Paolo Napoletano
Tailoring Adverse Event Prediction in Type 1 Diabetes with Patient-Specific Deep Learning Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Effective management of Type 1 Diabetes requires continuous glucose monitoring and precise insulin adjustments to prevent hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. With the growing adoption of wearable glucose monitors and mobile health applications, accurate blood glucose prediction is essential for enhancing automated insulin delivery and decision-support systems. This paper presents a deep learning-based approach for personalized blood glucose prediction, leveraging patient-specific data to improve prediction accuracy and responsiveness in real-world scenarios. Unlike traditional generalized models, our method accounts for individual variability, enabling more effective subject-specific predictions. We compare Leave-One-Subject-Out Cross-Validation with a fine-tuning strategy to evaluate their ability to model patient-specific dynamics. Results show that personalized models significantly improve the prediction of adverse events, enabling more precise and timely interventions in real-world scenarios. To assess the impact of patient-specific data, we conduct experiments comparing a multimodal, patient-specific approach against traditional CGM-only methods. Additionally, we perform an ablation study to investigate model performance with progressively smaller training sets, identifying the minimum data required for effective personalization-an essential consideration for real-world applications where extensive data collection is often challenging. Our findings underscore the potential of adaptive, personalized glucose prediction models for advancing next-generation diabetes management, particularly in wearable and mobile health platforms, enhancing consumer-oriented diabetes care solutions.
Lightweight Sequential Transformers for Blood Glucose Level Prediction in Type-1 Diabetes
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) affects millions worldwide, requiring continuous monitoring to prevent severe hypo- and hyperglycemic events. While continuous glucose monitoring has improved blood glucose management, deploying predictive models on wearable devices remains challenging due to computational and memory constraints. To address this, we propose a novel Lightweight Sequential Transformer model designed for blood glucose prediction in T1D. By integrating the strengths of Transformers' attention mechanisms and the sequential processing of recurrent neural networks, our architecture captures long-term dependencies while maintaining computational efficiency. The model is optimized for deployment on resource-constrained edge devices and incorporates a balanced loss function to handle the inherent data imbalance in hypo- and hyperglycemic events. Experiments on two benchmark datasets, OhioT1DM and DiaTrend, demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art methods in predicting glucose levels and detecting adverse events. This work fills the gap between high-performance modeling and practical deployment, providing a reliable and efficient T1D management solution.
Cross-Camera Distracted Driver Classification through Feature Disentanglement and Contrastive Learning
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:The classification of distracted drivers is pivotal for ensuring safe driving. Previous studies demonstrated the effectiveness of neural networks in automatically predicting driver distraction, fatigue, and potential hazards. However, recent research has uncovered a significant loss of accuracy in these models when applied to samples acquired under conditions that differ from the training data. In this paper, we introduce a robust model designed to withstand changes in camera position within the vehicle. Our Driver Behavior Monitoring Network (DBMNet) relies on a lightweight backbone and integrates a disentanglement module to discard camera view information from features, coupled with contrastive learning to enhance the encoding of various driver actions. Experiments conducted on the daytime and nighttime subsets of the 100-Driver dataset validate the effectiveness of our approach with an increment on average of 9\% in Top-1 accuracy in comparison with the state of the art. In addition, cross-dataset and cross-camera experiments conducted on three benchmark datasets, namely AUCDD-V1, EZZ2021 and SFD, demonstrate the superior generalization capability of the proposed method.
Deep Learning Hyperspectral Pansharpening on large scale PRISMA dataset
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:In this work, we assess several deep learning strategies for hyperspectral pansharpening. First, we present a new dataset with a greater extent than any other in the state of the art. This dataset, collected using the ASI PRISMA satellite, covers about 262200 km2, and its heterogeneity is granted by randomly sampling the Earth's soil. Second, we adapted several state of the art approaches based on deep learning to fit PRISMA hyperspectral data and then assessed, quantitatively and qualitatively, the performance in this new scenario. The investigation has included two settings: Reduced Resolution (RR) to evaluate the techniques in a supervised environment and Full Resolution (FR) for a real-world evaluation. The main purpose is the evaluation of the reconstruction fidelity of the considered methods. In both scenarios, for the sake of completeness, we also included machine-learning-free approaches. From this extensive analysis has emerged that data-driven neural network methods outperform machine-learning-free approaches and adapt better to the task of hyperspectral pansharpening, both in RR and FR protocols.
Improving Image Captioning Descriptiveness by Ranking and LLM-based Fusion
Jun 20, 2023



Abstract:State-of-The-Art (SoTA) image captioning models often rely on the Microsoft COCO (MS-COCO) dataset for training. This dataset contains annotations provided by human annotators, who typically produce captions averaging around ten tokens. However, this constraint presents a challenge in effectively capturing complex scenes and conveying detailed information. Furthermore, captioning models tend to exhibit bias towards the ``average'' caption, which captures only the more general aspects. What would happen if we were able to automatically generate longer captions, thereby making them more detailed? Would these captions, evaluated by humans, be more or less representative of the image content compared to the original MS-COCO captions? In this paper, we present a novel approach to address previous challenges by showcasing how captions generated from different SoTA models can be effectively fused, resulting in richer captions. Our proposed method leverages existing models from the literature, eliminating the need for additional training. Instead, it utilizes an image-text based metric to rank the captions generated by SoTA models for a given image. Subsequently, the top two captions are fused using a Large Language Model (LLM). Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, as the captions generated by our model exhibit higher consistency with human judgment when evaluated on the MS-COCO test set. By combining the strengths of various SoTA models, our method enhances the quality and appeal of image captions, bridging the gap between automated systems and the rich, informative nature of human-generated descriptions. This advance opens up new possibilities for generating captions that are more suitable for the training of both vision-language and captioning models.
Unsupervised Deep Learning-based clustering for Human Activity Recognition
Nov 10, 2022


Abstract:One of the main problems in applying deep learning techniques to recognize activities of daily living (ADLs) based on inertial sensors is the lack of appropriately large labelled datasets to train deep learning-based models. A large amount of data would be available due to the wide spread of mobile devices equipped with inertial sensors that can collect data to recognize human activities. Unfortunately, this data is not labelled. The paper proposes DISC (Deep Inertial Sensory Clustering), a DL-based clustering architecture that automatically labels multi-dimensional inertial signals. In particular, the architecture combines a recurrent AutoEncoder and a clustering criterion to predict unlabelled human activities-related signals. The proposed architecture is evaluated on three publicly available HAR datasets and compared with four well-known end-to-end deep clustering approaches. The experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of DISC on both clustering accuracy and normalized mutual information metrics.
A deep scalable neural architecture for soil properties estimation from spectral information
Oct 26, 2022Abstract:In this paper we propose an adaptive deep neural architecture for the prediction of multiple soil characteristics from the analysis of hyperspectral signatures. The proposed method overcomes the limitations of previous methods in the state of art: (i) it allows to predict multiple soil variables at once; (ii) it permits to backtrace the spectral bands that most contribute to the estimation of a given variable; (iii) it is based on a flexible neural architecture capable of automatically adapting to the spectral library under analysis. The proposed architecture is experimented on LUCAS, a large laboratory dataset and on a dataset achieved by simulating PRISMA hyperspectral sensor. 'Results, compared with other state-of-the-art methods confirm the effectiveness of the proposed solution.
A health telemonitoring platform based on data integration from different sources
Jul 28, 2022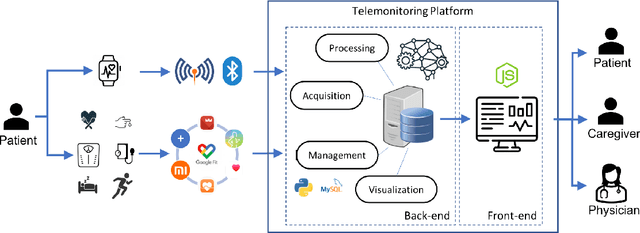
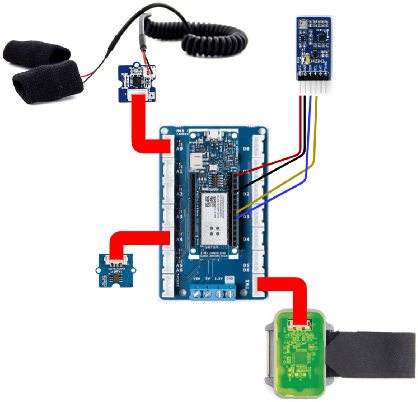
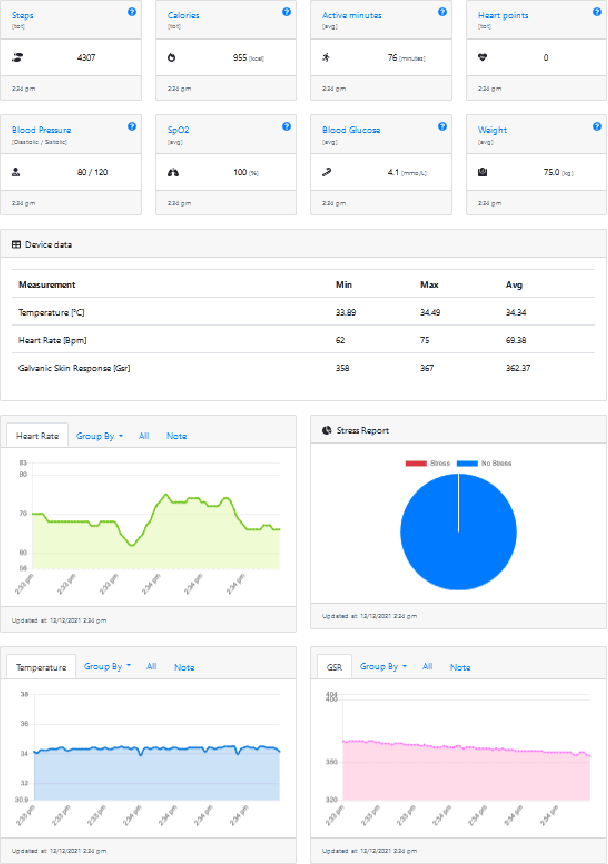
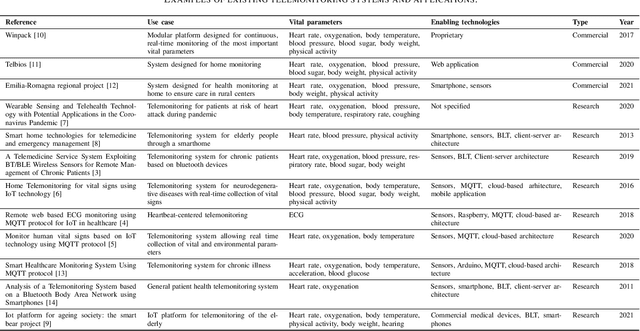
Abstract:The management of people with long-term or chronic illness is one of the biggest challenges for national health systems. In fact, these diseases are among the leading causes of hospitalization, especially for the elderly, and huge amount of resources required to monitor them leads to problems with sustainability of the healthcare systems. The increasing diffusion of portable devices and new connectivity technologies allows the implementation of telemonitoring system capable of providing support to health care providers and lighten the burden on hospitals and clinics. In this paper, we present the implementation of a telemonitoring platform for healthcare, designed to capture several types of physiological health parameters from different consumer mobile and custom devices. Consumer medical devices can be integrated into the platform via the Google Fit ecosystem that supports hundreds of devices, while custom devices can directly interact with the platform with standard communication protocols. The platform is designed to process the acquired data using machine learning algorithms, and to provide patients and physicians the physiological health parameters with a user-friendly, comprehensive, and easy to understand dashboard which monitors the parameters through time. Preliminary usability tests show a good user satisfaction in terms of functionality and usefulness.
Semi-supervised cross-lingual speech emotion recognition
Jul 14, 2022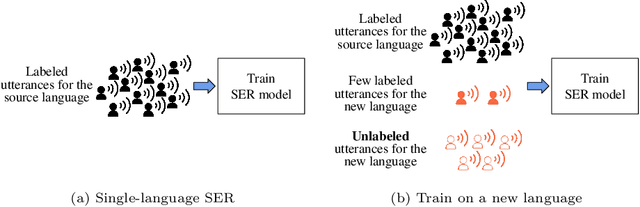
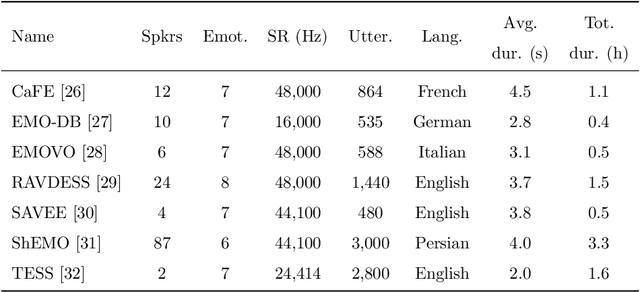
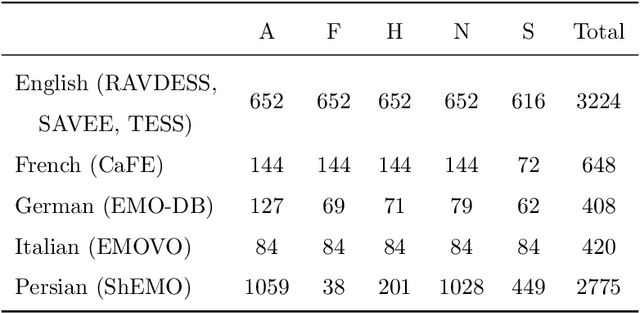
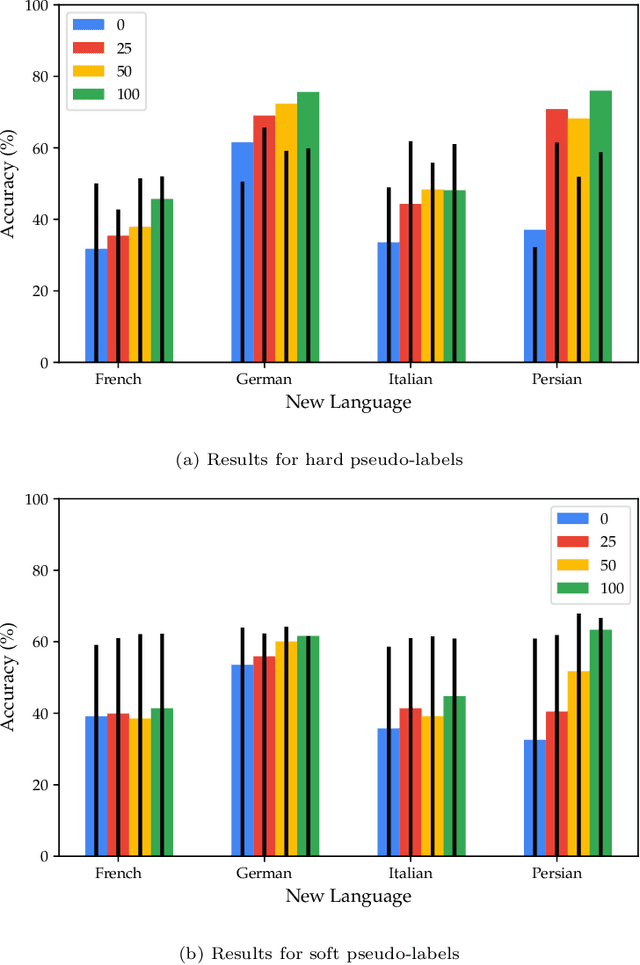
Abstract:Speech emotion recognition (SER) on a single language has achieved remarkable results through deep learning approaches over the last decade. However, cross-lingual SER remains a challenge in real-world applications due to (i) a large difference between the source and target domain distributions, (ii) the availability of few labeled and many unlabeled utterances for the new language. Taking into account previous aspects, we propose a Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) method for cross-lingual emotion recognition when a few labels from the new language are available. Based on a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), our method adapts to a new language by exploiting a pseudo-labeling strategy for the unlabeled utterances. In particular, the use of a hard and soft pseudo-labels approach is investigated. We thoroughly evaluate the performance of the method in a speaker-independent setup on both the source and the new language and show its robustness across five languages belonging to different linguistic strains.
Unsupervised Segmentation of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images with Superpixels
Apr 26, 2022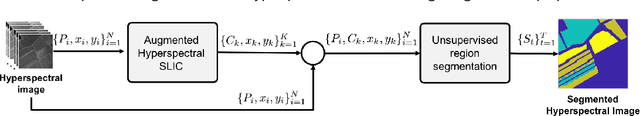

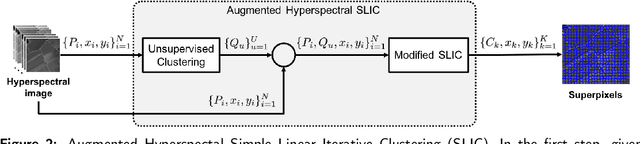

Abstract:In this paper, we propose an unsupervised method for hyperspectral remote sensing image segmentation. The method exploits the mean-shift clustering algorithm that takes as input a preliminary hyperspectral superpixels segmentation together with the spectral pixel information. The proposed method does not require the number of segmentation classes as input parameter, and it does not exploit any a-priori knowledge about the type of land-cover or land-use to be segmented (e.g. water, vegetation, building etc.). Experiments on Salinas, SalinasA, Pavia Center and Pavia University datasets are carried out. Performance are measured in terms of normalized mutual information, adjusted Rand index and F1-score. Results demonstrate the validity of the proposed method in comparison with the state of the art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge