Pablo Ortega-Kral
Grounding Robot Policies with Visuomotor Language Guidance
Oct 10, 2024
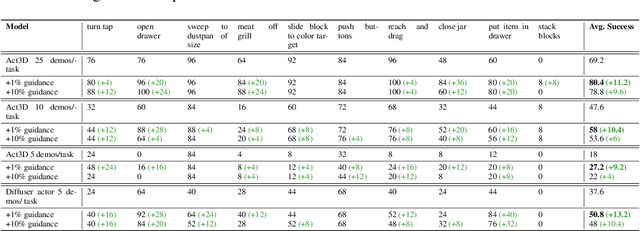


Abstract:Recent advances in the fields of natural language processing and computer vision have shown great potential in understanding the underlying dynamics of the world from large-scale internet data. However, translating this knowledge into robotic systems remains an open challenge, given the scarcity of human-robot interactions and the lack of large-scale datasets of real-world robotic data. Previous robot learning approaches such as behavior cloning and reinforcement learning have shown great capabilities in learning robotic skills from human demonstrations or from scratch in specific environments. However, these approaches often require task-specific demonstrations or designing complex simulation environments, which limits the development of generalizable and robust policies for new settings. Aiming to address these limitations, we propose an agent-based framework for grounding robot policies to the current context, considering the constraints of a current robot and its environment using visuomotor-grounded language guidance. The proposed framework is composed of a set of conversational agents designed for specific roles -- namely, high-level advisor, visual grounding, monitoring, and robotic agents. Given a base policy, the agents collectively generate guidance at run time to shift the action distribution of the base policy towards more desirable future states. We demonstrate that our approach can effectively guide manipulation policies to achieve significantly higher success rates both in simulation and in real-world experiments without the need for additional human demonstrations or extensive exploration. Project videos at https://sites.google.com/view/motorcortex/home.
Amelia: A Large Model and Dataset for Airport Surface Movement Forecasting
Jul 30, 2024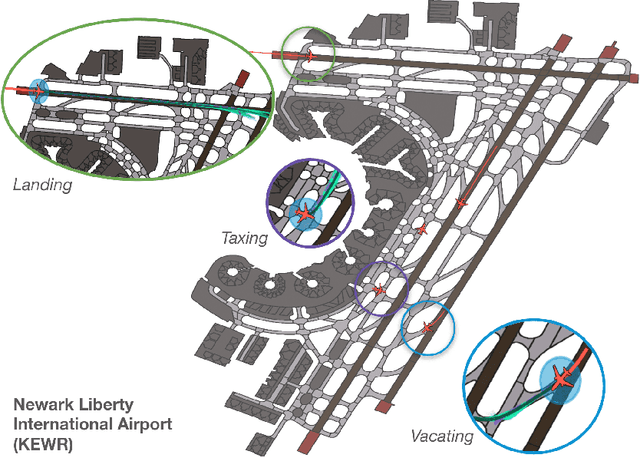

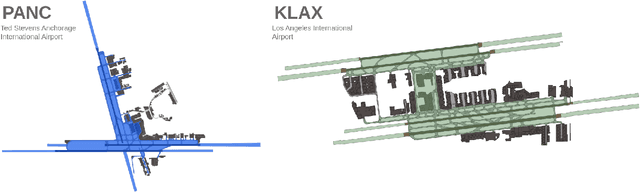
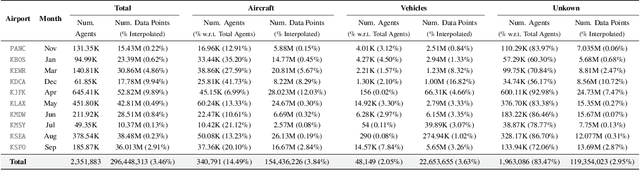
Abstract:The growing demand for air travel requires technological advancements in air traffic management as well as mechanisms for monitoring and ensuring safe and efficient operations. In terminal airspaces, predictive models of future movements and traffic flows can help with proactive planning and efficient coordination; however, varying airport topologies, and interactions with other agents, among other factors, make accurate predictions challenging. Data-driven predictive models have shown promise for handling numerous variables to enable various downstream tasks, including collision risk assessment, taxi-out time prediction, departure metering, and emission estimations. While data-driven methods have shown improvements in these tasks, prior works lack large-scale curated surface movement datasets within the public domain and the development of generalizable trajectory forecasting models. In response to this, we propose two contributions: (1) Amelia-48, a large surface movement dataset collected using the System Wide Information Management (SWIM) Surface Movement Event Service (SMES). With data collection beginning in Dec 2022, the dataset provides more than a year's worth of SMES data (~30TB) and covers 48 airports within the US National Airspace System. In addition to releasing this data in the public domain, we also provide post-processing scripts and associated airport maps to enable research in the forecasting domain and beyond. (2) Amelia-TF model, a transformer-based next-token-prediction large multi-agent multi-airport trajectory forecasting model trained on 292 days or 9.4 billion tokens of position data encompassing 10 different airports with varying topology. The open-sourced model is validated on unseen airports with experiments showcasing the different prediction horizon lengths, ego-agent selection strategies, and training recipes to demonstrate the generalization capabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge