Pavan Holur
Beyond Fact Retrieval: Episodic Memory for RAG with Generative Semantic Workspaces
Nov 10, 2025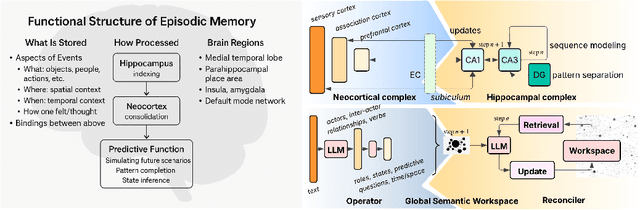
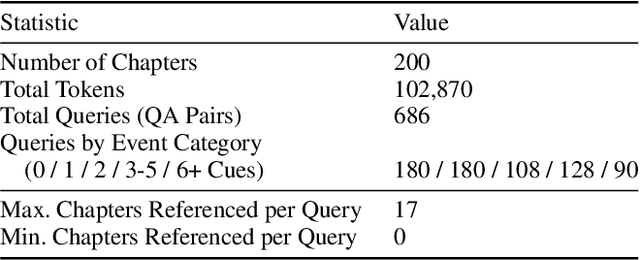
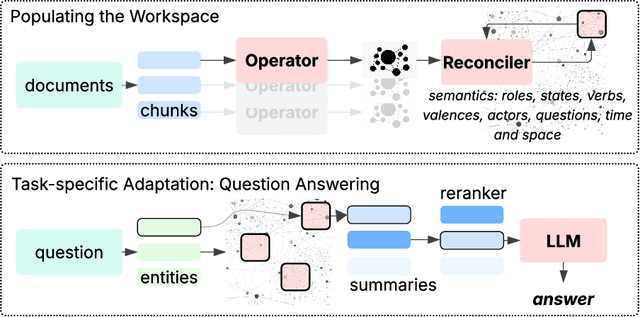
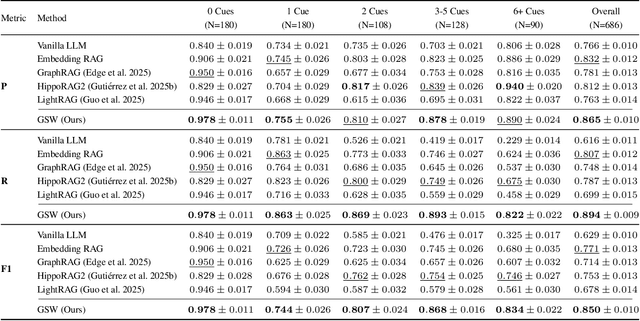
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) face fundamental challenges in long-context reasoning: many documents exceed their finite context windows, while performance on texts that do fit degrades with sequence length, necessitating their augmentation with external memory frameworks. Current solutions, which have evolved from retrieval using semantic embeddings to more sophisticated structured knowledge graphs representations for improved sense-making and associativity, are tailored for fact-based retrieval and fail to build the space-time-anchored narrative representations required for tracking entities through episodic events. To bridge this gap, we propose the \textbf{Generative Semantic Workspace} (GSW), a neuro-inspired generative memory framework that builds structured, interpretable representations of evolving situations, enabling LLMs to reason over evolving roles, actions, and spatiotemporal contexts. Our framework comprises an \textit{Operator}, which maps incoming observations to intermediate semantic structures, and a \textit{Reconciler}, which integrates these into a persistent workspace that enforces temporal, spatial, and logical coherence. On the Episodic Memory Benchmark (EpBench) \cite{huet_episodic_2025} comprising corpora ranging from 100k to 1M tokens in length, GSW outperforms existing RAG based baselines by up to \textbf{20\%}. Furthermore, GSW is highly efficient, reducing query-time context tokens by \textbf{51\%} compared to the next most token-efficient baseline, reducing inference time costs considerably. More broadly, GSW offers a concrete blueprint for endowing LLMs with human-like episodic memory, paving the way for more capable agents that can reason over long horizons.
Creating an AI Observer: Generative Semantic Workspaces
Jun 07, 2024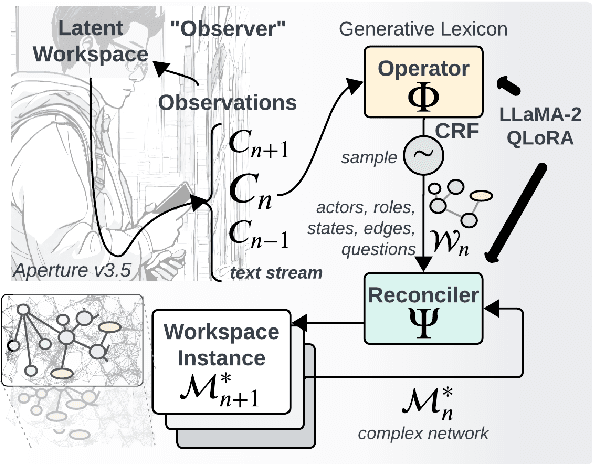
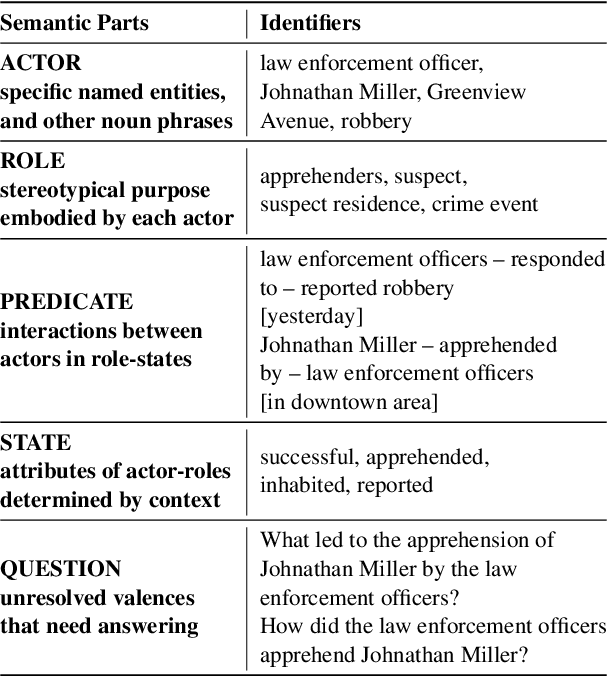
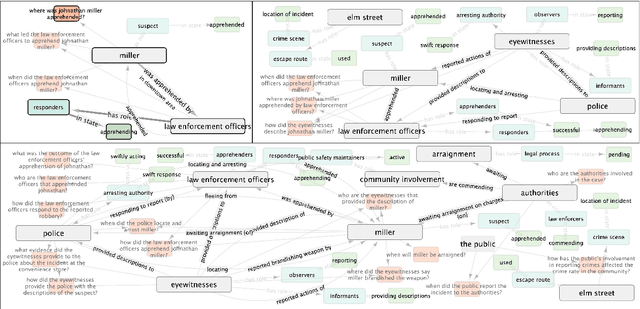
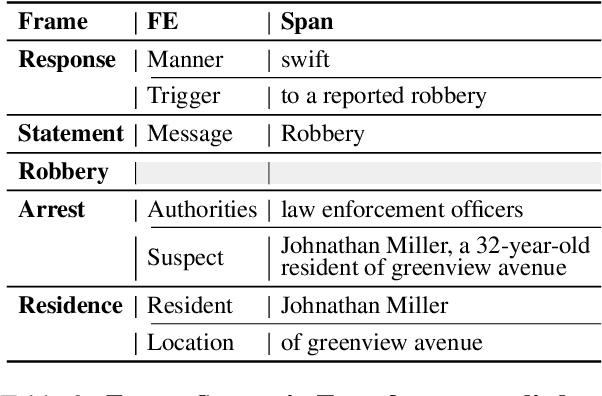
Abstract:An experienced human Observer reading a document -- such as a crime report -- creates a succinct plot-like $\textit{``Working Memory''}$ comprising different actors, their prototypical roles and states at any point, their evolution over time based on their interactions, and even a map of missing Semantic parts anticipating them in the future. $\textit{An equivalent AI Observer currently does not exist}$. We introduce the $\textbf{[G]}$enerative $\textbf{[S]}$emantic $\textbf{[W]}$orkspace (GSW) -- comprising an $\textit{``Operator''}$ and a $\textit{``Reconciler''}$ -- that leverages advancements in LLMs to create a generative-style Semantic framework, as opposed to a traditionally predefined set of lexicon labels. Given a text segment $C_n$ that describes an ongoing situation, the $\textit{Operator}$ instantiates actor-centric Semantic maps (termed ``Workspace instance'' $\mathcal{W}_n$). The $\textit{Reconciler}$ resolves differences between $\mathcal{W}_n$ and a ``Working memory'' $\mathcal{M}_n^*$ to generate the updated $\mathcal{M}_{n+1}^*$. GSW outperforms well-known baselines on several tasks ($\sim 94\%$ vs. FST, GLEN, BertSRL - multi-sentence Semantics extraction, $\sim 15\%$ vs. NLI-BERT, $\sim 35\%$ vs. QA). By mirroring the real Observer, GSW provides the first step towards Spatial Computing assistants capable of understanding individual intentions and predicting future behavior.
Embed-Search-Align: DNA Sequence Alignment using Transformer Models
Sep 20, 2023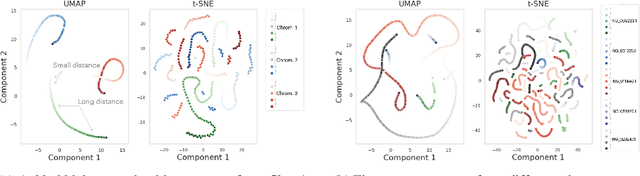
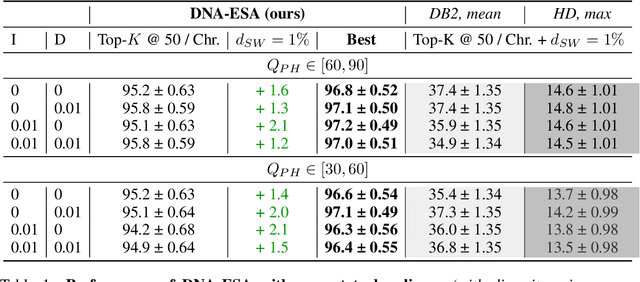
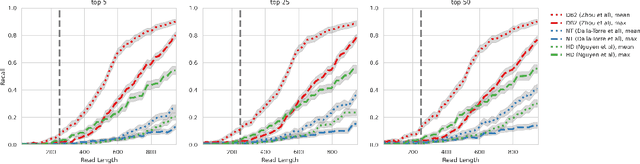
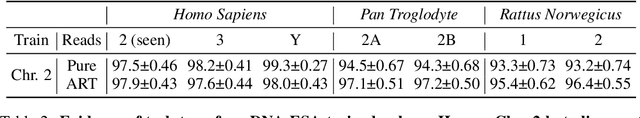
Abstract:DNA sequence alignment involves assigning short DNA reads to the most probable locations on an extensive reference genome. This process is crucial for various genomic analyses, including variant calling, transcriptomics, and epigenomics. Conventional methods, refined over decades, tackle this challenge in two steps: genome indexing followed by efficient search to locate likely positions for given reads. Building on the success of Large Language Models (LLM) in encoding text into embeddings, where the distance metric captures semantic similarity, recent efforts have explored whether the same Transformer architecture can produce numerical representations for DNA sequences. Such models have shown early promise in tasks involving classification of short DNA sequences, such as the detection of coding vs non-coding regions, as well as the identification of enhancer and promoter sequences. Performance at sequence classification tasks does not, however, translate to sequence alignment, where it is necessary to conduct a genome-wide search to successfully align every read. We address this open problem by framing it as an Embed-Search-Align task. In this framework, a novel encoder model DNA-ESA generates representations of reads and fragments of the reference, which are projected into a shared vector space where the read-fragment distance is used as surrogate for alignment. In particular, DNA-ESA introduces: (1) Contrastive loss for self-supervised training of DNA sequence representations, facilitating rich sequence-level embeddings, and (2) a DNA vector store to enable search across fragments on a global scale. DNA-ESA is >97% accurate when aligning 250-length reads onto a human reference genome of 3 gigabases (single-haploid), far exceeds the performance of 6 recent DNA-Transformer model baselines and shows task transfer across chromosomes and species.
Which side are you on? Insider-Outsider classification in conspiracy-theoretic social media
Mar 30, 2022
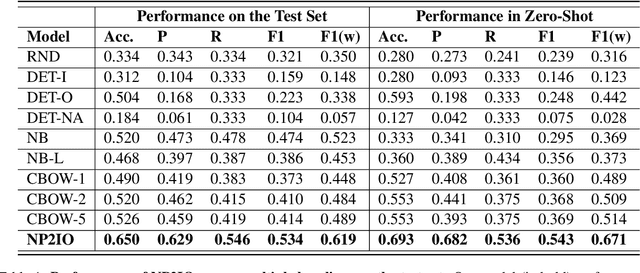
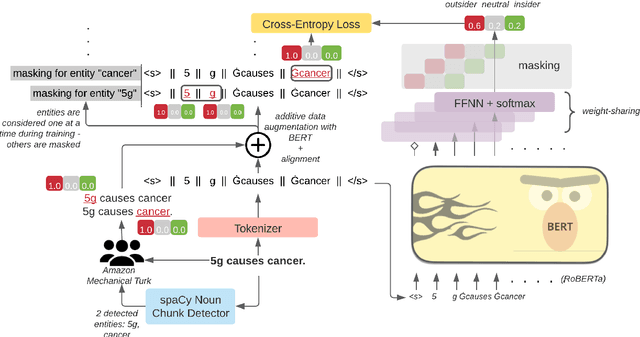
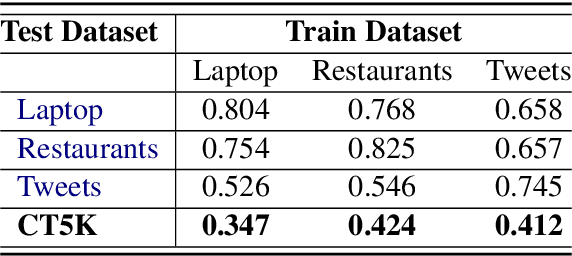
Abstract:Social media is a breeding ground for threat narratives and related conspiracy theories. In these, an outside group threatens the integrity of an inside group, leading to the emergence of sharply defined group identities: Insiders -- agents with whom the authors identify and Outsiders -- agents who threaten the insiders. Inferring the members of these groups constitutes a challenging new NLP task: (i) Information is distributed over many poorly-constructed posts; (ii) Threats and threat agents are highly contextual, with the same post potentially having multiple agents assigned to membership in either group; (iii) An agent's identity is often implicit and transitive; and (iv) Phrases used to imply Outsider status often do not follow common negative sentiment patterns. To address these challenges, we define a novel Insider-Outsider classification task. Because we are not aware of any appropriate existing datasets or attendant models, we introduce a labeled dataset (CT5K) and design a model (NP2IO) to address this task. NP2IO leverages pretrained language modeling to classify Insiders and Outsiders. NP2IO is shown to be robust, generalizing to noun phrases not seen during training, and exceeding the performance of non-trivial baseline models by $20\%$.
Modeling Social Readers: Novel Tools for Addressing Reception from Online Book Reviews
May 07, 2021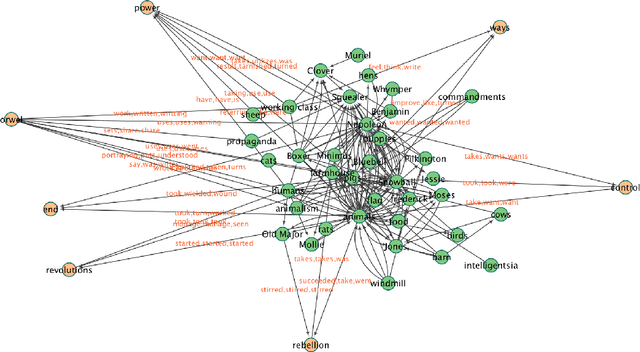
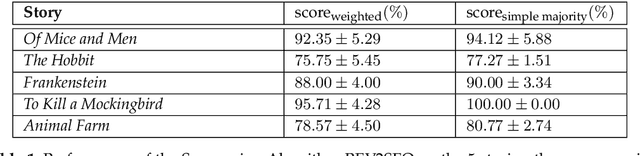
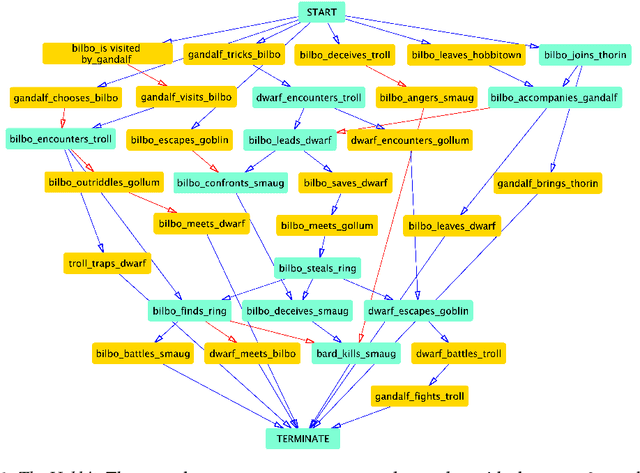
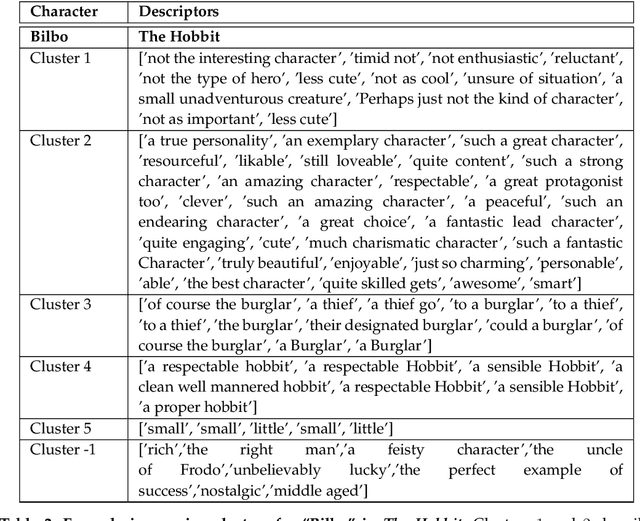
Abstract:Readers' responses to literature have received scant attention in computational literary studies. The rise of social media offers an opportunity to capture a segment of these responses while data-driven analysis of these responses can provide new critical insight into how people "read". Posts discussing an individual book on Goodreads, a social media platform that hosts user discussions of popular literature, are referred to as "reviews", and consist of plot summaries, opinions, quotes, or some mixture of these. Since these reviews are written by readers, computationally modeling them allows one to discover the overall non-professional discussion space about a work, including an aggregated summary of the work's plot, an implicit ranking of the importance of events, and the readers' impressions of main characters. We develop a pipeline of interlocking computational tools to extract a representation of this reader generated shared narrative model. Using a corpus of reviews of five popular novels, we discover the readers' distillation of the main storylines in a novel, their understanding of the relative importance of characters, as well as the readers' varying impressions of these characters. In so doing, we make three important contributions to the study of infinite vocabulary networks: (i) an automatically derived narrative network that includes meta-actants; (ii) a new sequencing algorithm, REV2SEQ, that generates a consensus sequence of events based on partial trajectories aggregated from the reviews; and (iii) a new "impressions" algorithm, SENT2IMP, that provides finer, non-trivial and multi-modal insight into readers' opinions of characters.
Conspiracy in the Time of Corona: Automatic detection of Covid-19 Conspiracy Theories in Social Media and the News
Apr 28, 2020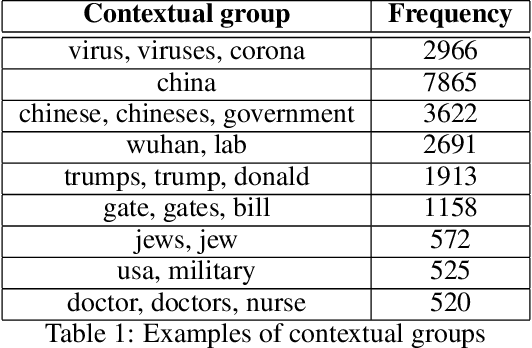
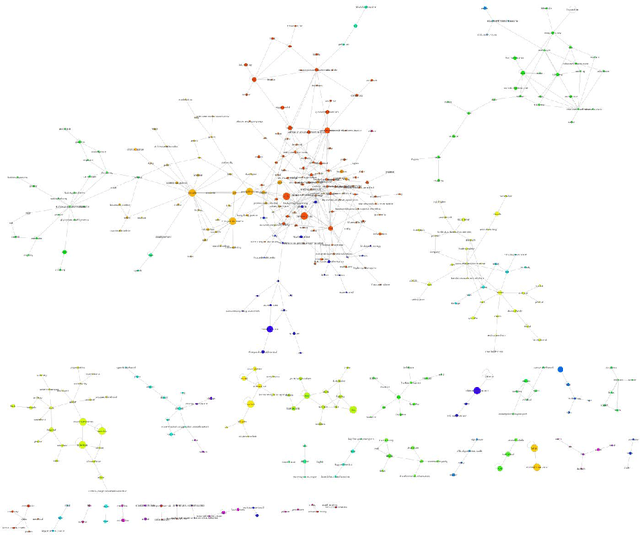
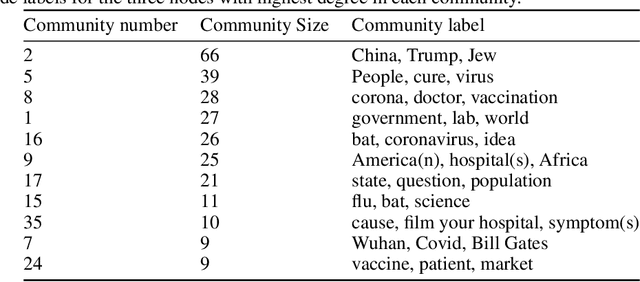
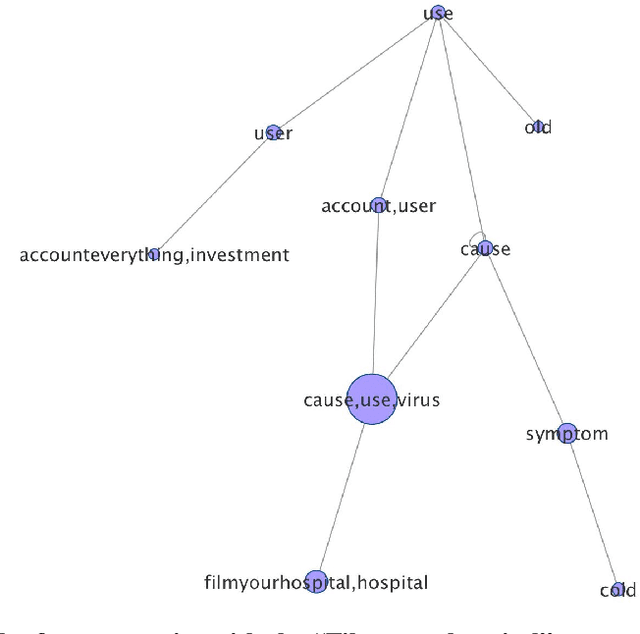
Abstract:Rumors and conspiracy theories thrive in environments of low confidence and low trust. Consequently, it is not surprising that ones related to the Covid-19 pandemic are proliferating given the lack of any authoritative scientific consensus on the virus, its spread and containment, or on the long term social and economic ramifications of the pandemic. Among the stories currently circulating are ones suggesting that the 5G network activates the virus, that the pandemic is a hoax perpetrated by a global cabal, that the virus is a bio-weapon released deliberately by the Chinese, or that Bill Gates is using it as cover to launch a global surveillance regime. While some may be quick to dismiss these stories as having little impact on real-world behavior, recent events including the destruction of property, racially fueled attacks against Asian Americans, and demonstrations espousing resistance to public health orders countermand such conclusions. Inspired by narrative theory, we crawl social media sites and news reports and, through the application of automated machine-learning methods, discover the underlying narrative frameworks supporting the generation of these stories. We show how the various narrative frameworks fueling rumors and conspiracy theories rely on the alignment of otherwise disparate domains of knowledge, and consider how they attach to the broader reporting on the pandemic. These alignments and attachments, which can be monitored in near real-time, may be useful for identifying areas in the news that are particularly vulnerable to reinterpretation by conspiracy theorists. Understanding the dynamics of storytelling on social media and the narrative frameworks that provide the generative basis for these stories may also be helpful for devising methods to disrupt their spread.
An Automated Pipeline for Character and Relationship Extraction from Readers' Literary Book Reviews on Goodreads.com
Apr 20, 2020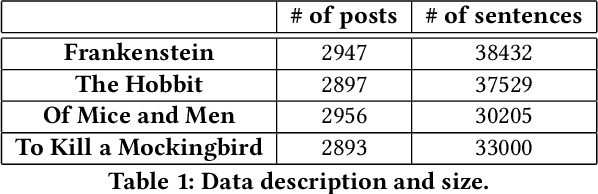
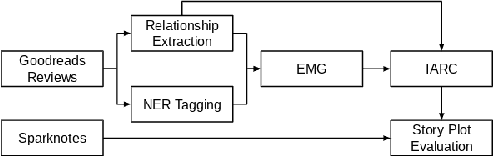
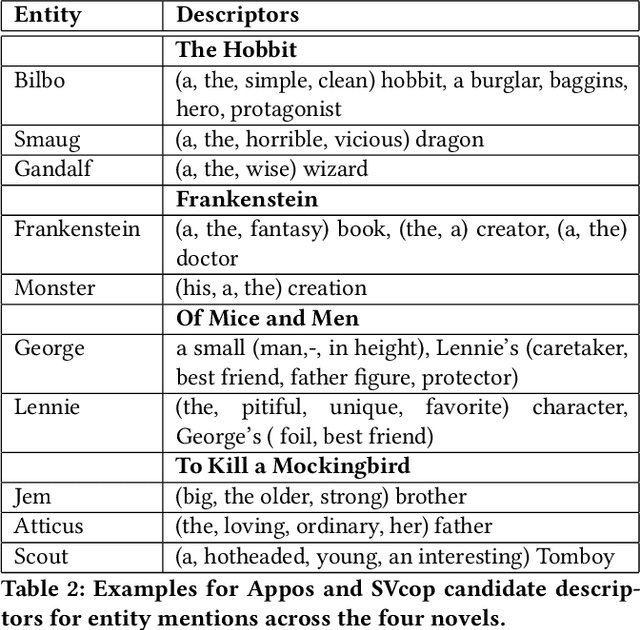
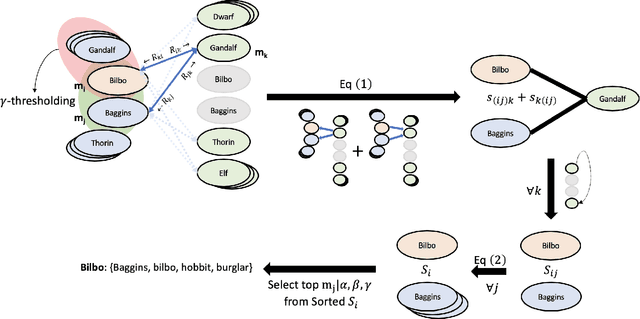
Abstract:Reader reviews of literary fiction on social media, especially those in persistent, dedicated forums, create and are in turn driven by underlying narrative frameworks. In their comments about a novel, readers generally include only a subset of characters and their relationships, thus offering a limited perspective on that work. Yet in aggregate, these reviews capture an underlying narrative framework comprised of different actants (people, places, things), their roles, and interactions that we label the "consensus narrative framework". We represent this framework in the form of an actant-relationship story graph. Extracting this graph is a challenging computational problem, which we pose as a latent graphical model estimation problem. Posts and reviews are viewed as samples of sub graphs/networks of the hidden narrative framework. Inspired by the qualitative narrative theory of Greimas, we formulate a graphical generative Machine Learning (ML) model where nodes represent actants, and multi-edges and self-loops among nodes capture context-specific relationships. We develop a pipeline of interlocking automated methods to extract key actants and their relationships, and apply it to thousands of reviews and comments posted on Goodreads.com. We manually derive the ground truth narrative framework from SparkNotes, and then use word embedding tools to compare relationships in ground truth networks with our extracted networks. We find that our automated methodology generates highly accurate consensus narrative frameworks: for our four target novels, with approximately 2900 reviews per novel, we report average coverage/recall of important relationships of > 80% and an average edge detection rate of >89\%. These extracted narrative frameworks can generate insight into how people (or classes of people) read and how they recount what they have read to others.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge