probabilistic loss functions and inference-time random sampling. Experimental results indicate that while the modeling of the central tendencies is achievable, modeling of the uncertainty in subjective responses proves significantly more challenging with currently available approaches even when empirical estimates of variations in the responses are available.
Understanding Pedestrian Movement Using Urban Sensing Technologies: The Promise of Audio-based Sensors
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:While various sensors have been deployed to monitor vehicular flows, sensing pedestrian movement is still nascent. Yet walking is a significant mode of travel in many cities, especially those in Europe, Africa, and Asia. Understanding pedestrian volumes and flows is essential for designing safer and more attractive pedestrian infrastructure and for controlling periodic overcrowding. This study discusses a new approach to scale up urban sensing of people with the help of novel audio-based technology. It assesses the benefits and limitations of microphone-based sensors as compared to other forms of pedestrian sensing. A large-scale dataset called ASPED is presented, which includes high-quality audio recordings along with video recordings used for labeling the pedestrian count data. The baseline analyses highlight the promise of using audio sensors for pedestrian tracking, although algorithmic and technological improvements to make the sensors practically usable continue. This study also demonstrates how the data can be leveraged to predict pedestrian trajectories. Finally, it discusses the use cases and scenarios where audio-based pedestrian sensing can support better urban and transportation planning.
Leveraging Negative Signals with Self-Attention for Sequential Music Recommendation
Sep 20, 2023
Abstract:Music streaming services heavily rely on their recommendation engines to continuously provide content to their consumers. Sequential recommendation consequently has seen considerable attention in current literature, where state of the art approaches focus on self-attentive models leveraging contextual information such as long and short-term user history and item features; however, most of these studies focus on long-form content domains (retail, movie, etc.) rather than short-form, such as music. Additionally, many do not explore incorporating negative session-level feedback during training. In this study, we investigate the use of transformer-based self-attentive architectures to learn implicit session-level information for sequential music recommendation. We additionally propose a contrastive learning task to incorporate negative feedback (e.g skipped tracks) to promote positive hits and penalize negative hits. This task is formulated as a simple loss term that can be incorporated into a variety of deep learning architectures for sequential recommendation. Our experiments show that this results in consistent performance gains over the baseline architectures ignoring negative user feedback.
ASPED: An Audio Dataset for Detecting Pedestrians
Sep 12, 2023



Abstract:We introduce the new audio analysis task of pedestrian detection and present a new large-scale dataset for this task. While the preliminary results prove the viability of using audio approaches for pedestrian detection, they also show that this challenging task cannot be easily solved with standard approaches.
AVASpeech-SMAD: A Strongly Labelled Speech and Music Activity Detection Dataset with Label Co-Occurrence
Nov 02, 2021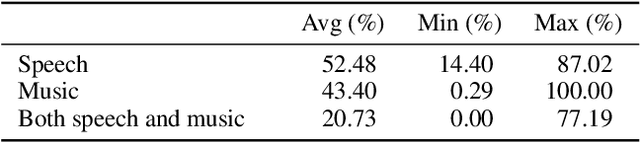
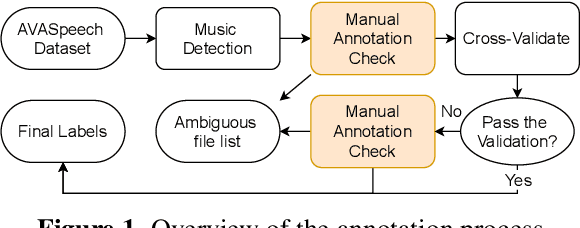

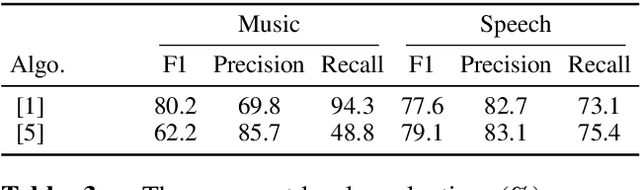
Abstract:We propose a dataset, AVASpeech-SMAD, to assist speech and music activity detection research. With frame-level music labels, the proposed dataset extends the existing AVASpeech dataset, which originally consists of 45 hours of audio and speech activity labels. To the best of our knowledge, the proposed AVASpeech-SMAD is the first open-source dataset that features strong polyphonic labels for both music and speech. The dataset was manually annotated and verified via an iterative cross-checking process. A simple automatic examination was also implemented to further improve the quality of the labels. Evaluation results from two state-of-the-art SMAD systems are also provided as a benchmark for future reference.
Improving Music Performance Assessment with Contrastive Learning
Aug 03, 2021



Abstract:Several automatic approaches for objective music performance assessment (MPA) have been proposed in the past, however, existing systems are not yet capable of reliably predicting ratings with the same accuracy as professional judges. This study investigates contrastive learning as a potential method to improve existing MPA systems. Contrastive learning is a widely used technique in representation learning to learn a structured latent space capable of separately clustering multiple classes. It has been shown to produce state of the art results for image-based classification problems. We introduce a weighted contrastive loss suitable for regression tasks applied to a convolutional neural network and show that contrastive loss results in performance gains in regression tasks for MPA. Our results show that contrastive-based methods are able to match and exceed SoTA performance for MPA regression tasks by creating better class clusters within the latent space of the neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge