Paul Segars
SYN-LUNGS: Towards Simulating Lung Nodules with Anatomy-Informed Digital Twins for AI Training
Feb 28, 2025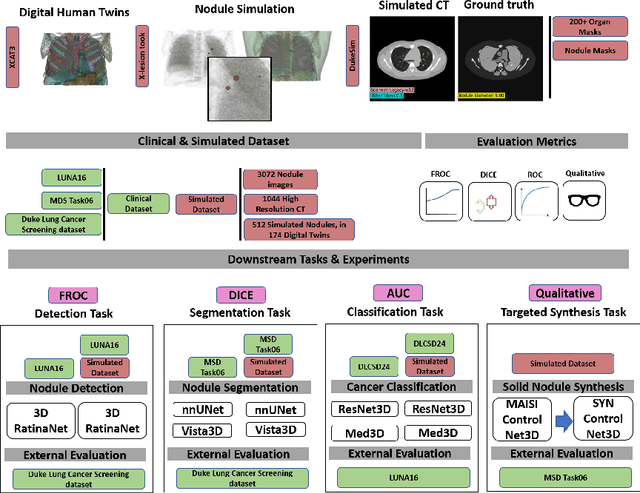
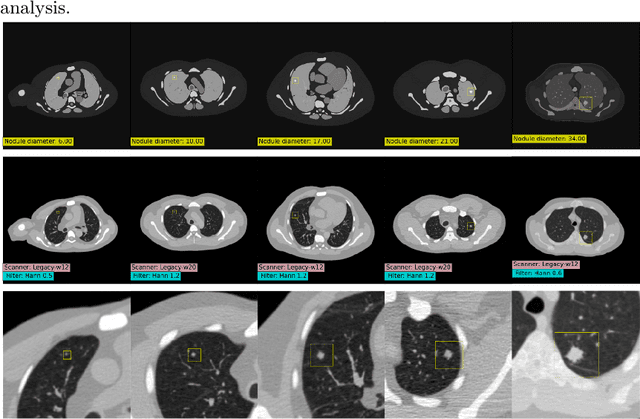
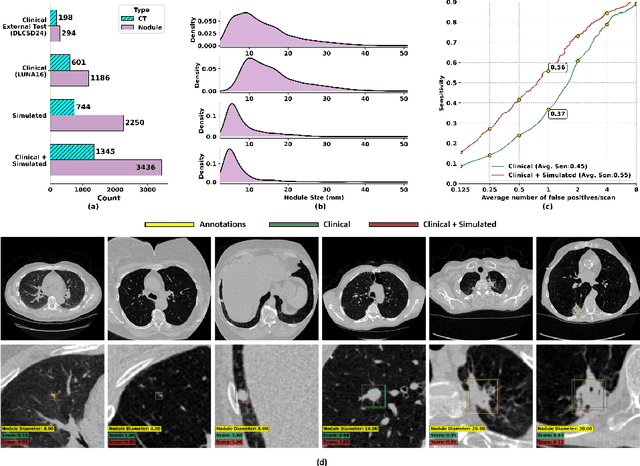
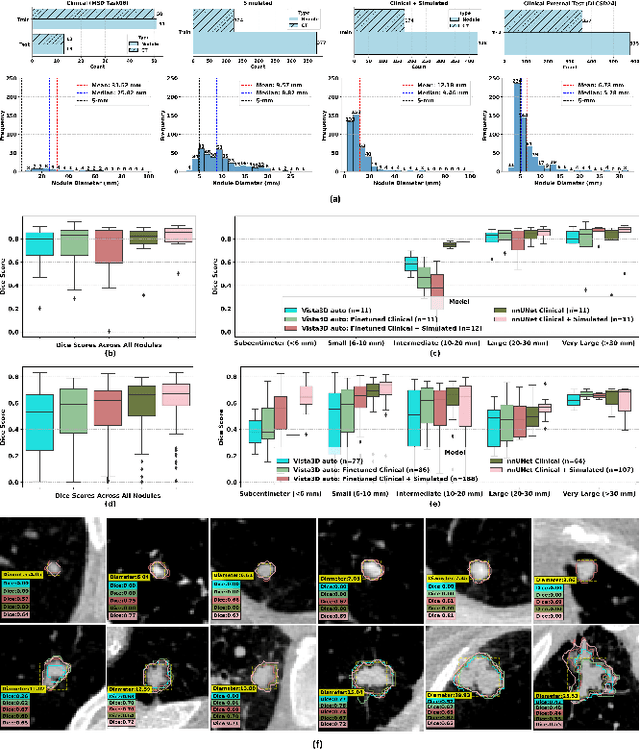
Abstract:AI models for lung cancer screening are limited by data scarcity, impacting generalizability and clinical applicability. Generative models address this issue but are constrained by training data variability. We introduce SYN-LUNGS, a framework for generating high-quality 3D CT images with detailed annotations. SYN-LUNGS integrates XCAT3 phantoms for digital twin generation, X-Lesions for nodule simulation (varying size, location, and appearance), and DukeSim for CT image formation with vendor and parameter variability. The dataset includes 3,072 nodule images from 1,044 simulated CT scans, with 512 lesions and 174 digital twins. Models trained on clinical + simulated data outperform clinical only models, achieving 10% improvement in detection, 2-9% in segmentation and classification, and enhanced synthesis.By incorporating anatomy-informed simulations, SYN-LUNGS provides a scalable approach for AI model development, particularly in rare disease representation and improving model reliability.
XCAT-2.0: A Comprehensive Library of Personalized Digital Twins Derived from CT Scans
May 18, 2024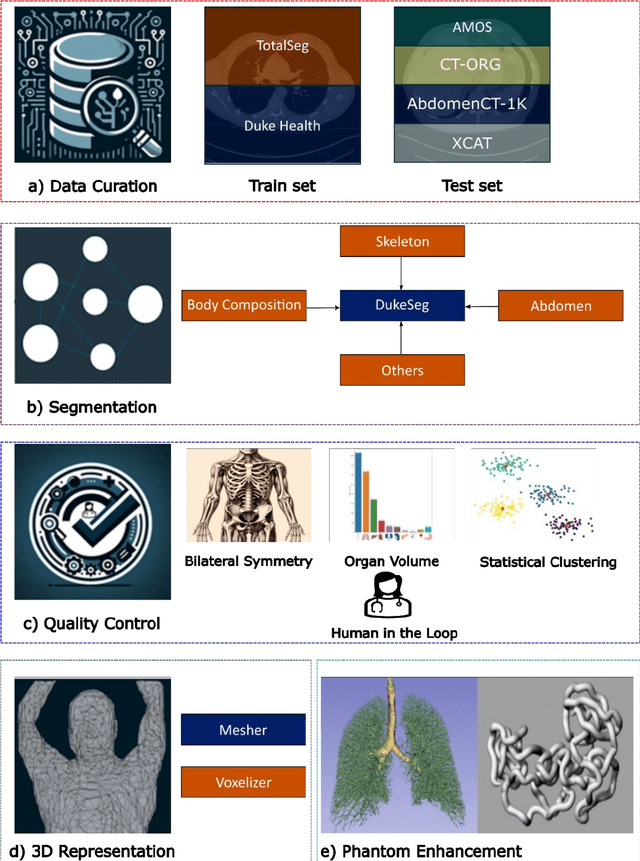
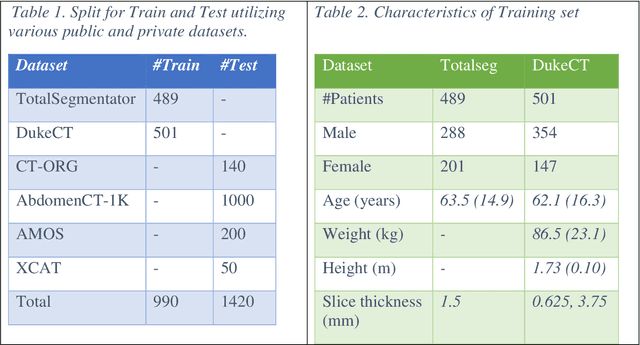
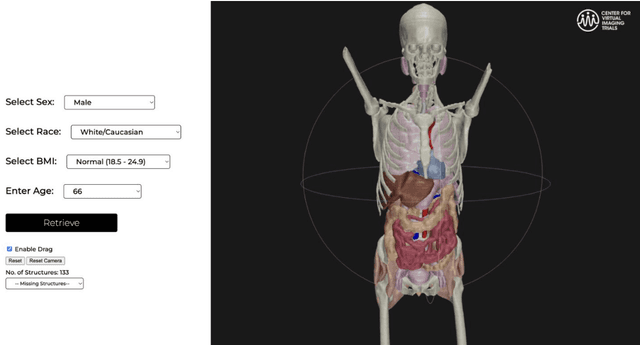
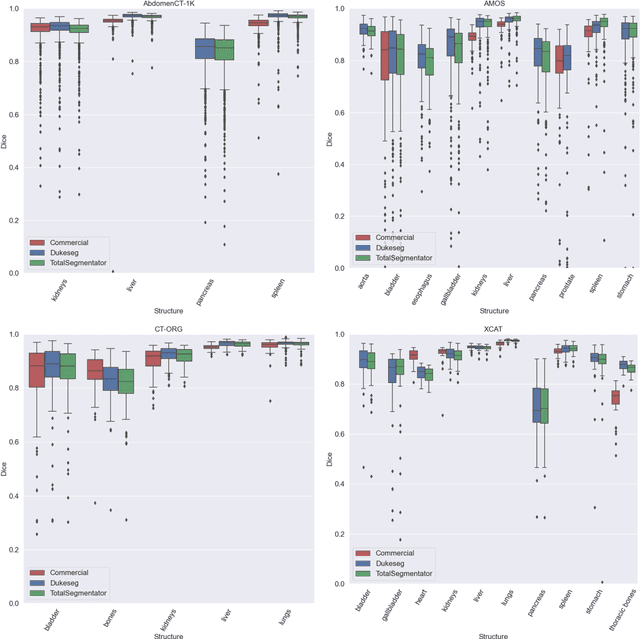
Abstract:Virtual Imaging Trials (VIT) offer a cost-effective and scalable approach for evaluating medical imaging technologies. Computational phantoms, which mimic real patient anatomy and physiology, play a central role in VIT. However, the current libraries of computational phantoms face limitations, particularly in terms of sample size and diversity. Insufficient representation of the population hampers accurate assessment of imaging technologies across different patient groups. Traditionally, phantoms were created by manual segmentation, which is a laborious and time-consuming task, impeding the expansion of phantom libraries. This study presents a framework for realistic computational phantom modeling using a suite of four deep learning segmentation models, followed by three forms of automated organ segmentation quality control. Over 2500 computational phantoms with up to 140 structures illustrating a sophisticated approach to detailed anatomical modeling are released. Phantoms are available in both voxelized and surface mesh formats. The framework is aggregated with an in-house CT scanner simulator to produce realistic CT images. The framework can potentially advance virtual imaging trials, facilitating comprehensive and reliable evaluations of medical imaging technologies. Phantoms may be requested at https://cvit.duke.edu/resources/, code, model weights, and sample CT images are available at https://xcat-2.github.io.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge